Class 11th
Get insights from 8k questions on Class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New question posted
4 months agoNew answer posted
4 months agoBeginner-Level 5
As you know, electrovalent bonds result very strong electrostatic attraction force. All the factors that help maximize this electrostatic attraction are important for the formation of the ionic bond. Here are the important factors;
- Low ionization energy Metal
- High electron affinity Non Metal
- Large-sized cations
- Small-sized anions
- Electronegativity equal to or greater than 1.7
New answer posted
4 months agoBeginner-Level 5
Covalent and electrovalent bonding are the two major chemical bonding processes. These two bonds are different from each other in multiple aspects. Check the table below to know a concise summary of the differences.
| Particular | Covalent Bond | Ionic Bond |
| Formation | Due to the complete transfer of electrons | Due to the sharing of electron pairs |
| Ion formation | No ions formed | Cations and Anions formed. |
| Nature | Electrostatic attraction between ions | Electrostatic attraction between nuclei and shared electrons |
| Strength | Strong | Less strong |
| Melting/Boiling point | High due to a strong bond | lower due to weaker bond |
| Polarity | Highley Polar | Non-Polar |
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
C? H? + 5O? → 3CO? + 4H? O
C? H? + (13/2)O? → 4CO? + 5H? O
∴ 2 mol C? H? is given
∴ 13 mol O? is required for combustion of Butane
∴ Total mol of O? = 5 + 13 = 18
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
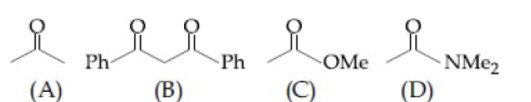
B is the most acidic as it is active methylene group. D is least acidic due to crossconjugation in conjugate base.
∴ Option 3 follows
New answer posted
4 months agoNew answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
Excess of nitrogen and phosphorus is primarily responsible for eutrophication and hence an indicator of polluted environment.
New question posted
4 months agoNew answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
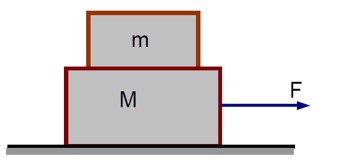
For the combined system of mass M and m, the acceleration under an applied force F is:
a = F / (M + m)
The static friction force (f_s) on the top block (m) provides its acceleration:
f_s = MA = m * [F / (M + m)] = mF / (M + m)
For the top block not to slip, the required static friction must be less than or equal to the maximum possible static friction (μmg):
f_s ≤ μmg
mF / (M + m) ≤ μmg
F ≤ μ (M + m)g
Using the values implied in the solution:
F ≤ 21 N
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers