Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Fourteen
Get insights from 85 questions on Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Fourteen, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Fourteen
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct option is d.
Water-soluble vitamins are those in the B group. B group vitamins cannot be stored in our systems since they are quickly excreted; but, because they are B12 insoluble in water, our bodies may store the vitamin. Because our systems are unable to store these vitamins, options (a), (b), and (c) are excluded.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct option is c.
The four bases contained in DNA are adenine, guanine, thymine, and cytosine. Adenine, uracil, guanine, and cytosine are the four bases of RNA. As a result, RNA does not include thymine as in place of thymine, it has uracil which is a lesser stable nucleotide base and is somewhat responsible for RNA's instability but also lends it some flexibility to change.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct option is a.
Proteins contain one or more polypeptide chains. When each polypeptide of a protein's amino acids is joined in a precise order, a proteins' main structure is referred to as its primary structure. This one is the linear structure with no bonds other than the ones between adjacent amino acids. The sequence of amino acids in the primary structure is pre-determined by the genetic code of an individual and thus is a specific sequence.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct option is c.
The pyranose form of glucose, which has a five-membered ring structure, is found. As a result, option (c) is wrong.
Glucose is a six-carbon monosaccharide with an aldehyde group. As a result, it's referred to as an aldohexose. As a result, the statement in option (a) is correct.
When glucose is cooked with HI, n-hexane is produced. All six carbon atoms in glucose are linked together in a straight chain during this procedure. As a result, the statement in option (b) is correct.
The aldehyde group is not free in the cyclic structure. As a result,
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The Correct option is b.
Nucleic acids are nucleotide polymers linked together by phosphodiester linkage. DNA and RNA are two examples. Nucleotides are formed by linking of nucleosides with three phosphate groups consuming a significant amount of energy making it an endothermic reaction.
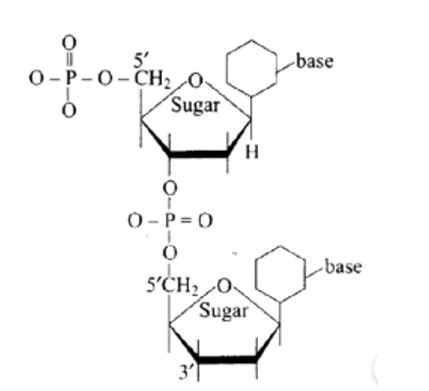
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) 5′ and 3′ linkages are present between pentose sugars of nucleotides.
Phosphodiester links the two nucleotides together to form a dinucleotide.
Between the pentose sugars of nucleotides, there are 5′ and 3′ connections. In the process of adding phosphate to a dinucleotide, a significant quantity of energy is consumed.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The Correct option is b.
Ascorbic acid is the chemical name for vitamin C. Aspartic acid is an amino acid, adipic acid is a dicarboxylic acid with an eight-carbon chain, and saccharic acid is a dicarboxylic acid made by oxidising glucose with HNO3 Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin that serves a variety of activities in the human body.
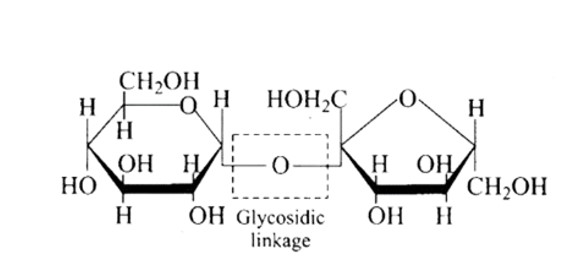
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The Correct option is b.
The structure described in option (b) reflects sucrose, which has a C1−C2 glycosidic bond between α−D− glucose and β−D− fructose.
This is a non-reducing sugar since the reducing groups of glucose and fructose are involved in the creation of glycosidic linkages.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Hydrogen bonds hold the α− helical structure of proteins together. A polypeptide chain creates all potential hydrogen bonds by twisting into a
right-handed helix with the −NH group of each amino acid residue hydrogen linked to a>C=O neighboring turn of helix.
Correct option is C
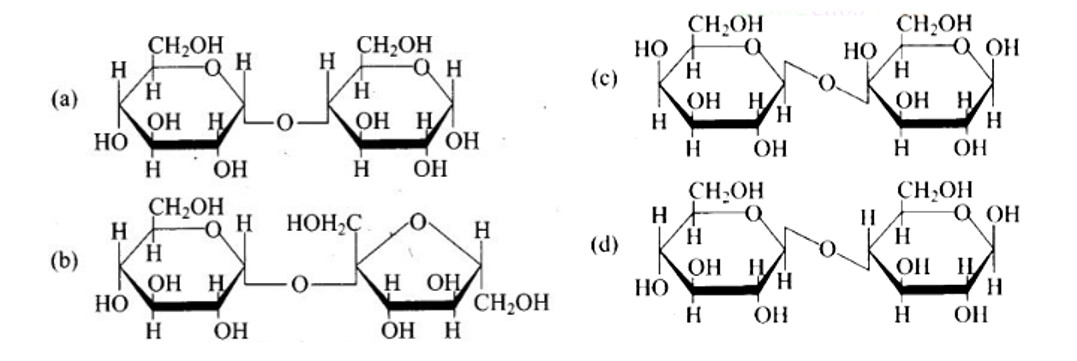
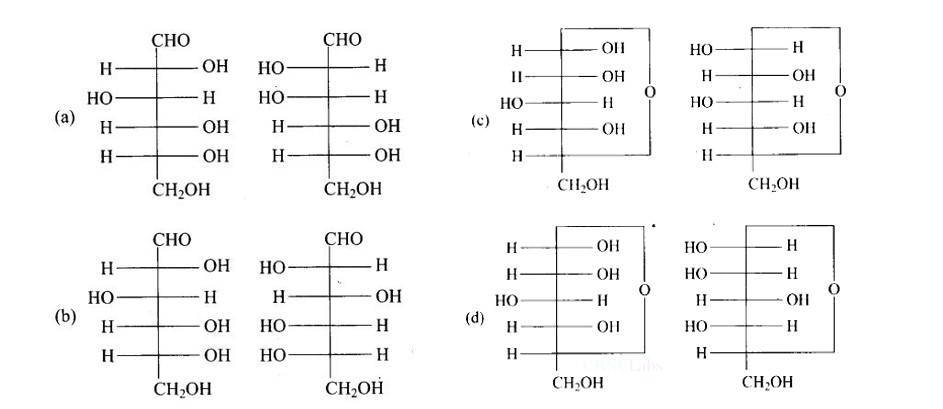
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The configuration of different anomers at C-I is distinct. It is known as the form if the hydroxyl group (-OH) is present on the right side of anomeric carbon, and it is known as the? form if the hydroxyl group is present on the left side. As a result, option (c) represents anomers among all the supplied pairs.
Correct option is c.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers