Thermodynamics
Get insights from 325 questions on Thermodynamics, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Thermodynamics
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
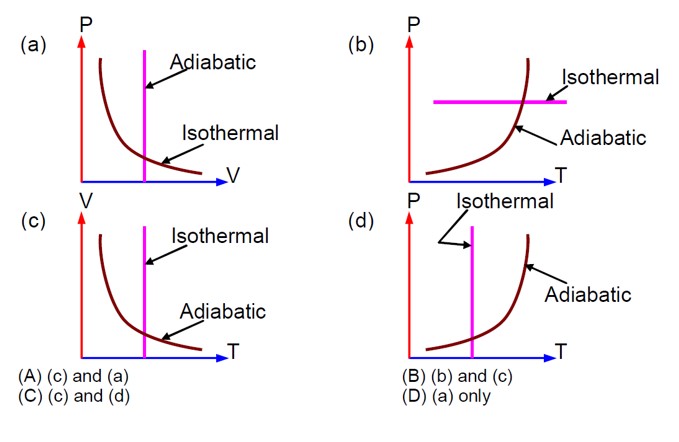
Pressure decreases with an increase in volume in both isothermal and adiabatic processes. In an adiabatic process, as volume decreases, pressure increases with the increase in temperature.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
In an LCR series AC circuit, the phase difference φ between current and voltage is: φ = tan? ¹ (X? - X? ) / R)
If each vibrational mode contributes two degrees of freedom and the total degrees of freedom f = 3 + 3 + 4 = 10, then:
β = 1 + 2/f = 1 + 2/10 = 1.2
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
3CaO + 2Al → 3Ca + Al? O?
ΔH? = ΣΔH? (Products) - ΣΔH? (Reactants)
ΔH? = [ (0) + (-1675) ] - [ (3 * -635) + (0) ]
ΔH? = -1675 - (-1905) = -1675 + 1905 = 230 kJ
Ans = 230
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
U = U? + U? = (n? /N_A) (F? R/2)T? + (n? /N_A) (F? R/2)T?
For the mixture: U = (n? +n? )/N_A * (FR/2)T
F = (n? F? + n? F? ) / (n? + n? )
Equating the expressions for U and solving for T gives:
T = (n? F? T? + n? F? T? ) / (n? F? + n? F? )
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
η = 1 - T_C / T_H
η = 1 - 400/800 = 1 - ½ = ½
η = W/Q_H ⇒ ½ = W/Q_H ⇒ Q_H = 2W = 2 * 1200 = 2400 J
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
f = f_Translational + f_Rotational + f_Vibrational
f = 3 + 3 + 48 = 54 (Since each vibrational mode has two degrees of freedom)
γ = 1 + 2/f = 1 + 2/54 = 1 + 1/27 = 28/27 ≈ 1.03
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
1/4 m (210)² = m (0.03) x (4.2) x 1000 x ΔT ; Q = mSΔt
ΔT = (210) (210)/ (4) (4.2) (0.03) (1000) = 87.5°C
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers