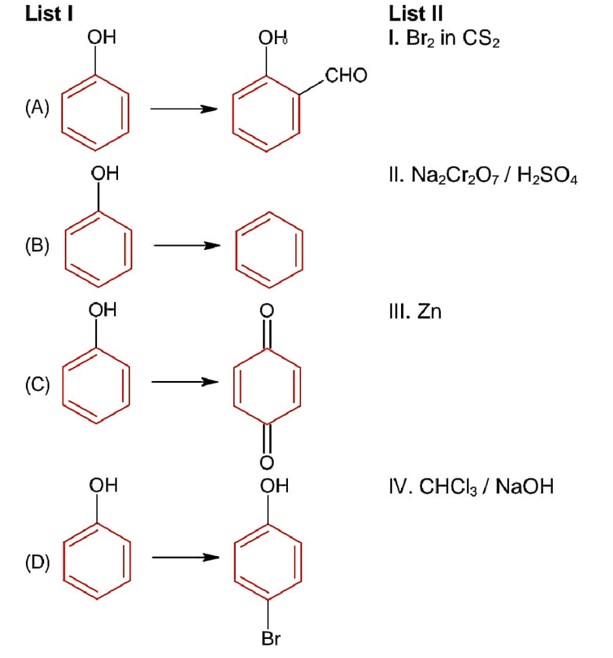
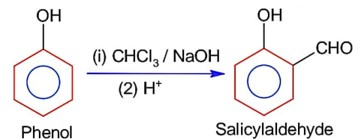
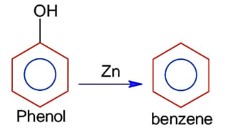
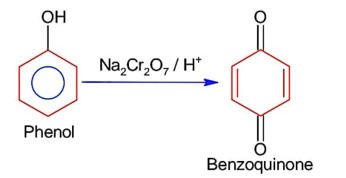
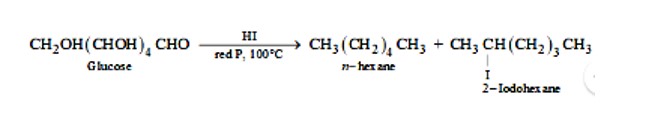Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Fourteen
Get insights from 85 questions on Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Fourteen, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Fourteen
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Helix (2°) structure of protein is stabilized by intermolecular H-bonding.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
In maltose, two units of a-D-glucose are linked by glycosidic linkage at C1 and C4 as shown.
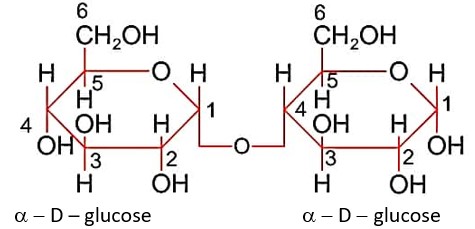
a - D – glucose a - D - glucose
Maltose has hemiacetal link so it is reducing sugar.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Chlorine nitrate as hydrolysis gives hypohalous acid and nitric acid as,
Chlorine nitrate on reaction with HCl produces Cl2 and HNO3 as,
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
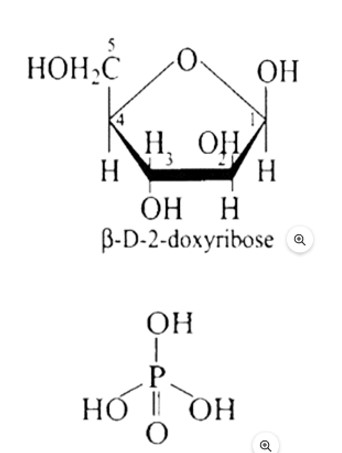
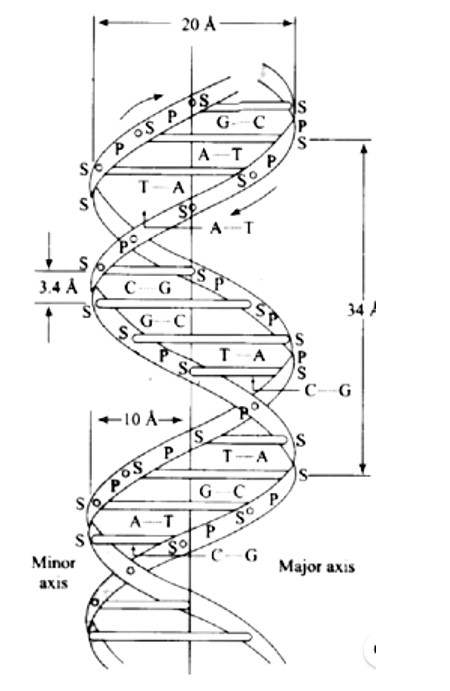
When DNA is fully degraded, a pentose sugar, phosphoric acid, and nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds known as bases are produced. Below is a diagram illustrating the structure of sugar and phosphoric acid.
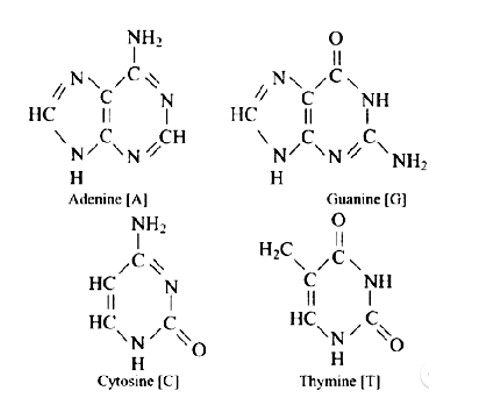
DNA contains four bases adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T). The structures of all bases are shown below.
The attachment of a base to the 1'-position of sugar produces a nucleoside. When a nucleoside attaches to phosphoric acid at the sugar moiety's 5? position, a nucleotide is formed. Nucleotides are linked through the phosphodiester linkage
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Proteins can have a single polypeptide chain or many polypeptide chains as their basic structure. A considerable number of α - amino acids are joined in a particular sequence in each polypeptide chain. The specific order in which the various α− amino acids found in a protein are linked to one another is the protein's primary structure. Any change to the main structure, i.e. the amino acid sequence, results in a different protein
Protein secondary structure: Secondary structure defines how polypeptide chains are folded or structured. As a result, the shape or conform
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Plants and animals employ the following carbohydrates as storage molecules:
(i) Starch, cellulose, sucrose, and other sugars make up the majority of plant material.
(ii) Animals' bodies contain glycogen. Glycogen is commonly referred to as animal starch as a result of this. Glycogen is found in the liver, muscles, and brain, and an enzyme converts glycogen to glucose when the body wants it.
(iii) Cellulose is a type of cellulose that can be found in wood and fabric fibre.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The following evidences are used to assign the given structure:
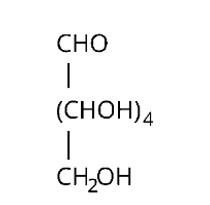
Molecular formula; of the molecule glucose is found to be C6H12O6.
Straight chain structure: When an aqueous solution of glucose reacts with sodium amalgam, sorbitol (a hexahydric alcohol) is produced by the reaction.
Glucose after a prolonged time of heating with hydroiodic acid and red phosphorus at 100oC gives a mixture of n-hexane and 2-iodohexane as two products. The reaction is depicted below:
Five hydroxyl groups: When glucose is acetylated in the presence of acetic anhydride, it produce
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long answer type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The open chain structure of glucose explained the majority of its properties. However, it fails to explain the following facts:
I Although glucose has an aldehydic group, it does not undergo all aldehydic reactions.
(a) Glucose does not react with ammonia, for example.
(b) Glucose does not create an addition product when it combines with sodium bisulphite.
(c) Glucose does not pass the Schiff's test or the 2, 4-DNP test, unlike other aldehydes.
(ii) Glucose forms an oxime when it reacts with hydroxylamine, but glucose pentaacetate does not. This proves that g
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers