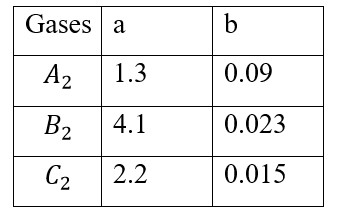
States of Matter
Get insights from 92 questions on States of Matter, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about States of Matter
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 9
- atom
or
or
Hence, number of different lines possible
Minimally, both can have same transition i.e etc.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
From ΔT? = K? * m, and ΔT? = 15°C
∴ m = ΔT? / K? = 15 / 1.86 = 8.06
So the amount of propyl alcohol to be added.
= m * molwt = 8.06 * 60 = 483.6 g
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
At Boyle's Temperature ; gas behaves ideally for a range of pressure.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
P? = 1atm
P? = 1atm * 40/100 = 0.40atm
V? = 100 cm³
V? =?
At constant temperature, P? V? = P? V?
So V? = (P? V? ) / P? = (1atm * 100 cm³) / 0.40 atm = 250cm³
Hence, the volume of bulb B = (250 –100) cm³ = 150 cm³
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
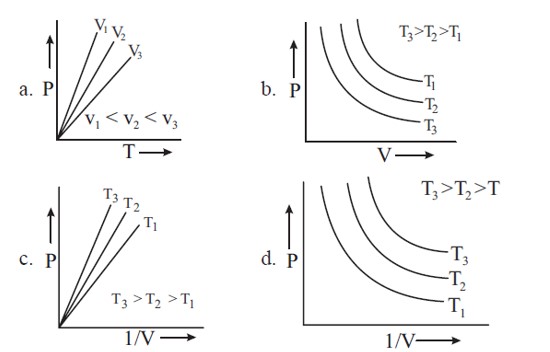
PV = nRT
P = nRT . (1/V)
Plot of P vs (1/V) would be straight line passing through origin having slope = nRT.
At high temperatures, P vs (1/V) would have greater slope.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
Covalent bonding is NOT an intermolecular force while rest all are considered as intermolecular forces.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
n (B) = 3/2
n (B) = 3, n (O) = 2
n (Total) = 3 + 2 = 5
X (B) = n (B) / n (T) = 3/5
X (O) = n (O) / n (T) = 2/5
P (S) = P° (B)X (B) + P° (O)X (O)
P (S) = 280 * (3/5) + 420 * (2/5)
= 336 mm of Hg
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers