Moving Charges and Magnetism
Get insights from 125 questions on Moving Charges and Magnetism, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Moving Charges and Magnetism
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
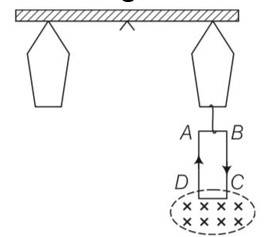
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation – for equilibrium balance net torque should be zero
Mgl= Wcoill
500gl = Wcoill
Wcoil= 500 9.8N
Taking moment of force about mid point then magnetic field
Mgl+mgl=Wcoill+IBlsin90
Mgl=BILl
M= -3kg= 1g
New question posted
9 months agoNew answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- |A+B|=|A-B|
=
4|A|B|cos =0
|A|2+|B|2cos =0
A=0 or B=0 so . so A perpendicular B
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
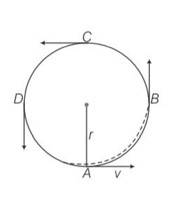
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- a, b, c
Explanation- (i) Speed will constant throughout
(ii) Velocity will be tangential in the direction of motion
(iii) Centripetal acceleration will be a= v2/r, will always be towards centre of the circular path.
(iv) Angular momentum is constant in magnitude and direction out of the plane perpendicularly as well.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- a, c
Explanation – as we know average acceleration is aav=
But when acceleration is not uniform Vav is not equal to v1+v2/2
So we can write
= v2-v1 (t2-t1)
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
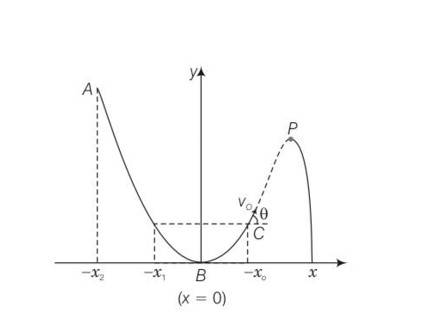
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- c
Explanation– as the given track y=x2 is a frictionless track thus total energy will be same throughout the journey.
Hence total energy at A = total energy at P . at B the particle is having only Ke but at P some KE is converted to P
Hence (KE)B = (KE)P
Total energy at A = PE= total energy at B = KE= total energy at P
= PE+KE
Potential energy at A is converted to KE and PE at P hence
(PE)P< (PE)A
Hence (height)P= (height)A
As height of p < height of A
Hence path length AB > path length BP
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- a,b,c
Explanation – H=
H1=Vo2sin2 1/2g , H2=Vo2sin2 2/2g
H1>H2
Vo2sin2 1/2g= Vo2sin2 2/2g
Sin2 1>sin2 2
Sin2 1 – sin2 2>0
(Sin 1 – sin 2)( Sin 1 + sin 2)>0
Sin 1>sin 2 or 1 >2
T=
T1= , T2=
T1> T2
R=
Sin 1>sin 2
Sin2 1> sin2 2
R1>R2
Total energy for the first particle
U1=K.E+P.E=1/2m1
U2= K.E+P.E= 1/2m2
Total energy for the second particle
So m1= m2 then U1=U2
So m1>m2 then U1>U2
So m1
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- a, b
Explanation - |A+B|= |A|or |A+B|2=|A|2
|A|2 +|B|2+2|A|B|cos = |A|2
|B| (|B|+2|A|cos )= 0
|B|=0 or |B|+2|A|cos =0
Cos =
If A and B are antiparallel then =180
-1=
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer- b, d
Explanation – given A+B+C = 0
B
B +B =0
B
B
A
(A )
It cannot be zero
(b) (A ).C= (B ).C=0 . if b|C then B =0 then (B )
(c) (A )=X=ABsin . The direction of X is perpendicular to the plane containing A and B (A )
(d) if c2= A2+B2, then angle between A and B is 900
(A ).C= (AB sin900X).C=AB (X.C)
= ABC cos900= 0
New question posted
9 months agoTaking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 687k Reviews
- 1800k Answers