Moving Charges and Magnetism
Get insights from 125 questions on Moving Charges and Magnetism, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Moving Charges and Magnetism
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- the cyclist covers OPRQO path.
As we know whenever an object performing circular motion, acceleration is called centripetal acceleration and is always directed towards the centre.
so there will be centripetal acceleration a= v2/r
So a= 100/1km= 100/1000=0.1m/s2 along RO.

New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
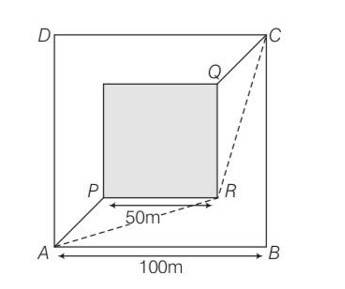
Explanation – Tsand=
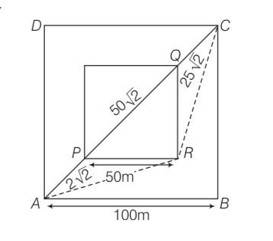
= 50
Time taken Toutside=
AR=
RC= AR=
Toutside= 2AR= 50
Tsand
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
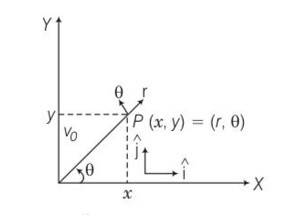
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation – r=cos ?…….1
…….2
Multiplying eq1 by sin and 2 with cos and adding
Rsin
= ?( )=j
= rsin
n(rcos )=i
b)r
= -cos
c)r=cos
dr/dt=d/dt(cos )=w[-cos ]
d)L= MoLT0
e)a=1unit , r=
v= dr/dt=
v=
= w
a=
a=
=
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- a) for x direction ux= u+vocos
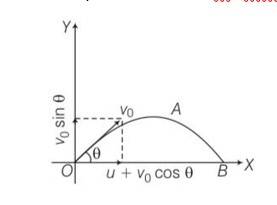
uy=velocity in y direction= v0sin
now tan
b) let t be the time flight y =0 uy=vosin
y= uyt+1/2 ayt2
0= vosin +
So T =
c) horizontal range R, = (u+vocos T= (u+vocos )
d) for range to be maximum dR/d
4vocos2
So cos =
e) cos =
so
f) if u=0 0
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
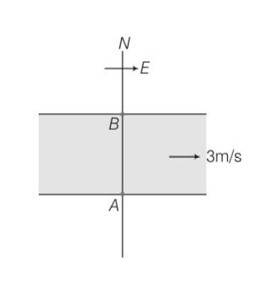
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation – speed of river Vr= 3m/s
Speed of swimmer Vs= 4m/s
(a) when swimmer starts swimming due north then its resultant velocity
V=
tan so 'N
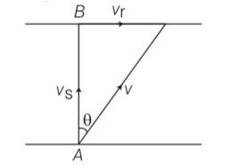
(b) to reach at point B resultant velocity will be
V=
tan
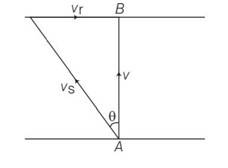
(c) time taken by swimmer t =d/v= d/4s
in case b time taken by swimmer to cross the river
t1=d/v=d/
so t
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation – Vr= a? +b?
Velocity vg= 5m/s
Velocity of rain w.r.t girl = Vr-Vg= a? +b? -5?
= (a-5)? +b?
a-5=0, a=5
case II
vg = 10m/s?
Vrg= Vr - Vg
= a? +b? -10? = (a-10)? +b?
Rain appear to be fall at 45 degree so = b/a-10 =1
So b =-5
Velocity of rain = a? +b?
Vr = 5? -5?
Speed of rain Vr=
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- y=O, uy= Vocos
ay=-gcos , t =T
applying equation of kinematics
y=uyt+ t2
0 = Vocos +T2
T=
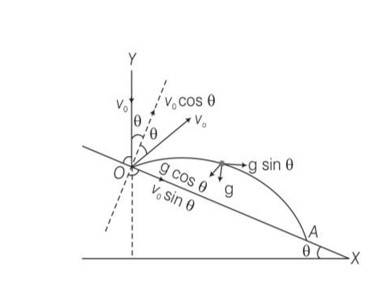
T= 2V0/g
X= L, ux=Vosin , ax= gsin , t=T=
X=uxt+
L= Vosin
L= sin
New answer posted
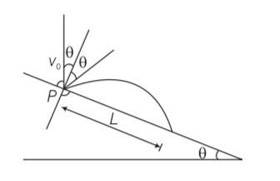
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
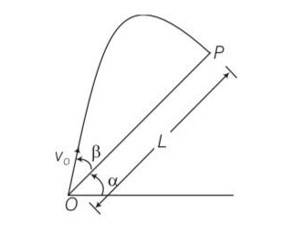
Explanation – particle is projected from the point O.
Let time taken in reaching from point O to point P is T.
for journey O to P
y=0,uy= Vosin ,ay= -gcos
y=uyt +
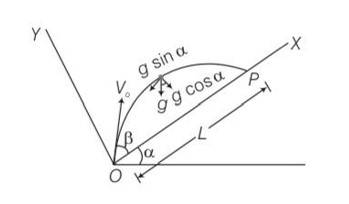
0= Vosin
T[Vosin T]=0
T = time of flight =
Motion along OX
x= L ,ux= Vocos , ax= -gsin
t =T =
x= uxt+
L= V0cos +
L= T[V0cos ]
L= [Vocos ]
L=
Z= sin
= sin
=
= ½ [sin2]
=
= [sin(2 )-sin ]
For z maximum
2 ,
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation – target T is at horizontal distance x= R+ and between point of projection y= -h
Maximum horizontal range R= …………1
Horizontal component of initial velocity = Vocos
Vertical component of initial velocity = -Vosin
So h = (-Vosin )t + 2………….2
R+ = Vocos
So t=
Substituting value of t in 2 we get
So h = (-V0sin )
H = -(R+ )tan +
, h = -(R+ )tan +
So h = -(R+ ) +
So h = -(R+ )+
So h = -R- +(R+ )
h=
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- speed of jackets = 125m/s
Height of hill = 500m
To cross the hill vertical component of velocity should be grater than this value uy=
So u2= ux2+uy2
Horizontal component of initial velocity ux =
Time taken to reach the top of hill t=
Time taken to reach the ground in 10 sec = 75 (10)= 750m
Distance through which the canon has to be moved =800-750=50m
Speed with which canon can move = 2m/s
Time taken canon = 50/2= 25s
Total time t= 25+10+10= 45s
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 687k Reviews
- 1800k Answers