Wave Optics
Get insights from 88 questions on Wave Optics, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Wave Optics
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- resolving power =1/d = = dmin= where is the wavelength of light
So dmin=
= = 0.12 10-9m
= = 0.2 10-3
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- When angle of incidence is equal to Brewster's angle, the transmitted light is unpolarised and reflected light is plane polarised.
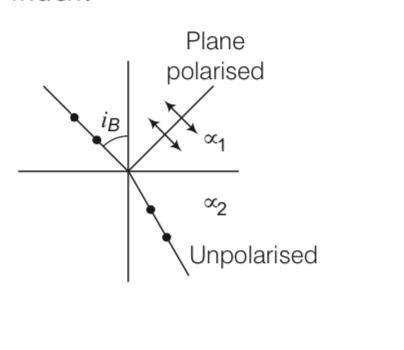
Consider the diagram in which unpolarised light is represented by dot and plane polarised light is represented By arrows.
Polarisation by reflection occurs when the angle of incidence Is the Brewster's angle
So tanib = where 2< 1
When the light rays travels in such a medium, the critical angle is
Sinic=
Where 2< 1
As tanib > sinic for large angles ibc
Thus the polarisation by reflection occurs definitely.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- As per the given question, monochromatic light emerging from polaroid (I) is plane polarised. When polaroid (II) is placed infront of this polaroid (I), and rotated till no light passes through polaroid (II), then (I) and (II) are set in crossed positions, i.e., pass axes of I and II are at 90°.
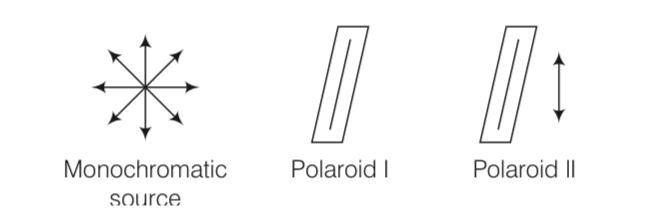
Consider the above diagram where a third polaroid (III) is placed between polaroid (I) and polaroid II.
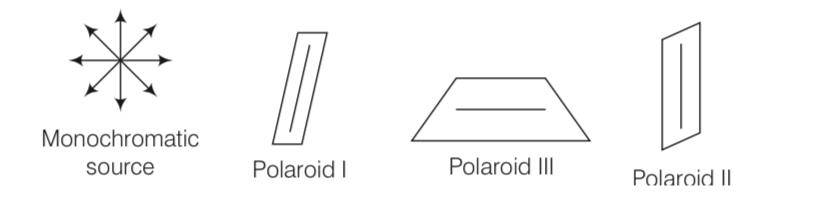
When a third polaroid (III) is placed in between (I) and (II), no light will emerge from (II), if pass axis of (III) is parallel to pass axis of (I) or (II). In
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- angular resolution of the eye? = 5.8 x 10-4
linear distance between two dots is l= 2.54/300=0.84 10-2cm
? = l/z
z=l/? = = 14.5cm
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- As we know that the frequencies of sound waves lie between 20 Hz to 20 kHz so that their wavelength ranges between 15 m to 15 mm. The diffraction occur if the wavelength of waves is nearly equal to slit width.
As the wavelength of light waves is 7000 *10-10 m to 4000 10-10m. The slit width is very near to the wavelength of sound waves as compared to light waves. Thus, the diffraction of sound waves is more evident in daily life than that of light waves.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- We know that the sun is at very large distance from the earth. Assuming sun as spherical, it can be considered as point source situated at infinity. Due to the large distance the radius of wavefront can be considered as large (infinity) and hence, wavefront is almost plane.
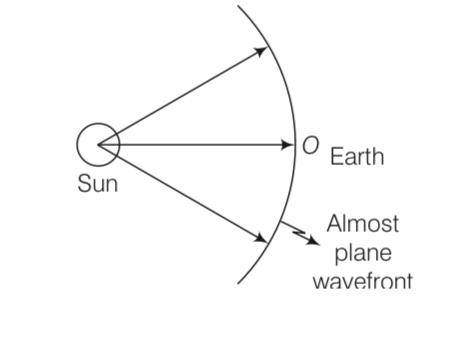
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- The point image I1, due to L1 is at the focal point. Now, due to the converging lens L2, let final image formed is I which is point image, hence the wavefront for this image will be of spherical symmetry.
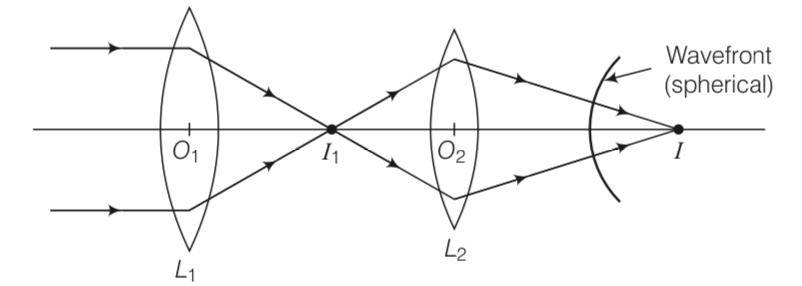
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- When we are considering a point source of sound wave. The disturbance due to the source propagates in spherical symmetry that is in all directions. The formation of
wavefront is in accordance with Huygen's principle.
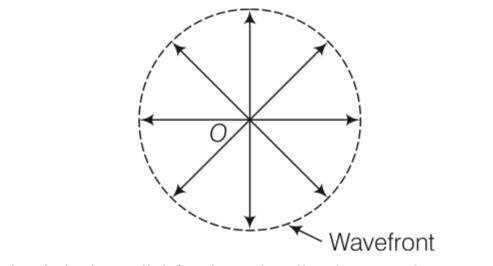
So, Huygen's principle is valid for longitudinal sound waves also.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- refractive index = 1.38 refractive index = 1.5
0
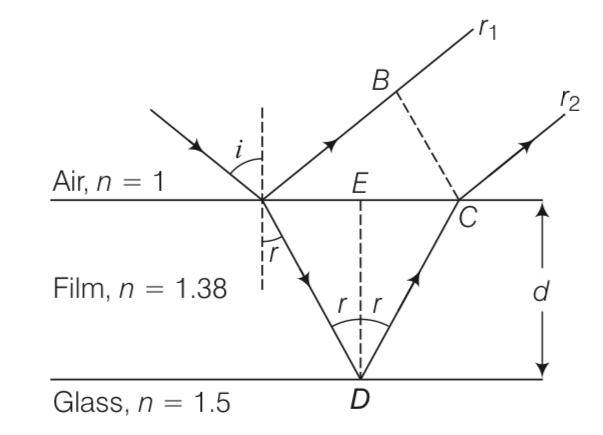
Consider a ray incident at an angle i. A part of this ray is reflected from the air-film interface And apart refracted inside.
This is partly reflected at the film-glass interface and a part transmitted. A part of the
reflected ray is reflected at the film-air interface and a part transmitted as r2 parallel to r 1. Of course successive reflections and transmissions will keep on decreasing the amplitude of the wave. Hence, rays r 1 and r2 shall dominate the behaviour. If incident light is to be transmitted thro
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-All points with the same optical path length must have the same phase.
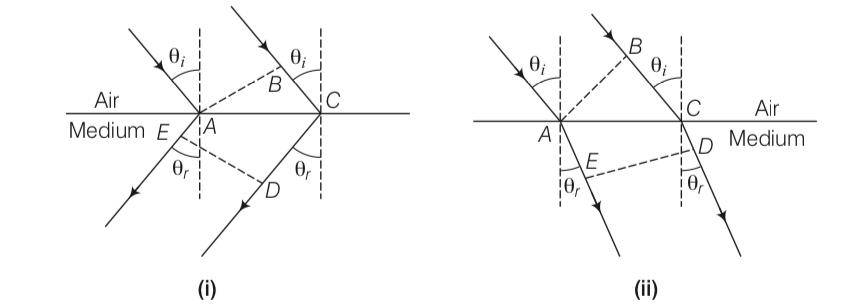
So – =BC-–
BC= (CD-AE)
BC>0, si must be greater than AD
But in other figure
–
So BC= –
But clearly here BE is less than zero
To proving snells law we know that
BC=ACsin and CD-AE=ACsin
So n= sini/sinr
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 687k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
