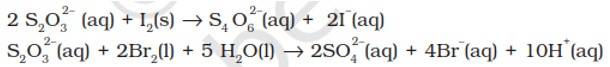Redox Reactions
Get insights from 164 questions on Redox Reactions, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Redox Reactions
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) F. Fluorine being the most electronegative element shows only a -ve oxidation state of -1.
(b) Cs. Alkali metals because of the presence of a single electron in the valence shell, exhibit an oxidation state of +1.
(c) I. Because of the presence of seven electrons in the valence shell, I shows an oxidation state of -1 (in compounds of I with more electropositive elements such as H, Na, K, Ca, etc.) or an oxidation state of +1 compounds of I with more electronegative elements, i.e., O, F, etc.) and because of the presence of d-orbitals it also exhibits +ve oxidation states of +3, +5 and +7.
(d) Ne. It is an inert gas (with high ioni
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The unbalanced chemical reaction is:
Mn3+ (aq) → Mn2+ (aq) + MnO2? (s) + H+ (aq)
The oxidation half reaction is,
Mn3+ (aq) → MnO2? (s).
To balance oxidation number, one electron is added on R.H.S.
Mn3+ (aq) → MnO2? (s) + e−
4 protons are added to balance the charge.
Mn3+ (aq) → MnO2? (s) + 4H+ (aq) + e−
2 water molecules are added to balance O atoms.
The reduction half reaction is Mn3+ (aq) → Mn2+ (aq).
An electron is added to balance oxidation number.
Mn3+ (aq) + e− → Mn2+ (aq)
Two half-cell reactions are added to obtain balanced chemical equation.
2Mn3+ (aq) + 2H2? O (l) → Mn2+ (aq) + MnO2? (s) + 4H+ (aq)
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Let x be the O.N. of C.
O.N. of C in cyanogen, (CN)2 = 2 (x – 3) = 0 or x = +3
O.N. of C in cyanide ion, CN- = x – 3 = -1 or x = +2
O.N. of C in cyanate ion, CNO =x-3-2 = -l or x: = +4
The four information about the reaction are:
(i) The reaction involves decomposition of cyanogen, (CN)2 in the alkaline medium to cyanide ion, CN and cyanate ion, CNO–.
(ii) The O.N. of C decreases from +3 in (CN)2 to +2 in CN–ion and increases from +3 in (CN)2 to +4 in CNO– ion. Thus, cyanogen is simultaneously reduced to cyanide ion and oxidised to cyanate ion.
(iii) It is an example of a redox reaction in general an
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a)
Oxidation number method:
The oxidation number of P decreases from 0 to -3 and increases from 0 to +2. Hence, P4? is oxidizing as well as reducing agent.
During reduction, the total decrease in the oxidation number for 4 P atoms is 12.
During oxidation, total increase in the oxidation number for 4 P atoms is 4.
The increase in the oxidation number is balanced with decrease in the oxidation number by multiplying H2? PO2−? with 3.
P4? (s) + OH− (aq) → PH3? (g) + 3H2? PO2−? (aq)
To balance O atoms, multiply OH− ions by 6.
P4? (s) + 6OH− (aq) → PH3? (g) + 3H2? PO2−? (aq)
To balance H atoms, 3 water
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) The balanced half reaction equations are:
Oxidation half equation:
I− (aq) → I2 (s) - (i)
Reduction half reaction equation:
MnO4− (aq) → MnO2 (aq) - (ii)
Balance I atoms and charges in the oxidation half reaction.
2I− (aq) → I2 (s) + 2e−
In the reduction half reaction, the oxidation number of Mn changes from +7 to +4. Hence, add 3 electrons to reactant side of the reaction.
MnO4− (aq) + 3e−→ MnO2 (aq)
Balance charge in the reduction half reaction by adding 4 hydroxide ions to product side.
MnO4− (aq) + 3e− → MnO2 (aq)+4OH−
To balance O atoms, add 2 water molecules to reactant s
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Reactions (a) and (b) indicate that H3PO2 (hypophosphorous acid) is a reducing agent and thus reduces both AgNO3 and CuSO4 to Ag and Cu respectively. Conversely, both AgNO3 and CuSO4 act as oxidising agent and thus oxidise H3PO2to H3PO4 (orthophosphoric acid) Reaction (c) suggests that [Ag (NH3)2]+ oxidises C6H5CHO (benzaldehyde) to C6H5COO– (benzoate ion) but reaction (d) indicates that Cu2+ ions cannot oxidise C6H5CHO to C6H5COO–. Therefore, from the above reactions, we conclude that Ag+ ion is a strong deoxidising agent than Cu2+ ion.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
XeO64−? oxidizes F− and F− reduces XeO64−?
Hence, the given reaction occurs.
The oxidation number of Xe decreases from +8 to +6. The oxidation number of F increases from -1 to 0.
Thus, Na4? XeO6? is a stronger oxidising agent than F−.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Fluorine oxidizes chloride ion to chlorine, bromide ion to bromine and iodide ion to iodine respectively.
F2? + 2Cl− → 2F− + Cl2?
F2? + 2Br− → 2F− + Br2?
F2? + 2I− → 2F− + I2?
Chlorine oxidizes bromide ion to bromine and iodide ion to iodine.
Cl2? + Br− → 2Cl− + Br2?
Cl2? + I− → 2Cl− + I2?
Bromine oxidizes iodide ion to iodine.
Br2? + I− → 2Br− + I2?
But bromine and chlorine cannot oxidize fluoride to fluorine. Hence, fluorine is the best oxidizing agent amongst the halogens. The decreasing order of the oxidizing power of halogens is F2? >Cl2? >Br2? >I2?
HI and HBr can reduce sulphuric acid
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The average O.N. of S in S2O32- is +2 while in S4O62- it is + 2.5. The O.N. of S in SO42- is +6. Since Br2 is a stronger oxidising agent than I2, it oxidises S of S2O32- to a higher oxidation state of +6 and hence forms SO42- ion. I2, however, being weaker oxidising agent oxidises S of S2O32- ion to a lower oxidation of +2.5 in S4O62- ion. It is because of this reason that thiosulphate reacts differently with Br2 and I2.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Substance oxidised | Substance reduced | Oxidising agent | Reducing agent |
(a) C6H12O6 | AgBr | C6H12O6 | |
(b) HCHO | [Ag (NH3)2]+ | [Ag (NH3)2]+ | HCHO |
(c) HCHO | Cu2+ | HCHO | |
(d) N2H4 | H2O2 | N2H4 | |
(e) Pb | PbO2 | Pb |
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers