Work, Energy and Power
Get insights from 177 questions on Work, Energy and Power, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Work, Energy and Power
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
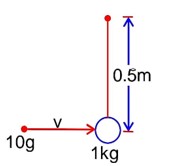
Work done is equal to change in K.E.
W1 -> work done by mg
W2 -> work done by air friction
W2 = -0.68 mgh
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
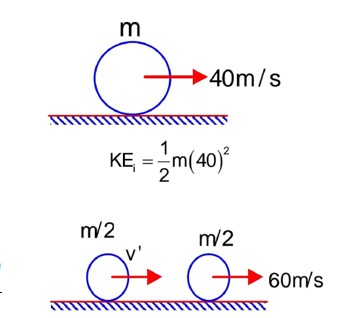
Using conservation of linear momentum:
=> 40 * 3m = 60 * m + v * 2m
=> v = 30 m/s
Fractional change in kinetic energy = 1
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
Velocity of bob after collision,
v1
From Conservation of Momentum,
->v = 400 m/s
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
The two main types of potential energy are:
- Gravitational Potential Energy - Energy stored due to an object's position in a gravitational field (PE = mgh).
- Elastic Potential Energy - Energy stored in deformed elastic objects like springs or stretched materials (PE = ½kx²).
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
The best way to find potential energy is to use the relationship
and integrating the conservative force over the path.
For common cases, apply the standard potential energy formulas:
- PE = mgh for gravity
- PE = ½kx² for springs.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers