Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Get insights from 189 questions on Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
(i) Hydrogen bond (d) HF
(ii) Resonance (e) O3
(iii) Ionic bond (b) LiF
(iv) Covalent solid (a) C
Explanation :-
(i) In hydrogen fluoride HF, hydrogen forms
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
(i) NO (c) 2.5
(ii) CO (d) 3.0
(iii) O22- (a) 1.5
(iv) O2
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
(i) H3O+ (e) Pyramidal
(ii) HC? CH (a) Linear
(iii) ClO2- &nb
New answer posted
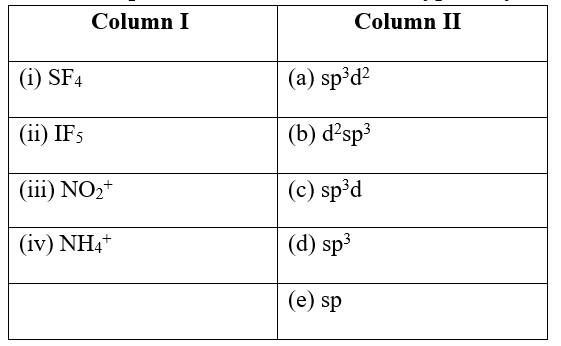
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
(i) SF4 (c) sp3d
(ii) IF5 (a) sp3d2
(iii) NO2+ (e) sp
(iv) NH4+ &nbs
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (i) and option (ii)
(i) NaCl being an ionic compound is a good conductor of electricity in the molten state. It is not a bad conductor of electricity in solid state. So, the statement mentioned in the question is not correct. Hence, this is the correct answer.
(ii) There is no difference in the arrangement of atoms in the canonical structures. The difference is in the arrangement of electron pairs in the canonical structures. So, the statement mentioned in the question is not correct. Hence, this is the correct answer.
(iii) The hybrid orbitals have the same
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (iii) and (iv)
The formula of bond order is:
Bond order = ( Nb- Na)
Number of bonding and antibonding electrons can be found from the molecular electronic configuration of the species.
(i) Total number of electrons in N2 is 14. So, its molecular electronic configuration will be
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2, π2p2x , π2p2y, s2pz2
The bond order will be:
( 10-4)= 3
(ii) The total number of electrons in N2 - is 15. So, its molecular electronic configuration will be:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2, π2p2x , π2p2y, s2pz2 π*2p1x
The bond order will be:
( 10-5)=
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (i) and (iv)
(i) N2 will have 14 electrons in its structure. So, its electronic configuration will be:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2, π2p2x , π2p2y, s2pz2
According to the molecular electronic configuration of N2 it does not contain any unpaired electrons, it will be diamagnetic in nature.
(ii) N22– will have 16 electrons in its structure. So, its molecular electronic configuration will be:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2, π2p2x , π2p2y, s2pz2, , π*2p1y
According to the molecular electronic configuration of 2 N2 -, it has two unpaired electrons in π*2p1x ,
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (iii) and (iv)
(i) The hybridization of the central carbon atom in CO3 2- is 2 sp as the carbon is bonded with three oxygen atoms. So, the given statement is incorrect.
(ii) The resonance structure of CO32- has one C= O double bonds and two C- O single bonds. So, the statement is incorrect.
(iii) The net charge on three oxygen atoms is -2, hence the average formal charge on each oxygen atom is 0.67 units. So, the given statement is correct.
(iv) As it can be seen from the resonating structures that the structures of the bonds are not fixed. Hence, all the C-
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (iii) and (iv)
(i) The number of valence electrons in CO2 is 14. The oxygen atom attached to the carbon atom forms a double bond. Therefore, the hybridization of the structure is sp2. Thus, carbon dioxide is linear in shape.
(ii) The number of valence electrons in CCl4 is 32. The structure of CCl4 is arranged in a tetrahedral manner. The chlorine atoms are arranged such that the hybridization is sp3.
(iii) The number of valence electrons in O3 is 24. The hybridization of the molecule is sp2 and due to the presence of lone pair of electrons on the central oxy
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (i) and (ii)
The species having the same number of electrons are known as isoelectronic species.
The number of electrons in CO species is 14; 8 electrons from oxygen atom and 6 electrons from carbon atom.
The number of electrons in NO+ is 14; 8 electrons from oxygen atom, 7 electrons from nitrogen atom and 1 electron will be subtracted due to the positive charge on the species.
The number of electrons in N2 is 14 ; 7 from each nitrogen atom.
The number of electrons in SnCl2 is 84 ;50 from the tin atom and 17 from each chlorine atom.
The number of electrons in NO2
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers