Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Fourteen
Get insights from 85 questions on Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Fourteen, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Fourteen
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
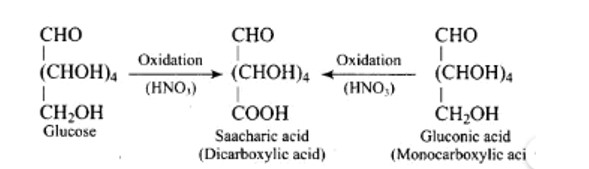
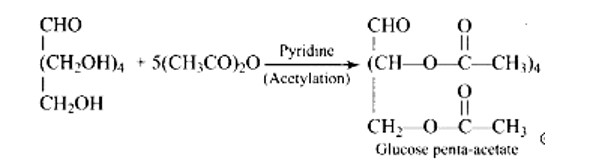
Glucose with acetic anhydride in the presence of pyridine or a few drops of concentrated H2SO4, leads to productions of penta-acetyl derivatives which shows that there are five hydroxyl groups. One hydroxyl group is a primary (1? ) alcoholic, whereas the other four (C2, C3, C4, and C5) hydroxyl or −OH groups are all labelled as secondary (2? ) alcoholics.
When glucose (or gluconic acid) is oxidized in the presence of HNO3, it produces saccharic acid (a dicarboxylic acid), showing that the primary (1? ) alcoholic group is oxidized to −COOH, but only under extreme of
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Enzyme active sites bind the substrate molecule in a favourable location so that the reagent may attack it effectively. At each site in an enzyme, there is a substrate binding site to which the substrate binds and the reaction then proceeds.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Starch has α - glucose units, and cellulose has β−D− glucose units. In starch and glycogen, there is α−I glycosidic linkage, and in cellulose, there is glycosidic connection β - between glucose units.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Two monosaccharide molecules are linked by an oxide bond generated by the loss of a water molecule. Glycosidic linkage is the joining of two monosaccharide units by an oxygen atom.
Disaccharides, trisaccharides, and polysaccharides all have glycosidic linkage.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Nucleosides are linked to phosphoric acid at the 5′ position of the sugar moiety to produce a nucleotide. Furthermore, phosphodiester linkage between the 5′ and 3′ carbon atoms of pentose sugar bonds nucleotides (two molecules) together to generate dinucleotide. Phosphoric acid aids in the formation of this connection.
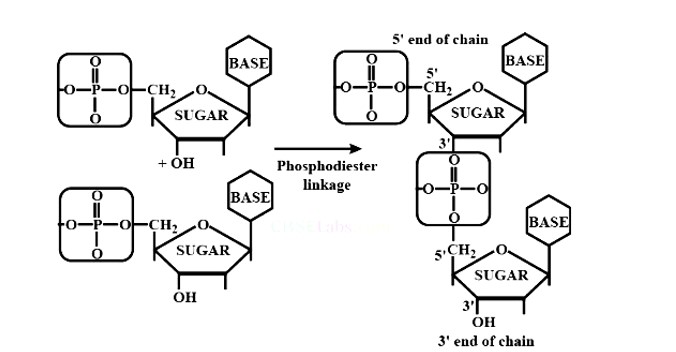
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
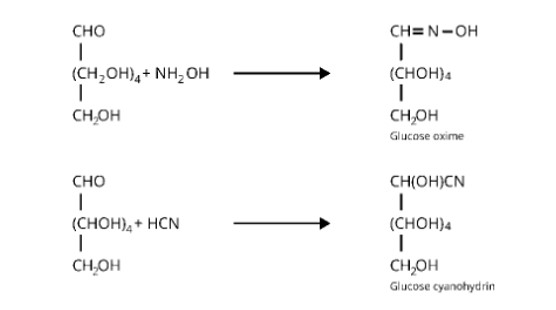
Glucose reacts with hydroxylamine to form a monoxime, which is then combined with one molecule of hydrogen cyanide to form cyanohydrin. The reactions are shown in the table below.
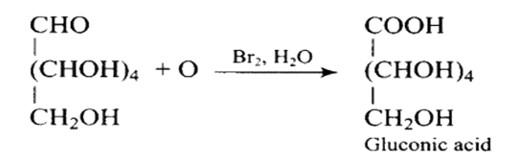
It has a carbonyl group as a consequence, which can be an aldehyde or a ketone. Gluconic acid, a carboxylic acid containing six carbon atoms, is formed when glucose is gently oxidised with bromine water.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Biocatalysts are enzymes that act as catalysts in biological reactions. They reduce the size of activation energy by finding a suitable path. Because the enzyme sucrase reduces the activation energy of sucrose hydrolysis from to, enzyme-catalyzed reactions occur at a much faster rate than traditionally catalysed ones.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Physical or chemical changes damage hydrogen bonding and other attractive factors. In addition, globules uncoil and the helix uncoils, resulting in a thread-like molecule. As a result, the biological activity of protein secondary and tertiary structures is lost entirely or partially. Protein denaturation is the term for this.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Since both acidic (−COOH) and basic (−NH2) groups present in amino acids, it act like salts rather than simple amines or carboxylic acids. In Ans, a −COOH a group can release a proton and an amine group can take a proton, resulting in the formation of a dipolar ion known as zwitterion.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Sucrose acts as a dextrorotatory molecule. It produces a mixture of glucose and fructose when hydrolyzed, with particular rotations of +52.5? and −92.4? The net resultant mixture is laevorotatory because fructose laevorotation is greater than glucose dextrorotation. The sign of rotation shifts from dextro to laevo as a result of sucrose hydrolysis, and the resulting compound is known as invert sugar.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers