Work, Energy and Power
Get insights from 177 questions on Work, Energy and Power, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Work, Energy and Power
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
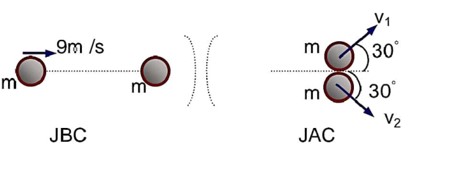
Using conversation of momentum in direction perpendicular to the original direction of motion,
mv1 sin 30° = mv2 sin 30°
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
Power calculations can also differ based on the nature of forces, which are as follows:
- Conservative Forces: Here, work done is path-independent. e.g., gravity, spring force
- Non-Conservative Forces: Work depends on the path. e.g., friction
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 9
by conservation of mechanical energy
K.Ei + P.Ei = K.Ef + P.Ef
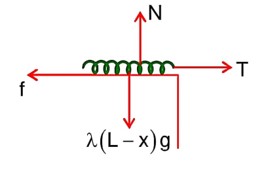
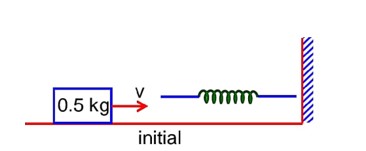
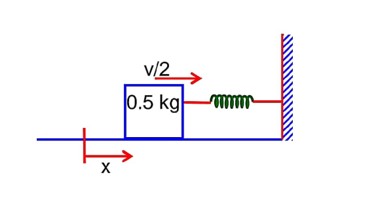
k = 600 N/m1
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
Velocity just before striking the ground
v? = √2gh
v? = √ (2*10*10) = 10√2 m/s
v? = -10√2?
If it reaches the same height, speed remains same after collision only the direction changes.
v? = 10√2 m/s
v? = 10√2?
|Impulse| = m|Δv|
= m|10√2? - (-10√2? )|
= 0.15 [2 (10√2)]
= 3√2 kg m/s
= 4.2 kg m/s
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
