Work, Energy and Power
Get insights from 177 questions on Work, Energy and Power, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Work, Energy and Power
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
If you look closely at the formula of kinetic energy (1/2*m*v^2), the velocity is squared which automatically gives a positive integer. And mass of the body can never be a negative value, which leads to the result being a positive integer.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
The 1/2 is a result of mathematical calculation, which occurs when we integrate? vdv in the formula of work done according to Newton's second law of motion. Without this, the final result will turn out to be twice of the actual value.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
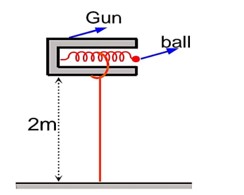
Let ball starts its motion with horizontal velocity v0, so with the help of conservation of mechanical energy, we can write
t = Time required to fall the ball =
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
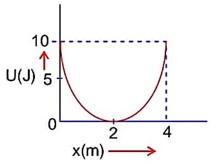
Maximum energy = 10 J
K = 5
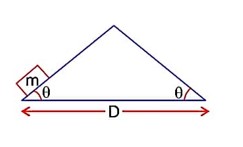
Given Tpendulum = Tspring
g = 4m/s2
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
Energy required to melt
Q =
->3.53 * 104 J
Heat produce in wire
H = l2RT
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
By work energy theorem
Work done = change in K.E.
Work done by friction work done by spring
As 90% of K.E. is losed by friction so that
-K -> -16 * 105
K = 16 * 105
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
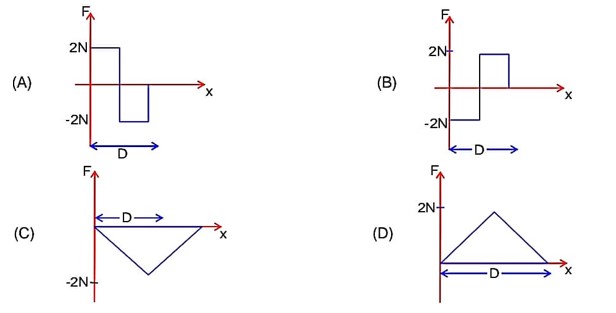
Object is moving in upward direction with constant velocity so in upward motion (+2N) and for downward motion (-2N) So option (1) is correct representation.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers