Class 12th
Get insights from 11.8k questions on Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Given, D.E. is
which is of the form
Where
So, I.F
So, the solution is
Is the required general solution.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
6. In solids the constituent particles are found to possess fixed positions and can only oscillate about their mean positions and hence they are said to be incompressible and rigid.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The given D.E. is
which is of form
We have, P = 2
So, I.F.
The solution is
Hence, equation, (1) becomes,
Is the required solution.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
5. The liquids and gases both are categorised as fluids as they show the ability to flow and also their molecules can move past one another freely.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
4. Let the formula of sample be (Fe2+)x (Fe3+) yO
From the formula of the compound the equation can be formed as-
x+ y= 0.93 . (i)
Total positive charge on ferrous and ferric ions should balance the two units of negative charge on oxygen. Hence,
2x+ 3y= 2 . (ii)
⇒ x+ y=1. (iii)
On subtracting equation (i) from equation (iii) we have
y-y=1 - 0.93
12y=0.07
y= 0.14
On putting the value of y in equation (i)
we get, x+ 0.14 = 0.93
⇒x = 0.93 – 0.14
⇒x = 0.79
Fraction of Fe2+ ions present in the sample is = 0.81
Metal deficiency defect is found to be present in the sample
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
3. The conductivity of a semiconductor is very low and it can be increased by adding small impurities and this process is known as doping.
Doping can be done with an impurity which is electron rich or electron deficient-
n-type semiconductors- Si or Ge (group-14 elements) are doped with electron rich impurity (group-15 elements like P or As) and are known as n-type semiconductors. In them the conductivity is due to the extra electron or delocalized electron.
When intrinsic semiconductors like Si or Ge are doped with pentavalent elements like P or As, they occupy some of the lattice sites in silicon or germaniu
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
2. A ccp structure unit cell is divided into 8 small cubes. Each small cube has atoms at alternate corners as shown in the figure. In all, each small cube has 4 atoms. When these are joined to one another, they make a regular tetrahedron. Thus, there is one tetrahedral void in each small cube and 8 tetrahedral voids in total. Each of the eight small cubes has one void in one unit cell of ccp structure. We know that ccp structure has four atoms per unit cell. Thus, the number of tetrahedral voids is twice the number of atoms.
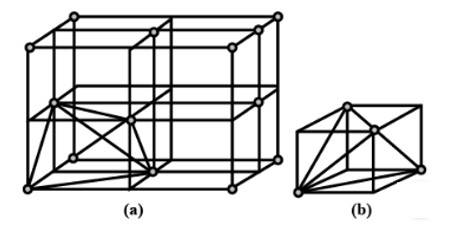
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
1. When any atom is surrounded by six atoms it creates an octahedral void. In fcc, body centre is surrounded by six atoms present at the face centre. And hence one octahedral void is present at the body centre of each unit cell.
No. of octahedral void at the centre of 12 edge = 12 * = 3
No. of octahedral void at body centre = 1
Total no. of octahedral void in ccp = 3+1+4
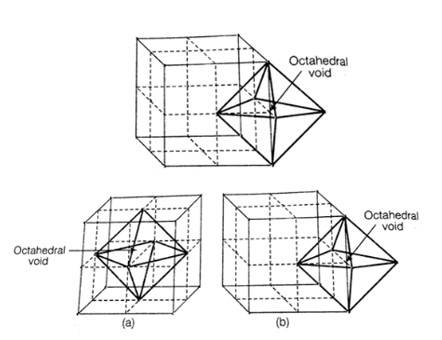
Location of octahedral voids per unit cell of ccp or fcc lattice (a) at body centre of the cube and (b) at the centre of each edge (only one such void is shown)
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 684k Reviews
- 1800k Answers