NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12 Physics Chapter Four Moving Charges and Magnetism is a great study material for Class 12 students who are in the science stream. The chapter offers a comprehensive set of Multiple Choice Questions and short answer type questions. It includes numerical problems and conceptual questions to improve the conceptual clarity and problem-solving skills of students. Those who will prepare from Shiksha's Class 12 Chapter Four Moving Charges and Magnetism exemplar will be able to score good marks in the CBSE Board exam and other entrance exams like JEE and NEET.
The students can also download the Moving Charges and Magnetism NCERT PDF from this page and study offline whenever they want from any location, without the requirement of any internet connection. The questions covered in the exemplar are based on the key concepts of moving charges and magnetism, including Ampere’s circuital law, Biot–Savart law, the principle of the cyclotron, motion of charged particles in a magnetic field, and magnetic force on a current-carrying conductor.
Exemplar is like a practice book of the NCERT textbook concepts. By practicing from here, the students can improve their analytical and problem-solving skills as the solutions are well-structured and given in a step-by-step method. It is like a self-assessment tool with which students can do a quick revision.
Shiksha also provides topic-wise PDF of the NCERT Class 12 Physics.
- Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Four Moving Charges and Magnetism
- Important Formulas Related to Physics Chapter 4 NCERT Exemplar
- Moving Charges and Magnetism Questions and Answers
- Chapters List
- Moving Charges and Magnetism Short Answer Type Questions
- Moving Charges and Magnetism Multiple Choice Questions
- 29th June 2022 (Second Shift)
- JEE Maisn 2020
Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Physics Chapter Four Moving Charges and Magnetism
The Moving Charges and Magnetism NCERT PDF provides well-structured solutions for Chapter Four. The students can download it from this page and can study whenever they want to, from anywhere, and at their preferred time. The variety of questions is based on the key concepts of the chapter. Practicing them boosts the confidence of the students, and they understand when and how to apply the concepts and formulas of the chapter. It is a revision-friendly and time-saving study material that is ideal for concept reinforcement and self-study. If one thoroughly completes this exemplar, they make a strong foundation for the chapter and get ready to score high in the examinations.
Students can also practice the questions given in the NCERT Solutions of Chapter 4 - Moving Charges and Magnetism.
Related Links Below
| NCERT Solutions Class 11 and 12 For PCM | NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics |
| NCERT Class 12 Notes | NCERT Notes for Class 11 & 12 |
Important Formulas Related to Physics Chapter 4 NCERT Exemplar
The following are the important formulas of Chapter 4, Class 12 Physics:
Magnetic Force on a Moving Charge
Magnetic Force on a Current-Carrying Conductor
Magnetic Field Due to a Long Straight Conductor
Biot–Savart Law (Elemental Form)
Ampere’s Circuital Law
Magnetic Field Inside a Solenoid
Magnetic Field at Center of Circular Loop
Lorentz Force
Radius of Circular Path
Time Period and Cyclotron Frequency
Moving Charges and Magnetism Questions and Answers
| 1. A 100 turn rectangular coil ABCD (in X-Y plane) is hung from one arm of a balance (shown in figure). A mass 500 g is added to the other arm to balance the weight of the coil. A current 4.9 A passes through the coil and a constant magnetic field of 0.2 T acting inward (in x-z plane) is switched on such that only arm CD of length 1 cm lies in the field. How much additional mass m must be added to regain the balance? |
| Explanation – for equilibrium balance net torque should be zero Mgl= Wcoill 500gl = Wcoill Wcoil= 500 9.8N Taking moment of force about mid point then magnetic field Mgl+mgl=Wcoill+IBlsin90 Mgl=BILl M= -3kg= 1g |
| 2. A rectangular conducting loop consists of two wires on two opposite sides of length l joined together by rods of length d. The wires each are of the same material but with cross-sections differing by a factor of 2. The thicker wire has a resistance R and the rods are of low resistance, which in turn are connected to a constant voltage source V0. The loop is placed in a uniform magnetic field B at 45° to its plane. Find T, the torque exerted by the magnetic field on the loop about an axis through the centres of rods. |
| Explanation- the thicker wire has a resistance R, then the other wire has a resistance @R as the wires are of the same material but different area
|
| 3. An electron and a positron are released from (0, 0, 0) and (0, 0, 1.5R) respectively, in a uniform magnetic field B = B0i, each with an equal momentum of magnitude p = eBR. Under what conditions on the direction of momentum will the orbits be non-intersecting circles? |
| Explanation- Since, B is along the x-axis, for a circular orbit the momenta of the two particles are in the y-z plane. Let P1 and P2 be the momentum of the electron and positron, respectively. Both traverse a circle of radius R of opposite sense. Let P1 make an angle θ with the y-axis P2 must make the same angle. |
| 4. A uniform conducting wire of length 12a and resistance R is wound up as a current carrying coil in the shape of (i) an equilateral triangle of side a, (ii) a square of sides a, and (iii) a regular hexagon of sides a. The coil is connected to a voltage source V0. Find the magnetic moment of the coils in each case. |
| Explanation- as we know magnetic moment = nIA For equilateral triangle M= nIA= 4I( ) M= Ia2 For square , n=3 so total length of wire is 12a M= nIA= 3I(a2) = 3Ia2 For regular hexagon of side a , n=2 so total length = 12a M= nIA=2( )= 3 a2I |
Commonly asked questions
The component of a vector r along X-axis will have maximum value if
(a) r is along positive Y-axis
(b) r is along positive X-axis
(c) r makes an angle of 45° with the X-axis
(d) r is along negative Y-axis
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- b
Explanation – ler r makes an angle with positive x axis component if r along x-axis.
So rx= |r|cos
(rx)maximum= |r| (cos )maximum
= |r|cos = r
=00
R is along positive x-axis.
Two long wires carrying current I1, and I2are arranged as shown in figure. The one carrying current I1 is along the x-axis. The other carrying current I2 is along a line parallel to the y-axis given by x = 0 and z = d. Find the force exerted at O2 because of the wire along the x-axis.
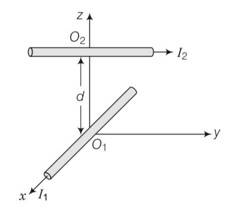
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation – in biot savart law, magnetic field B is parallel to idlr and idl have its direction along the direction of flow of current.
Here, for the direction of magnetic field at O2, due to wire carrying I1 current is B| parallel idl r or I k, but it is -j
So the direction at O2 is along y-direction.
The direction of magnetic force exerted at O2 because of the wire along x-axis
F= ilB=j (-j)=0
So the force is zero.
A charged particle would continue to move with a constant velocity in a region wherein,
(a) E = 0,B≠0 (b) E≠0,B≠0
(c) E≠0,B = 0 (d) E = 0, B = 0
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- force on charge particle due to both electric and magnetic field . now if electric force and magnetic field is zero then electric field and magnetic field is also zero.
Magnetic field is only responsible for constant velocity of charge particle if B=0 then E =0 if B is not equal to zero then electric field is also not equal to zero
Biot-Savart law indicates that the moving electrons (velocity v) produce a magnetic field B such that
(a) B is perpendicular to v.
(b) B is parallel to v.
(c) it obeys inverse cube law.
(d) it is along the line joining the electron and point of observation.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer – (a)
Explanation- in biot savarts law magnetic field is perpendicular to v
A multirange current meter can be constructed by using a galvanometer circuit as shown in figure. We want a current meter that can measure 10 mA, 100 mA and 1 mA using a galvanometer of resistance 10 Ω and that produces maximum deflection for current of 1 mA. Find S1 ,S2 and S3 that have to be used.
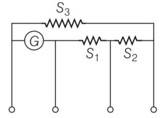
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- iG (G) = (I1-IG) (S1+S2+S3) for I1= 10mA
iG (G+S1) = (I2-IG) (S2+S3) for I2= 100mA
iG (G+S1+S2) = (I3-IG) (S3) for I3= 1A
S1= 1W, S2= 0,1W and S3= 0.01W
Do magnetic forces obey Newton’s third law. Verify for two current elements dl1= dl i located at the origin and dl2 = dl j located at(0, R, 0). Both carry current I.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- In Biot-Savart’s law, magnetic field B is parallel (II) to id × r and idl have its direction along the direction of flow of current.
Here, for the direction of magnetic field, At dl2, located at (0, R,0) due to wire d1 is given by B I | dl × r or I ×j (because point (0, R,0)lies on y-axis), but I × j= k
So, the direction of magnetic field at d2 is along z-direction.
The direction of magnetic force exerted at d2 because of the first wire along the x-axis
F =i (l B) i.e., F| (i ) or along− j direction.
Therefore, force due to dl1 on dl2 is non-zero.
Now, for the direction of magnetic field, At d1, located at (0,0,0) due to wire d2 is given by
B I | dl × r or j ×−j (because origin lies on y-direction w.r.t. point (0, R,0).), but j ×−j =0.
So, the magnetic field at d1 does not exist.
Force due to dl2 on dl1 is zero.
So, magnetic forces do not obey Newton's third law.
A 100 turn rectangular coil ABCD (in X-Y plane) is hung from one arm of a balance (shown in figure). A mass 500 g is added to the other arm to balance the weight of the coil. A current 4.9 A passes through the coil and a constant magnetic field of 0.2 T acting inward (in x-z plane) is switched on such that only arm CD of length 1 cm lies in the field. How much additional mass m must be added to regain the balance?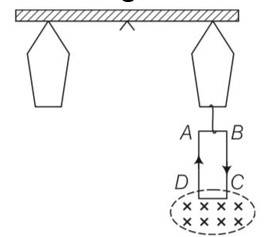
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation – for equilibrium balance net torque should be zero
Mgl= Wcoill
500gl = Wcoill
Wcoil= 500 9.8N
Taking moment of force about mid point then magnetic field
Mgl+mgl=Wcoill+IBlsin90
Mgl=BILl
M= -3kg= 1g
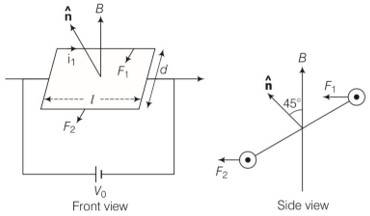
A rectangular conducting loop consists of two wires on two opposite sides of length l joined together by rods of length d. The wires each are of the same material but with cross-sections differing by a factor of 2. The thicker wire has a resistance R and the rods are of low resistance, which in turn are connected to a constant voltage source V0. The loop is placed in a uniform magnetic field B at 45° to its plane. Find T, the torque exerted by the magnetic field on the loop about an axis through the centres of rods.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- the thicker wire has a resistance R, then the other wire has a resistance @R as the wires are of the same material but different area
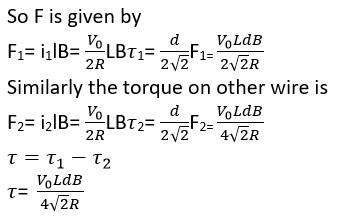
An electron and a positron are released from (0, 0, 0) and (0, 0, 1.5R) respectively, in a uniform magnetic field B = B0i, each with an equal momentum of magnitude p = eBR. Under what conditions on the direction of momentum will the orbits be non-intersecting circles?
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- Since, B is along the x-axis, for a circular orbit the momenta of the two particles are in the y-z plane. Let P1 and P2 be the momentum of the electron and positron, respectively. Both traverse a circle of radius R of opposite sense. Let P1 make an angle? with the y-axis P2 must make the same angle.
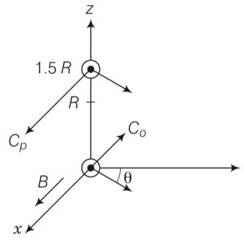
The centres of the respective circles must be perpendicular to the momenta and at a distance R. Let the centre of the electron be at Ce and of the positron at Cp . The coordinates of Ce is
Ce= (0, -Rsin )
Cp= (0, -Rsin )
The circles of the two shall not overlap if the distance between the two centers are
Greater than 2R.
Let d be the distance between Cp and Ce.
Let d be the distance between Cp and Ce.
So d2= (2Rsin )2+ ( )2
= 4R2sin2 + 2-6R2cos +4R2cos2
= 4R2+ 2-6R2cos
Since d has to be greater than 2R
So d2> 4R2
4R2+ 2-6R2cos > 4R2
Cos <3/8
A uniform conducting wire of length 12a and resistance R is wound up as a current carrying coil in the shape of (i) an equilateral triangle of side a, (ii) a square of sides a, and (iii) a regular hexagon of sides a. The coil is connected to a voltage source V0. Find the magnetic moment of the coils in each case.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- as we know magnetic moment = nIA
For equilateral triangle M= nIA= 4I ( )
M= Ia2
For square, n=3 so total length of wire is 12a
M= nIA= 3I (a2) = 3Ia2
For regular hexagon of side a, n=2 so total length = 12a
M= nIA=2 ( )= 3 a2I
Consider a circular current-carrying loop of radius R in the x-y plane with centre at origin. Consider the line integral ζ ( L ) = | | taken along z-axis.
(a) Show that 𝜁 ( ) monotonically increases with L.
(b) Use an appropriate Amperian loop to show that ζ ( ∞ ) = 𝜇0𝐼 , where I is the current in the wire.
(c) Verify directly the above result.
(d) Suppose we replace the circular coil by a square coil of sides R carrying the same current I. What can you say about ζ ( L ) and ζ ( ∞ ) ?
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- B (z) points in the same direction on z-axis and hence, J (L) isa monotonically function of L so B.dl = B.dl as cos 0 = 1
(b) but when L
So B 1/r3
(c) the magnetic field due to a circular current carrying loop of radius in the xy plane with centre at origin at any point lying at a distance of from origin.
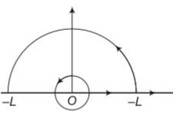
B=
Z=Rtan
dz=Rsec2
=
Five long wires A, B, C, D and E, each carrying current I are arranged to form edges of a pentagonal prism as shown in figure. Each carries current out of the plane of paper.
(a) What will be magnetic induction at a point on the axis 0? Axis is at a distance R from each wire.
(b) What will be the field if current in one of the wires (say A) is switched off?
(c) What if current in one of the wire (say A) is reversed?
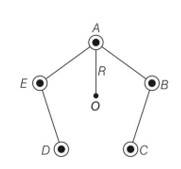
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- (a) Suppose the five wires A, B, C, D and E be perpendicular to the plane of paper at locations as shown in figure.
Thus, magnetic field induction due to five wires will be represented by various sides of a
closed pentagon in one order, lying in the plane of paper. So, its value is zero.
(b) Since, the vector sum of magnetic field produced by each wire at O is equal to 0.
Therefore, magnetic induction produced by one current carrying wire is equal in
magnitude of resultant of four wires and opposite in direction.
Therefore, the field if current in one of the wires (say A) is switched off is perpendicular to AO towards left.
(c) if current in wire A is reversed, then total magnetic field induction at O= magnetic field induction due to wire A + magnetic field induction due to wrie B, C, D and E
B=
Show that a force that does no Work must be a velocity dependent force.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- dW=F.dl=0
As dl = vdt
dW= Fvdt
dW= f.v=0
The magnetic force depends on v which depends on the inertial frame of reference. Does then the magnetic force differ from inertial frame to frame? Is it reasonable that-the net acceleration has a different value indifferent frames of reference?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- yes, the magnetic force differ from inertial frame to frame. The magnetic force is frame dependent.
The net acceleration which comes into existing out of this is however, frame independent for inertial frames.
Describe the motion of a charged particle in a cyclotron if the frequency of the radio frequency (rf) field were doubled.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation – here, the condition of magnetic resonance is violated.
When the frequency of radio frequency field were doubled, the time period of the radio frequency field were halved. Therefore, the duration in which particle completes half revolution inside the dees, radio frequency completes the cycle.
Hence, particle will accelerate and decelerate alternatively. So the radius of path in the dees will remain same.
A current carrying loop consists of 3 identical quarter circles of radius R, lying in the positive quadrants of the x-y, y-z and z-x planes with their centres at the origin, joined together. Find the direction and magnitude of B at the origin.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- general formula for magnetic field at center is
B=
B1= k for xy plane
B2= i for zy plane
B3= j for xz plane
After joining together B= (i+j+k)
A charged particle of charge e and mass m is moving in an electric field E and magnetic field B. Construct dimensionless quantities and quantities of dimension [T]-1
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- for a charge particle to move in circular path
Mv2/r = qvB
v/r=w= bq/m
w= v/r = = T-1
An electron enters with a velocity v = v0i into a cubical region (face parallel to coordinate planes) in which there are uniform electric and magnetic fields. The orbit of the electron is found to spiral down inside the cube in a plane parallel to the x-y plane. Suggest a configuration to fields E and B that can lead to it.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- considering magnetic field along B=Bk and electron enters with a velocity v=vi into a cubical region
The force on electron using Lorentz force = -e (vi Bk)= evBi
So the force F= -eE0 k accelerates along z axis which in turn increases the radius of circular path and hence particle transversed on spiral path.
A multirange voltmeter can be constructed by using a galvanometer circuit as shown in figure. We want to construct a voltmeter that can measure 2 V, 20 V and 200 V using a galvanometer of resistance 10 ? and that produces maximum deflection for current of 1 mA. Find R1, R2and R3 that have to be used,
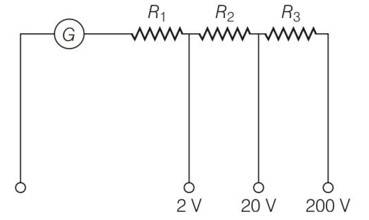
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- applying expression in different situation
For iG (G+R1) = 2 , for 2V range
iG (G+R1+R2) = 20 , for 20V range
iG (G+R1+R2+R3) = 2 , for 200V range
on solving we get R1= 1990ohm, R2= 18kohm, R3= 180k ohm
A long straight wire carrying current of 25 A rests on a table as shown in figure. Another wire PQ of length 1 m, mass 2.5 g carries the same current but in the opposite direction. The wire PQ is free to slide up and down. To what height will PQ rise?
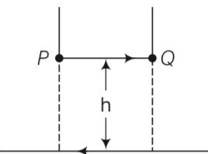
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- magnetic field produced by a long straight current carrying wire is
B= = , for h height distance
Magnetic force on small conductor is F= ilBsin = ilB
Also force, F =mg = l
h= = 51 10-4cm
Two charged particles traverse identical helical paths in a completely oppo-site sense in a uniform magnetic field B = B0k
(a) They have equal z-components of momenta
(b) They must have equal charges
(c) They necessarily represent a particle, anti-particle pair
(d) The charge to mass ratio satisfy
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer – (d)
Explanation- it is determined by its pitch
Pitch = = constant
So charge by mass ratio is also constant
A current carrying circular loop of radius R is placed in the x-y plane with centre at the origin. Half of the loop with x >0 is now bent so that it now lies in the y-z plane.
(a) The magnitude of magnetic moment now diminishes.
(b) The magnetic moment does not change.
(c) The magnitude of B at (0,0, z), z>>R increases.
(d) The magnitude of B at (0,0,z), z>>R is unchanged.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (a)
Explanation- magnetic moment, M = niA, when we decrease the radius by half its area is decrease by ¼ so the magnetic moment also.so magnetic moment diminishes.
An electron is projected with uniform velocity along the axis of a current carrying long solenoid. Which of the following is true?
(a) The electron will be accelerated along the axis
(b) The electron path will be circular about the axis
(c) The electron will experience a force at 45° to the axis and hence execute a helical path
(d) The electron will continue to move with uniform velocity along the axis of the solenoid
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (d)
Explanation- when electron move in the direction of velocity along the axis of current then angle is 180 which makes force according to the relation F=qvbsin . so electron will continue move with uniform velocity along axis of solenoid.
In a cyclotron, a charged particle
(a) Undergoes acceleration all the time
(b) Speeds up between the dees because of the magnetic field
(c) Speeds up in a dee
(d) Slows down within a dee and speeds up between dees
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer – (a)
Explanation – when a charge particle enter in cyclotron it will always accelerated with the help of oscillating electric field. But it will move with the same speed with the help of magnetic field.
A circular current loop of magnetic moment M is in an arbitrary orientation in an external magnetic field B. The work done to rotate the loop by 30° about an axis perpendicular to its plane is
(a) MB (b) (c) MB/2 (d) zero
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer. (d)
Explanation- W=MBcos , as the loop make 30 degree angle but angle made by axis of the loop with the direction of magnetic field, therefore work done is zero.
The gyro-magnetic ratio of an electron in an H-atom, according to Bohr model, is .
(a) Independent of which orbit it is in.
(b) Negative
(c) Positive
(d) Increases with the quantum number n.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer – (a)
Explanation- gyro magnetic ratio does not depend upon which electron is rotating.
Consider a wire carrying a steady current, I placed in a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to its length. Consider the charges inside the wire. It is known that magnetic forces do not work. This implies that,
(a) motion of charges inside the conductor is unaffected by B, since they do not absorb energy.
(b) Some charges inside the wire move to the surface as a result of B.
(c) If the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the force.
(d) If the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the magnetic force on the ions, assumed fixed within the wire.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (b, d)
Explanation- F=IlB, the direction of force is given by fleming's left hand rule and F is perpendicular to the direction of magnetic field. So work done is zero.
Two identical current carrying coaxial loops, carry current I in an opposite sense. A simple amperian loop passes through both of them once. Calling the loop as C,
(a) ?Bdl =m I
(b) the value of ?B.dl = ±2 I is independent of sense of C
(c) there may be a point on C where, B and dl are perpendicular
(d) B vanishes everywhere on C
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (b, c)
Explanation- if current is in opposite sense the? Bdl = 0, also there exist a point where b and dl is perpendicular.
A cubical region of space is filled with some uniform electric and magnetic fields. An electron enters the cube across one of its faces with velocity v and a positron enters via opposite face with velocity -v. At this instant,
(a) The electric forces on both the particles cause identical accelerations.
(b) The magnetic forces on both the particles cause equal accelerations.
(c) Both particles gain or loose energy at the same rate.
(d) The motion of the Centre of Mass (CM) is determined by B alone.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- (b, c, d)
Explanation- magnetic forces on both the particles cause equal acceleration because they both have equal velocity
Also they both gain or loose energy because direction of force in both cases is opposite.
And there is no change in center of mass of particles so it is determined by B alone.
Verify that the cyclotron frequency ω = eB/m has the correct dimensions of [T]-1
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- for a charge particle to move in circular path
Mv2/r = qvB
v/r=w= bq/m
w= v/r = = T-1
A particle is projected in air at some angle to the horizontal, moves along parabola as shown in Fig., where x and y indicate horizontal and vertical directions, respectively. Show in the diagram, direction of velocity and acceleration at points A, B and C.
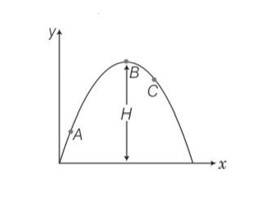
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- vsin = vertical component
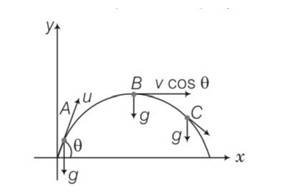
Vx= horizontal component of velocity =vcos = constant
Vy = vertical component of velocity =vsin
Velocity will always be tangential to the curve in the direction of motion and acceleration is always vertically downward and is equal to g.
A ball is thrown from a roof top at an angle of 45° above the horizontal. It hits the ground a few seconds later. At what point during its motion, does the ball have
(a) Greatest speed.
(b) Smallest speed.
(c) Greatest acceleration? Explain
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- at point B it will gain the same speed u and after that speed increases and will be maximum just before reaching point c.
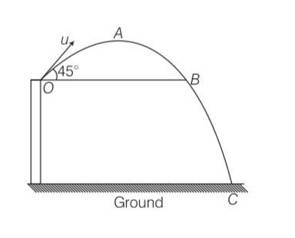
During journey from O to A speed decreases and will be maximum at point A and acceleration is always constant.
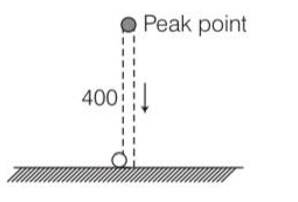
A football is kicked into the air vertically upwards. What is its (a) acceleration, and (b) velocity at the highest point?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- if the football is kicked into the air vertically upwards. Acceleration of football will always vertically downwards and equal to acceleration due to gravity. But when it reaches the highest point its velocity is zero and acceleration is retarding.
A, B and C are three non-collinear, non co-planar vectors. What can you say about direction of A × (B × C)?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation – the direction of (B ) will be perpendicular the plane containing B and B by right hand rule. A will lie in the plane of B and C and is perpendicular to vector A.
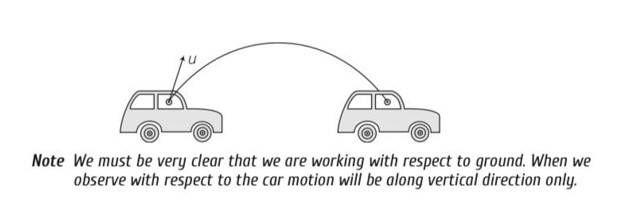
A boy travelling in an open car moving on a levelled road with constant speed tosses a ball vertically up in the air and catches it back. Sketch the motion of the ball as observed by a boy standing on the footpath. Give explanation to support your diagram.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation – The path of the ball observed by a boy standing on the footpath is parabolic. The horizontal speed of the ball is same as that of the car, therefore ball as well car travels equal horizontal distance, due to vertical speed, the ball follows parabolic path.
A boy throws a ball in air at 60° to the horizontal along a road with a speed of 10 m/s (36km/h). Another boy sitting in a passing by car observes the ball. Sketch the motion of the ball as observed by the boy in the car, if car has a speed of (18km/h). Give explanation to support your diagram.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation – The boy throws the ball at an angle of 60.
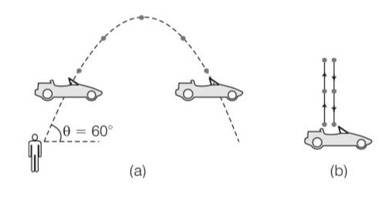
Horizontal component of velocity 4cos = 10cos60
=10 (1/2)
=5m/s.
so horizontal speed of the car is same, hence relative velocity of car and ball in the horizontal direction will be zero.
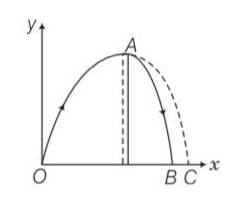
In dealing with motion of projectile in air, we ignore effect of air resistance on motion. This gives trajectory as a parabola as you have studied. What would the trajectory look like if air resistance is included? Sketch such a trajectory and explain why you have drawn it that way.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation – due to air resistance particle energy as well as horizontal component of velocity keep on decreasing making the fall steeper then rise. When we are neglecting air resistance path is parabola when we consider air resistance then path is asymmetric parabola.
A fighter plane is flying horizontally at an altitude of 1.5 km with speed 720 km/h. At what angle of sight (w.r.t. horizontal) when the target is seen, should the pilot drop the bomb in order to attack the target?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- when it be at position P, drops a bomb to hit a target T
Let
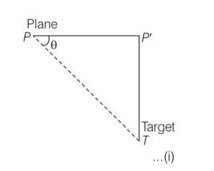
Speed of the plane =720km/h = 720 = 200m/s
Altitude of the plane P’T = 1.5km= 1500m
If bomb hits the target after time t then horizontal distance travelled by the bomb PP’=u =200t
Vertical distance travelled by the bomb P’T=1/2gt2
1500 = ½ (9.8)t2
So t2= 1500/4.9, t =
PP’=200 (17.49)m=
tan =P’T/P’P=1500/200 (17.49)=0.49287= tan23012’
(a) Earth can be thought of as a sphere of radius 6400 km. Any object (or a person) is performing circular motion around the axis of earth due to earth’s rotation (period 1 day). What is acceleration of object on the surface of the earth (at equator) towards its centre ? How does these accelerations compare with g = 9.8 m/s2?
(b) Earth also moves in circular orbit around sun once every year with on orbital radius of 11 1.5 10 × m . What is the acceleration of earth (or any object on the surface of the earth) towards the centre of the sun? How does this acceleration compare with g = 9.8 m/s2?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation – a) radius of earth =6400km= 6.4
Time period = 1 day = 24 = 86400s
Centripetal acceleration a= w2r= R(2 )2=4 2R/T
= = 0.034m/s2
b) time = 1yr=365 days= 365=3.15
centripetal acceleration = Rw2=
2
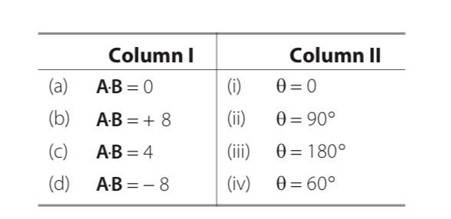
Given below in column I are the relations between vectors a, b and c and in column II are the orientations of a, b and c in the XY plane. Match the relation in column I to correct orientations in column II
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
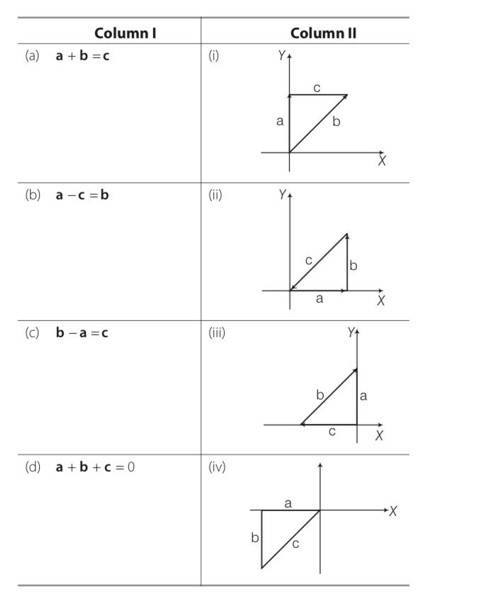
Explanation – here A and B vectors are joint by head and tail. So C= A+B
(a) from fig iv it is clear that c=a+b
(a) From fig iii it is clear that c+b=a so a-c=b
(b) From fig I it is clear that b=a+c so b-a =c
(c) From ii it is clear that -c= a+b so a+b+c=0
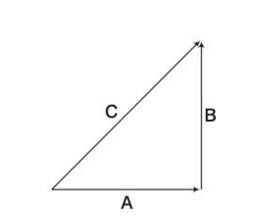
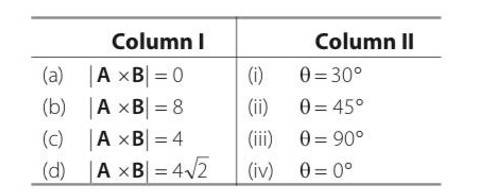
If A = 2 and B = 4, then match the relations in column I with the angle θ between A B and in column II. Column I Column II °
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- given |A|=2 and |B|=4
a)|A |=AB sin = 0
so 2 sin =0
so so it matches with iv
B) |A B|= ABsin =8
2 sin =8
So = 90 so it matches with option iii
c) |A B|= ABsin =4
so =30 so it matches with option i
d) |A B|= ABsin =4
so =45 so it matches with option ii
If A = 2 and B = 4, then match the relations in column I with the angle θ between A B and in column II. Column I Column II °
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- - given |A|=2 and |B|=4
a) |A |=AB cos = 0
so 2 cos =0
so so it matches with ii
b) |A B|= ABcos =8
2 cos =8
So = 0 so it matches with option i
c) |A B|= ABcos =4
so =60 so it matches with option iv
d) |A B|= ABcos =-8
so =180 so it matches with option iii
The angle between A= ȋ + ĵ and B = ȋ - ĵ is
(a) 45° (b) 90° (c) –45° (d) 180°
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- b
Explanation-A = i+j
B = i-j
A.B=|A|B|cos
(? +? ). (? -? ) = cos
Where is the angle between A and B
Cos = =
= 90o
Which one of the following statements is true?
(a) A scalar quantity is the one that is conserved in a process.
(b) A scalar quantity is the one that can never take negative values.
(c) A scalar quantity is the one that does not vary from one point to another in space.
(d) A scalar quantity has the same value for observers with different orientations of the axes.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- d
Explanation- a scalar quantity is independent of direction hence has the same value for observers with different orientations of the axes.
Shows the orientation of two vectors u and v in the XY plane. If u = aȋ + bĵ and
v=p ȋ + q ĵ . which of the following is correct?
(a) a and p are positive while b and q are negative.
(b) a, p and b are positive while q is negative.
(c) a, q and b are positive while p is negative.
(d) a, b, p and q are all positive.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- b
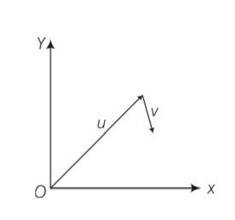
Explanation – u= a? + b? as u in the first quadrant, hence both components a and b will be positive. For v= p? + q? , as it is positive x direction and located downward hence x component p will be positive and y component q will be negative.
The horizontal range of a projectile fired at an angle of 15° is 50 m. If it is fired with the same speed at an angle of 45°, its range will be
(a) 60 m
(b) 71 m
(c) 100 m
(d) 141 m
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- c
Explanation - we know that =150 and R= 50m
Range, R=
50 =
So u2= 980
So u = m/s
So u= 14 = 31.304m/s
= 450, R=
R= = =
Consider the quantities, pressure, power, energy, impulse, gravitational potential, electrical charge, temperature, area. Out of these, the only vector quantities are
(a) Impulse, pressure and area
(b) Impulse and area
(c) Area and gravitational potential
(d) Impulse and pressure
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- b
Explanation – we know that impulse J= f. = , where F is force . is time duration and is change in momentum. As is a vector quantity, hence impulse is also a vector quantity. Sometimes area can also be treated as vector.
In a two dimensional motion, instantaneous speed v0 is a positive constant. Then which of the following are necessarily true?
(a) The average velocity is not zero at any time.
(b) Average acceleration must always vanish.
(c) Displacements in equal time intervals are equal.
(d) Equal path lengths are traversed in equal intervals.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- d
Explanation – speed = total distance travelled /time taken
Total distance travelled = path length
= speed time
We should be very careful with the fact, that speed is related with total distance covered not with displacement.
In a two dimensional motion, instantaneous speed v0 is a positive constant. Then which of the following are necessarily true?
(a) The acceleration of the particle is zero.
(b) The acceleration of the particle is bounded.
(c) The acceleration of the particle is necessarily in the plane of motion.
(d) The particle must be undergoing a uniform circular motion.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer-b, d
Explanation- as given motion is two-dimensional motion and given that instantaneous speed vo is positive constant. Acceleration is rate of change of velocity. hence it will also be in the plane of motion.
It is found that |A+B|=|A|. This necessarily implies,
(a) B = 0
(b) A,B are antiparallel
(c) A,B are perpendicular
(d) A.B ≤ 0
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- b, d
Explanation – given A+B+C = 0
B
B +B =0
B
B
A
(A )
It cannot be zero
(b) (A ).C= (B ).C=0 . if b|C then B =0 then (B )
(c) (A )=X=ABsin . The direction of X is perpendicular to the plane containing A and B (A )
(d) if c2= A2+B2, then angle between A and B is 900
(A ).C= (AB sin900X).C=AB (X.C)
= ABC cos900= 0
It is found that |A+B|=|A|. this necessarily implies.
(a) B=0
(b) A,B are antiparallel
(c) A,B are perpendicular
(d) A.B<0
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- a, b
Explanation - |A+B|= |A|or |A+B|2=|A|2
|A|2 +|B|2+2|A|B|cos = |A|2
|B| (|B|+2|A|cos )= 0
|B|=0 or |B|+2|A|cos =0
Cos =
If A and B are antiparallel then =180
-1=
Two particles are projected in air with speed vo at angles θ1 and θ2 (both acute) to the horizontal, respectively. If the height reached by the first particle is greater than that of the second, then tick the right choices
(a) Angle of projection : q1 > q2
(b) Time of flight : T1 > T2
(c) Horizontal range : R1 > R2
(d) Total energy : U1 > U2 .
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- a,b,c
Explanation – H=
H1=Vo2sin2 1/2g , H2=Vo2sin2 2/2g
H1>H2
Vo2sin2 1/2g= Vo2sin2 2/2g
Sin2 1>sin2 2
Sin2 1 – sin2 2>0
(Sin 1 – sin 2)( Sin 1 + sin 2)>0
Sin 1>sin 2 or 1 >2
T=
T1= , T2=
T1> T2
R=
Sin 1>sin 2
Sin2 1> sin2 2
R1>R2
Total energy for the first particle
U1=K.E+P.E=1/2m1
U2= K.E+P.E= 1/2m2
Total energy for the second particle
So m1= m2 then U1=U2
So m1>m2 then U1>U2
So m1
A particle slides down a frictionless parabolic (y + x2 ) track (A – B – C) starting from rest at point A (Fig. 4.2). Point B is at the vertex of parabola and point C is at a height less than that of point A. After C, the particle moves freely in air as a projectile. If the particle reaches highest point at P, then
(a) KE at P = KE at B
(b) Height at P = height at A
(c) Total energy at P = total energy at A
(d) Time of travel from A to B = time of travel from B to P.
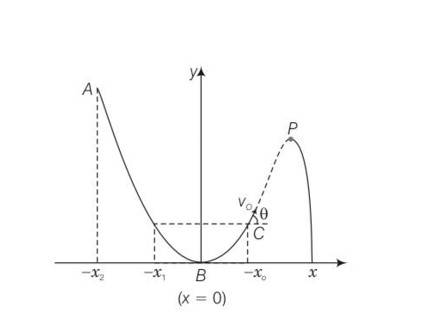
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- c
Explanation– as the given track y=x2 is a frictionless track thus total energy will be same throughout the journey.
Hence total energy at A = total energy at P . at B the particle is having only Ke but at P some KE is converted to P
Hence (KE)B = (KE)P
Total energy at A = PE= total energy at B = KE= total energy at P
= PE+KE
Potential energy at A is converted to KE and PE at P hence
(PE)P< (PE)A
Hence (height)P= (height)A
As height of p < height of A
Hence path length AB > path length BP
Following are four different relations about displacement, velocity and acceleration for the motion of a particle in general. Choose the incorrect one (s) :
(a) Vav=
(b) Vav=
(c) Vav=
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- a, c
Explanation – as we know average acceleration is aav=
But when acceleration is not uniform Vav is not equal to v1+v2/2
So we can write
= v2-v1 (t2-t1)
For a particle performing uniform circular motion, choose the correct statement(s) from the following:
(a) Magnitude of particle velocity (speed) remains constant.
(b) Particle velocity remains directed perpendicular to radius vector.
(c) Direction of acceleration keeps changing as particle moves.
(d) Angular momentum is constant in magnitude but direction keeps changing.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- a, b, c
Explanation- (i) Speed will constant throughout
(ii) Velocity will be tangential in the direction of motion
(iii) Centripetal acceleration will be a= v2/r, will always be towards centre of the circular path.
(iv) Angular momentum is constant in magnitude and direction out of the plane perpendicularly as well.
For two vectors A and B, A B A B + = − is always true when (a) A B = ≠ 0 (b) A⊥ B (c) A B = ≠ 0 and A and B are parallel or anti parallel (d) when either A or B is zero.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- |A+B|=|A-B|
=
4|A|B|cos =0
|A|2+|B|2cos =0
A=0 or B=0 so . so A perpendicular B
Chapters List
Moving Charges and Magnetism Short Answer Type Questions
Read here:
Subject-wise CBSE Questions for Quick Revision
| 1. Show that a force that does no Work must be a velocity dependent force. |
| Explanation- dW=F.dl=0 As dl = vdt dW= Fvdt dW= f.v=0 |
| 2. The magnetic force depends on v which depends on the inertial frame of reference. Does then the magnetic force differ from inertial frame to frame? Is it reasonable that-the net acceleration has a different value indifferent frames of reference? |
| Explanation- yes, the magnetic force differ from inertial frame to frame. The magnetic force is frame dependent. The net acceleration which comes into existing out of this is however, frame independent for inertial frames. |
| 3. Describe the motion of a charged particle in a cyclotron if the frequency of the radio frequency (rf) field were doubled. |
| Explanation – here, the condition of magnetic resonance is violated. When the frequency of radio frequency field were doubled, the time period of the radio frequency field were halved. Therefore , the duration in which particle completes half revolution inside the dees , radio frequency completes the cycle. Hence , particle will accelerate and decelerate alternatively. So the radius of path in the dees will remain same. |
| 4. Two long wires carrying current I1, and I2are arranged as shown in figure. The one carrying current I1 is along the x-axis. The other carrying current I2 is along a line parallel to the y-axis given by x = 0 and z = d. Find the force exerted at O2 because of the wire along the x-axis. |
| Explanation – in biot savart law , magnetic field B is parallel to idlr and idl have its direction along the direction of flow of current. Here, for the direction of magnetic field at O2, due to wire carrying I1 current is B|| parallel idl r or i k, but it is -j So the direction at O2 is along y-direction. The direction of magnetic force exerted at O2 because of the wire along x-axis F= ilB=j(-j)=0 So the force is zero. |
| 5. A current carrying loop consists of 3 identical quarter circles of radius R, lying in the positive quadrants of the x-y, y-z and z-x planes with their centres at the origin, joined together. Find the direction and magnitude of B at the origin. |
| Explanation- general formula for magnetic field at center is B= B1= k for xy plane B2= i for zy plane B3= j for xz plane After joining together B= (i+j+k) |
Moving Charges and Magnetism Multiple Choice Questions
| 1. Two charged particles traverse identical helical paths in a completely oppo-site sense in a uniform magnetic field B = B0k |
| Answer –(d) Explanation- it is determined by its pitch Pitch = = constant So charge by mass ratio is also constant |
| 2. Biot-Savart law indicates that the moving electrons (velocity v) produce a magnetic field B such that |
| Answer – (a) Explanation- in biot savarts law magnetic field is perpendicular to v |
| 3. A current carrying circular loop of radius R is placed in the x-y plane with centre at the origin. Half of the loop with x >0 is now bent so that it now lies in the y-z plane. |
| Answer- (a) Explanation- magnetic moment , M = niA , when we decrease the radius by half its area is decrease by ¼ so the magnetic moment also.so magnetic moment diminishes. |
| 4. An electron is projected with uniform velocity along the axis of a current carrying long solenoid. Which of the following is true? |
| Answer- (d) Explanation- when electron move in the direction of velocity along the axis of current then angle is 180 which makes force according to the relation F=qvbsin . so electron will continue move with uniform velocity along axis of solenoid. |
| 5. In a cyclotron, a charged particle |
| Answer – (a) Explanation – when a charge particle enter in cyclotron it will always accelerated with the help of oscillating electric field. But it will move with the same speed with the help of magnetic field. |
| 6. A circular current loop of magnetic moment M is in an arbitrary orientation in an external magnetic field B. The work done to rotate the loop by 30° about an axis perpendicular to its plane is (a)MB (b) (c) MB/2 (d) zero |
| Answer. (d) Explanation- W=MBcos , as the loop make 30 degree angle but angle made by axis of the loop with the direction of magnetic field, therefore work done is zero. |
| 7. The gyro-magnetic ratio of an electron in an H-atom, according to Bohr model, is . |
| Answer – (a) Explanation- gyro magnetic ratio does not depend upon which electron is rotating. |
| 8.Consider a wire carrying a steady current, I placed in a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to its length. Consider the charges inside the wire. It is known that magnetic forces do not work. This implies that, (b) some charges inside the wire move to the surface as a result of B. |
| Answer- (b,d) Explanation- F=IlB , the direction of force is given by fleming’s left hand rule and F is perpendicular to the direction of magnetic field. So work done is zero. |
| 9. Two identical current carrying coaxial loops, carry current I in an opposite sense. A simple amperian loop passes through both of them once. Calling the loop as C, (a) ФBdl =m I (b) the value of ФB.dl = ±2 I is independent of sense of C (c) there may be a point on C where, B and dl are perpendicular (d) B vanishes everywhere on C |
| Answer- (b,c) Explanation- if current is in opposite sense the ФBdl = 0 , also there exist a point where b and dl is perpendicular. |
| 10. A cubical region of space is filled with some uniform electric and magnetic fields. An electron enters the cube across one of its faces with velocity v and a positron enters via opposite face with velocity -v. At this instant, |
| Answer- (b,c,d) Explanation- magnetic forces on both the particles cause equal acceleration because they both have equal velocity Also they both gain or loose energy because direction of force in both cases is opposite. And there is no change in center of mass of particles so it is determined by B alone. |
| 11. A charged particle would continue to move with a constant velocity in a region wherein, (a) E = 0,B≠0 (b) E≠0,B≠0 (c) E≠0,B = 0 (d) E = 0, B = 0 |
| Explanation- force on charge particle due to both electric and magnetic field . now if electric force and magnetic field is zero then electric field and magnetic field is also zero. Magnetic field is only responsible for constant velocity of charge particle if B=0 then E =0 if B is not equal to zero then electric field is also not equal to zero |
| 12. Verify that the cyclotron frequency ω = eB/m has the correct dimensions of [T]-1 |
| Explanation- for a charge particle to move in circular path Mv2/r = qvB v/r=w= bq/m w= v/r = = T-1 |
Commonly asked questions
A small toy starts moving from the position of rest under a constant acceleration. If it travels a distance of 10m in t s, the distance travelled by the toy in the next t s will be:
According to question, we can write
10 =
At what temperature a gold ring of diameter 6.230cm be heated so that it can be fitted on a wooden bangle of diameter. 6.241cm? Both the diameters have been measured at room temperature (27°C).
(Given : coefficient of linear thermal expansion of gold aL = 1.4 × 10-5 K-1)
According to question, we can write
Two point charge Q each are placed at a distance d apart. A third point charge q is placed at a distance x from mid-point on the perpendicular bisector. The value of x at which charge q will experience the maximum Coulomb’s force is:
According to question, we can write
For maxima of force
The speed of light in media ‘A’ and ‘B’ are 2.0 × 1010 cm/s and 1.5 × 1010 cm/s respectively. A ray of light enters from the medium B to an incident angle ‘q’. If the ray suffers total internal reflection, then
According to question, we can write
In the following unclear reaction,
D
Mass number of D is 182 and atomic number is 74. Mass number and atomic number of D4 respectively will be________
Please find the solution below:
29th June 2022 (Second Shift)
29th June 2022 (Second Shift)
Commonly asked questions
A small toy starts moving from the position of rest under a constant acceleration. If it travels a distance of 10m in t s, the distance travelled by the toy in the next t s will be:
According to question, we can write
10 =
At what temperature a gold ring of diameter 6.230cm be heated so that it can be fitted on a wooden bangle of diameter. 6.241cm? Both the diameters have been measured at room temperature (27°C).
(Given : coefficient of linear thermal expansion of gold aL = 1.4 × 10-5 K-1)
According to question, we can write
Two point charge Q each are placed at a distance d apart. A third point charge q is placed at a distance x from mid-point on the perpendicular bisector. The value of x at which charge q will experience the maximum Coulomb’s force is:
According to question, we can write
For maxima of force
The speed of light in media ‘A’ and ‘B’ are 2.0 × 1010 cm/s and 1.5 × 1010 cm/s respectively. A ray of light enters from the medium B to an incident angle ‘q’. If the ray suffers total internal reflection, then
According to question, we can write
In the following unclear reaction,
D
Mass number of D is 182 and atomic number is 74. Mass number and atomic number of D4 respectively will be________
Please find the solution below:
The electric field at a point associated with a light wave is given by
E = 200
Given : h = 4.14 × 10-15 eVs
If the light fall on a metal surface having a work function of 2.50 eV, the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons will be
The light wave contains two lights of different frequencies, so
Maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectron = 5.9-2.5 = 3.42 eV
A capacitor is discharging through a resistor R. Consider in time t1 the energy stored in the capacitor reduces to half of its initial value and in time t2, the charge stored in the capacitor reduces to half of its initial value and in time t2 the charge stored reduces to one eight of its initial value. The ratio t1/t2 will be
According to Law of discharging of capacitor, we can write
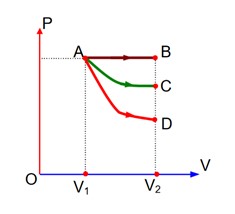
Starting with the same initial conditions, an ideal gas expands form volume V1 to V2 in the three different ways. The work done by the gas in W1 if the process is purely isothermal, W2, if the process is purely adiabatic and W3 if the process is purely isobaric. Then, choose the correct option
Process-AB Isobaric,
Process-AC Isothermal, and
Process-AD? Adiabatic
W2 < W1 < W3
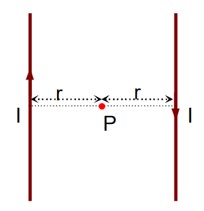
Two long current carrying conductors are placed parallel to each other at a distance of 8 cm between them. The magnitude of magnetic field produced at mid-point between the two conductors due to current flowing in them is 300 . the equal current flowing in the two conductors is
If currents are flowing in same direction, magnetic field will cancel each other, so the currents must flowing in opposite direction
I = 30 A
The time period of a satellite revolving around earth in a given orbit is 7 hours. If the radius of orbit is increased to three its previous value, then approximate new time period of the satellite will be
According to question, we can write
Increment in height of tower = h2 – h1 = 500 – 125 = 375 m
The TV transmission tower at a particular station has a height of 125 m. For doubling the coverage of its range, the height of the tower should be increased by
According to question, we can write
Increment in height of tower = h2 – h1 = 500 – 125 = 375 m
The motion of a simple pendulum executing S.H.M. is represented by the following equation. where time is measured in second. The length of pendulum is
According to question, we can write
A vessel contains 16g of hydrogen and 128g of oxygen at standard temperature and pressure. The volume of the vessel in cm3 is
According to question, we can write
Total moles of gas = n = nOxygen + nOxygen =
Volume of gas = 12 × 22.4 litre = 268.8 litre = 2.688 × 105 cm3
Given below are two statements:
Statement I : The electric force changes the speed of the charged particle and hence charges its kinetic energy; whereas the magnetic force does not change like kinetic energy of the charged particle.
Statement II : The electric force accelerates the positively charged particle perpendicular to the direction of electric field. The magnetic force accelerated the moving charged particle along the direction of magnetic field.
In the light of the above statements, chose the most appropriate answer from the option given below
According to Lorentz’s Force, we can write
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
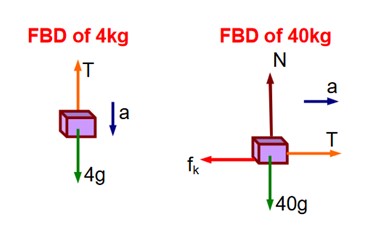
A block of mass 40kg slides over a surface, when a mass of 4kg is suspended through an inextensible massless string passing over frictionless pulley as shown below.
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the surface and block is 0.02. The acceleration of block is. (given g = 10 ms-2.)
According to Newton’s laws of motion, we can write
4a = 4g – T . (1), and
40a = T - fk = T (40g) ……………… (2)
Adding equations (1) and (2), we can write
44a = 40 – 0.02 × (400) = 32
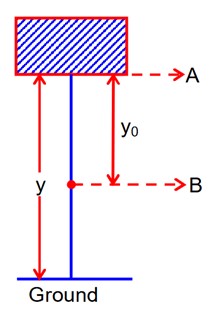
In the given figure, the block of mass m is dropped from the point ‘A’. The expression for kinetic energy of block when it reaches point ‘B’ is
According to conservation of energy, we can write
Gain in kinetic energy = Loss in potential energy
Kf – Kin = Uin - Uf
K - = mgy – mg (y – y0) = mgy0
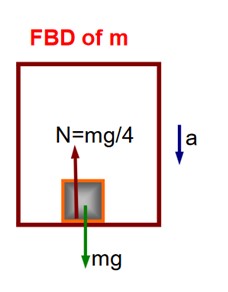
A block of mass M placed inside a box descends vertically with acceleration ‘a’. The block exerts a force equal to one-fourth of its weight on the floor of the box. The value of ‘a’ will be
According to Newton’s law of motion, we can write
ma = mg – N = mg
If the electric potential at any point (x, y, z)m in space is given by V = 3x2 volt. The electric field at the point (1, 0, 3)m will be
According to relation between field and potential, we can write
The combination of two identical cells, whether connected in series or parallel combination provides the same current through an external resistance of The value of internal resistance of each cell is
According to question, we can write
A person can throw a ball upto a maximum range of 100m. How high above the ground he can the same ball?
According to question, we can write
The Vernier constant of Vernier calipers is 0.1 mm and it has zero error of (-0.05) cm. White measuring diameter of a sphere, the main scale reading is 1.7 cm and coinciding vernier division is 5. The correct diameter will be__________ × 10-2 cm.
Least count of Vernier = 0.1mm
Reading of Vernier Scale = 5 × 0.1 = 0.5mm
The corrected diameter of sphere = Main Scale Reading + Vernier Scale reading + Zero correction = 1.7 + 0.05 + 0.05 = 1.8cm = 180 × 102 cm.
A small spherical ball of radius 0.1mm and density 104kgm-3 falls freely under gravity through a distance h before entering a tank of water. If, after entering the water the velocity inside water, then the value of h will be_________ m.
(Given g = 10 ms-2, viscosity of water = 1.0 × 10-5 N-sm-2).
mg = FB + Fv
In an experiment to determine the velocity of sound in air at room temperature using a resonance tube, the first resonance is observed when the air column has a length of 20.0 cm for a tuning form of frequency 400 Hz is used. The velocity of the sound at room temperature is 336 ms-1. The third resonance is observed when the air column has a length of ____________cm.
According to Concept of resonance tube, we can write
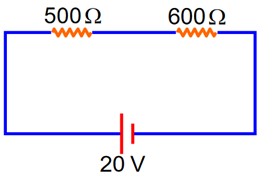
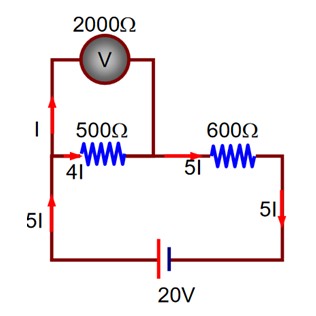
Two resistors are connected in series across a battery as shown in figure. If a voltmeter of resistance 2000 is used to measure the potential difference across 500 resister, the reading of the voltmeter will be_________ V.
According to Kirchhoff’s Law, we can write
20 + 2000I + 600 × 5I = 0
Reading of voltmeter = 2000I = 2000 ×
A potential barrier of 0.4V exists across a p-n junction. An electron enters the junction from the n-side with a speed of 6.0 × 105. The speed with which electron enters the p side will be the value of x is__________.
(Given mass of electron = 9 × 10-31 kg, charge on electron = 1.6 × 10-19 C.)
According to Work energy theorem, we can write
The displacement current of 4.425 is developed in the space between the plates of parallel plate capacitor when voltage is changing at a rate of 106 Vs-1. The area of each plate of the capacitor is 40 cm2. The distance between each plate of the capacitor is x × 10-3. The value of x is,
(Permittivity of free space,
According to definition of displacement current, we can write
The momentum of inertia of a uniform thin rod about a perpendicular axis passing through on end is I1. The same rod is into a ring and its moment of inertia about a diameter is I2. If then the value of x will be__________.
According to question, we can write
The half life of a radioactive substance is 5 years. After x years a given sample of the radioactive substance gets reduced to 6/25% of its initial value. The value of x is___________.
According to Nuclear activity, we can write
Time required = 4 ×
In a double slit experiment with monochromatic light, fringes are obtained on a screen placed at some distance from the plane of slits. If the screen is moved by 5 × 10-2m towards the slits, the change in fringe width is 3 × 10-3cm. If the distance between the slits is 1mm, then the wavelength of the light will be_____________ nm.
According to Young’s double slit experiment, we can write
An inductor of 0.5 mH, a capacitor of 200 and a resistor of 2 are connected in series with a 220V ac source. If the current is in phase with the emf, the frequency of ac source will be__________ × 102 Hz.
Since current is in phase with voltage, it means circuit is in resonance, so we can write
f =
JEE Maisn 2020
Commonly asked questions
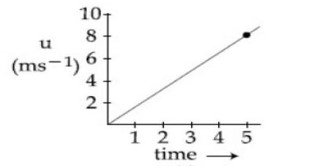
The speed verses time graph for a particle is shown in the figure. The distance travelled (in m ) by the particle during the time interval t = 0 to t = 5 s will be .....
Distance moved = Area under curve
= ½ * 8 * 5 = 20
The distance between an object and a screen is 100 cm. A lens can produce real image of the object on the screen for two different positions between the screen and the object. The distance between these two positions is 40 cm. If the power of the lens is close to (N/100) D where N is an integer, the value of N is
P = 1/f = (N/100)D
2x + 40 = 100
x = 30 cm
100 – x = 70 cm
1/v - 1/u = 1/f
1/70 - 1/ (-30) = 1/f
1/f = 1/70 + 1/30 = (3+7)/210 = 1/21
f = 21 cm = 0.21M
Power = 1/f = 1/0.21; D = (100)/21
N/100 D = 100/21
N = 10000/21 = 476.19
N = 476
The change in the magnitude of the volume of an ideal gas when a small additional pressure ΔP is applied at a constant temperature, is the same as the change when the temperature is reduced by a small quantity ΔT at constant pressure. The initial temperature and pressure of the gas were 300 K and 2 atm. respectively. If |ΔT| = C|ΔP| then value of C in (K/atm) is ….
T = constant
P = constant
PV = nRT
PdV = nRdT
PdV + VdP = 0
ΔV = nRΔT/P
dV = (-)VdP/P
|ΔV| = V (ΔP/P)
V/P ΔP = nRΔT/P
ΔT = V/nR ΔP
C = V/nR T/P = 300/2 = 150
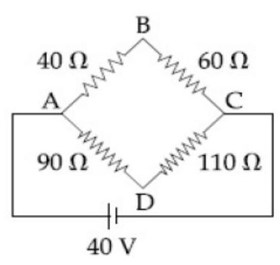
Four resistance 40Ω, 60Ω, 90Ω, and 110Ω make the arms of a quadrilateral ABCD. Across AC is a battery of emf 40 V and internal resistance negligible. The potential difference across BD in V is
i? = 40/100 = 2/5
i? = 40/200 = 1/5
V? – V? = 40i? = 40 × 2/5
V? – V? = 16
V? – Vd = 90i? = 90/5 = 18
V? – Vd = 18 – 16 = 2 volt
Orange light of wavelength 6000 × 10-10 m illuminates a single slit of width 0.6 × 10-4 m. the maximum possible number of diffraction minima produced on both sides of the central maximum is
λ = 6 × 10? M
d = 6 x 10? M
I = I? [ (sin (β)²/β²] ; β = (πdsinθ)/λ
θ = π/2 ; β = πd/λ
= (π (6 × 10? )/ (6 x 10? ) = 100π
So at ∞ also minima will form total number of minima = 2 × 100 = 200
Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Four Exam