Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Get insights from 189 questions on Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
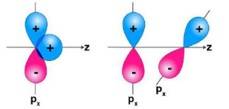
Ans: In the first figure given above, the area which is under + overlapping is equal to the area under +- overlap. Both the overlaps cancel out with each other as they are oppositely charged. Due to cancelling out of the overlaps the net overlap will be zero. In the second figure given above, both the p-orbitals are perpendicular to each other. Due to the, px py orbitals being perpendicular with each other, no overlap will be possible.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
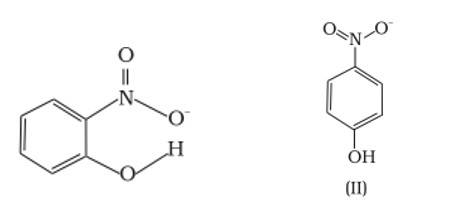
Ans: (a) Which of the two compounds will have intermolecular hydrogen bonding and which compound is expected to show intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
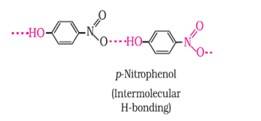
Ans: The intramolecular hydrogen bonding is shown by compound (I) and the intermolecular hydrogen bonding is shown by compound (II) . In compound (I) the NO2 and OH group are close together in comparison to that in compound (II) . So, that is why compound (I) shows intramolecular hydrogen bonding. The intermolecular hydrogen bonding in compound (II) is shown as:
(b) The melting point of a compound depends on, among other
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: In BrF5 the central bromine atom has 7 valence electrons. It makes five bonds with the fluorine atom and one lone pair of electron is left. Due to the lone pair-bond pair repulsions, BrF5 makes a structure of square pyramidal geometry. Due to the distortion of fluorine ions, each fluorine ion makes an angle of 90° . The square pyramidal shape of BrF5 is
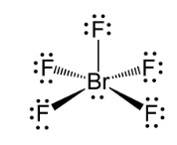
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The electronic configurations of O2+ and O2 - according to molecular orbital theory is:
O2+: σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 s2pz2, π2p2y , π2p2x, π*2p1x
O2- : σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 s2pz2, π2p2y , π2p2x, π*2p2y π*2p1x
The bond order of O2+
Bond order = ( Nb- Na)
Bond order = (10-5)=2.5
The bond order of O2-
(10-7)= = 1.5
As the bond order of O2+ is higher, it is more stable than O2 -, because higher the bond order more stable is the bond. Both the molecular species have the presence of unpaired electrons. So, they both are paramagnetic in
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: In the Lewis structure of PCl3, the phosphorus atom is surrounded by three bond pairs (chlorine atoms) and one lone pair. These four electron pairs are arranged in a tetrahedral geometry around the central phosphorus atom. Due to the presence of lone pair of electron on the phosphorus atom, PCl3 will have a distorted tetrahedral geometry. Thus, it will form a pyramidal shape and is non-linear in structure.
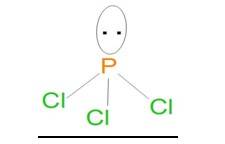
In H2S, the central sulphur atom is surrounded by two bond pairs and two lone pairs of electrons. It can be said that these four electron pairs are arranged in
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (iii)
Molecules from hydrogen to nitrogen shows this type of electronic configuration:
σ1s σ*1s< 2s < *2s< [ 2px = π2py] < 2pz< [ *2px = π*2py] σ*2pz in which σ2pz is filled after π2px and π2py
So, amongst the given elements only nitrogen will show this type of electronic configuration in which σ2pz molecular orbital is filled after π2py and π2px
The electronic configuration of N2 is:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2, π2p2x , π2p2y, s2pz2 π*2p1x
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (ii)
(i) The electronic configuration of O2 is:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 s2pz2 π2p2y π2p2x π*2p1y π*2p1x
Bond order = ( Nb- Na)
Bond order = (10-6)=2.0
The electronic configuration of N2 :
σ1s2 σ*1s2 σ2s2 σ*2s2 π2p2x, π2p2y σ2p2z
Bond order = (10-4)=3.0
So, the bond order of O2 , N2 will not be equal.
(ii) The electronic configuration of O2+ is:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 s2pz2,π2p2y , π2p2x, π*2p1x
Bond order = (10-5)=2.5
The electronic configuration of N2-
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 ,π2p2x , π2p2y, s2pz2 π*2p1x
Bond order = (10-5)=2.5
He
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (ii)
Nodal plane is a plane which passes through the nucleus and the probability of finding an electron on a nodal plane is zero. Amongst the above given molecular orbital, only π*2px contains two nodal planes. Rest of the molecular orbitals, σ∗1, π2px, π*2py contains one nodal plane.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i) The electronic configuration of dioxygen is:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 s2pz2 π2p2y π2p2x π*2p1y π*2p1x
(ii) As it can be seen from the electronic configuration of oxygen atom π*2p1X π*2p1Y the are partially. So, the statement given is incorrect.
(iii) The statement given is correct because there are five bonding molecular orbitals and four antibonding molecular orbital in oxygen molecules. Hence, the bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals are no equal.
(iv) The filled bonding orbitals are not the same as the number of filled antibonding orbi
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
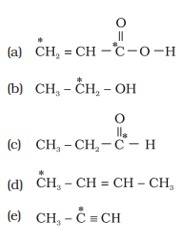
Ans: (i) Different types of hybridization in a carbon atom are:
(a) sp hybridization: The carbon atoms forming triple bonds with each other determines hybridized carbon. ( Cº C ).
(b) sp2 hybridization: The carbon atoms forming double bonds with each other determine sp2 hybridized carbon. (C=C). (c) sp3 hybridization: The carbon atoms forming single bonds with each other determine sp3 hybridized carbon. ( C-C).
(ii)The starred C atom is sp2 hybridised.
B] The starred C atom is sp3 hybridised.
C] The starred C atom is sp2 hybridised.
D] The starred C atom is sp3 hybridis
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers