Work, Energy and Power
Get insights from 177 questions on Work, Energy and Power, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Work, Energy and Power
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
The angular acceleration direction is given along angular velocity or opposite to angular velocity depending upon whether angular velocity magnitude is increasing or decreasing and this direction remains along the axis of circular motion.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
(1/2)kx² = (1/2)mv² ⇒ x = v√ (m/k) = 10 * √ (4/100) = 10 * (2/10) = 2m
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
With the help of definition of e, we can write
e = v? /v? = 2v/u ⇒ u = 2v/e . (2)
Putting the value of e in equation (1), we have
m? (2v/e) = (m? - m? )v ⇒ 2m? = em? - em? ⇒ m? /m? = (2+e)/e = 1 + 2/e > 2
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
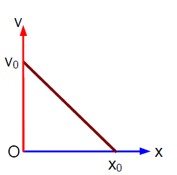
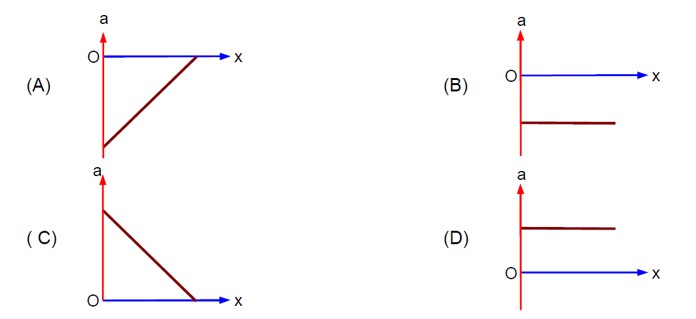
(v/v? ) + (x/x? ) = 1 ⇒ v = - (v? /x? )x + v?
⇒ a = dv/dt = - (v? /x? ) (v) = - (v? /x? ) [- (v? /x? )x + v? ] ⇒ a = (v? ²/x? ²)x - v? ²/x?
- Concept involved: Graph of kinematics
- Topic: Kinematics
- Difficulty level: Moderate
- Note: IIT-Jee-2005
- Point of Error: Writing Equation of straight line and differentiation
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 9
Using Conservation of Mechanical Energy at point-A and at point-B, we can write
K_B = U_A - U_B [Since K_A = 0]
⇒ (1/2)mv_B² = mg (h_A - h_B)
⇒ v_B = √ (2 * 10 * (10 - 5) = 10m/s
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 9
Deceleration, a = u² / 2S = 10² / (2 * 0.5) = 100 m/s².
Retarding force, F = MA = 0.1 * 100 = 10N
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 9
m (dv/dt) = P ⇒ ∫v dv = ∫ (P/m) dt ⇒ v = (2Pt/m)¹/²
⇒ ∫dx = ∫ (2P/m)¹/² t¹/² dt ⇒ x = (2P/m)¹/² (2/3)t³/² ⇒ x ∝ t³/²
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
For a bouncing object with initial height h = 5m and coefficient of restitution e = 0.9 (so e² =0.81):
Total distance traveled, d = h + 2e²h + 2e? h + . = h * (1 + e²) / (1 - e²)
Total time taken, t = √* (2h/g)* + 2√* (2e²h/g)* + 2√* (2e? h/g)* + . = √* (2h/g)* * (1 + e) / (1 - e)
Average speed = d/t = √* (gh/2)* * (1 + e²) / (1 + e)² = 5 * (1.81) / (1.9)² = 2.50 m/s
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
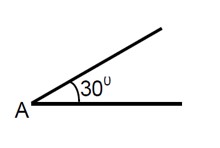
The acceleration 'a' is calculated as:
a = (g sinθ) / (1 + I/mr²) = (10 * sin30°) / (1 + 2/5) = 25/7 m/s²
The time 't' is calculated as:
t = 2v / a = (2 * 1) / (25/7) = 0.57 s
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers