Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Fourteen
Get insights from 85 questions on Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Fourteen, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Fourteen
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is an Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i)
Because enzyme active sites hold the substrate molecule in a favourable location, a reagent can successfully attack the substrate molecule in the presence of enzyme. As a result, reactions catalysed by enzymes are stereospecific.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is an Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (ii)
Non-essential amino acids are amino acids that can be synthesized in the body and need not be taken from outside through diet. Glycine is an example of non-essential amino acids and is available in plenty of foods.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is an Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (ii)
When DNA (or RNA) is completely hydrolyzed, it produces a 5 carbon based sugar called pentose sugar, phosphoric acid, and nitrogen-containing heterocyclic molecules (called bases). The sugar moiety of the nucleic acid, DNA is β−D−2− deoxyribose. Therefore, both assertion and reason are wrong statements.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is an Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (v)
All other naturally occurring alpha-amino acids, with the exception of glycine, are optically active due to the asymmetry of the α - carbon atom. Both of these ' D ' and ' L ' configurations are available. The majority of amino acids found in nature have a L− configuration. The group on the left side is used to designate L− amino acids.
naturally occurring amino acids have a configuration. The −NH2 group on the left side is used to indicate amino acids.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is an Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (iv)
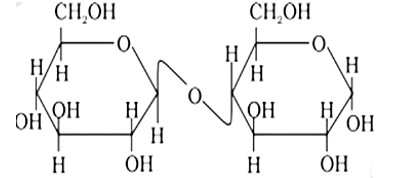
Maltose is made up of two? D? glucose units, one of which, C?1, is coupled to the C?4 of the other one. As a result, maltose contains a? glycosidic linkage. As a result, the assertion is a false statement, but the reason is true.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is an Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i)
Vitamins that are fat soluble are soluble in fats and oils but insoluble in water. They can be stored in the liver as well as adipose (fat-storing) tissues and are not excreted in urine . As a result, both assertion and reason are true assertions, and reason clarifies the assertion.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is an Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (iii)
Because D (+) - glucose causes plane polarised light to rotate to the right, it is
dextrorotatory. D denotes the relative configuration of glucose in regard to
glyceraldehyde in this situation. As a result, assertion is the proper statement, while
reason is the incorrect statement.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Matching Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
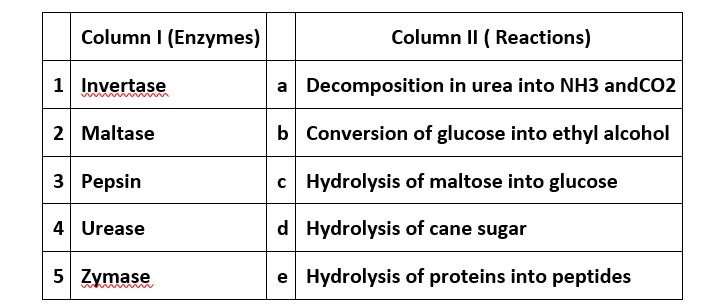
(i) → (d) (ii) → (c) (iii) → (e) (iv) → (a) (v) → (b)
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Matching Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
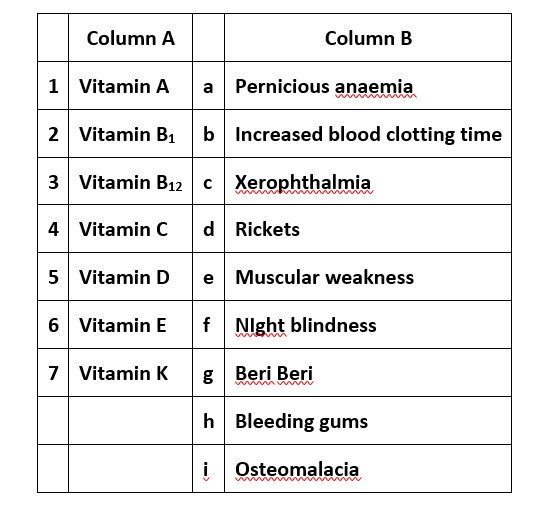
(i) → (c), (f) (ii) → (g) (iii) → (a) (iv) → (h) (v) → (d), (i) (vi) → (e), (vii) → (b)
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
When an egg is cooked, the soluble globular protein albumin transforms into an insoluble fibrous protein. Bioactivity is lost throughout the denaturation process.
(ii) Albumin protein's secondary and tertiary structures are destroyed, but the primary structure (which contains the -amino acid sequence) is unaffected.
Although egg white is a fluid Ans, when it is cooked, the proteins get denatured and solidify as a result of coagulation.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers