Moving Charges and Magnetism
Get insights from 125 questions on Moving Charges and Magnetism, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Moving Charges and Magnetism
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.28 Resistance of the galvanometer coil, G = 15 Ω
Current for which galvanometer shows full deflection, = 4 mA = 4 A
Range of ammeter has to be converted from 0 to 6 A, hence I = 6 A
A shunt resistor S is to be connected in parallel with the galvanometer to convert it to an ammeter. The value of S is given as
S = 10 mΩ
Hence, a shunt resistor of 10 mΩ is to be connected to galvanometer to convert it to an ammeter.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.27 Resistance of the galvanometer coil, G = 12 Ω
Current for which there is full scale deflection, = 3 mA = 3 A
Range of voltmeter = 0, to be converted to 18 V, hence V = 18 V
Let there be a resistor R connected in series with the galvanometer to convert it into a voltmeter. R is given as
R = - G = - 12 = 5988 Ω
Hence the required value of resistor is 5988 Ω
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.26 Length of the solenoid, L = 60 cm = 0.6 m
Radius of the solenoid, r = 4.0 cm = 0.04 m
It is given that there are 3 layers of windings of 300 turns each
Hence, total number of turns, n = 900
Length, l = 2 cm = 0.02 m
Mass of the wire, m = 2.5 g = 2.5 kg
Current flowing through the wire, I = 6 A
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/
We know, magnetic field produced inside the solenoid, B =
where = Permeability of free space = 4 T m
Magnetic force is given by the relation
F = Bil =
Also the force on the wire is equal to the weight of the wire, F = mg
mg =
I = = = 108 A
Hence, the current flowing through the solenoid is 108 A
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.25 Number of turns on the circular coil, n =20
Radius of the coil, r = 10 cm = 0.1 m
Magnetic field strength, B = 0.10 T
Current in the coil, I = 5.0 A
The total torque on the coil is zero because the field is uniform.
The total torque on the coil is zero because the field is uniform.
Cross-sectional area of the copper coil, A =
Number of free electrons per cubic meter of copper, N = /
Charge on the electron, e = 1.6 C
Magnetic force, F = Be where is the drift velocity of electrons
= = = 5 N
The average force on each electron is 5 N
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
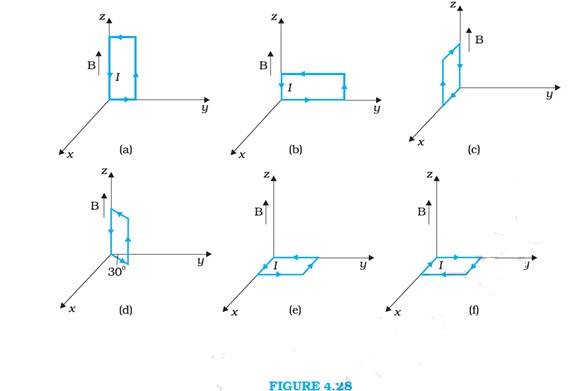
4.24 Magnetic field strength, B = 3000G = 3000 T = 0.3 T
Length of the rectangular loop, l = 10 cm
Width of the rectangular loop, b = 5 cm
Area of the loop, A = l = 10 = 50 = 50
Current in the loop, I = 12 A
Assume that the anti-clockwise direction of the current is positive and vice versa.
Torque, =
From the given figure, it can be observed that A is normal to the y-z plane and B is directed along z-axis.
= 12*( 50 = Nm
The Torque is Nm along the negative y-direction.
The force on the loop is zero because the angle between A & B is zero.
This case is similar to case (a). The answer is same as case (a)
Torque, = I
F
New question posted
9 months agoNew answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.23 Magnetic field strength, B = 1.5 T
Radius of the cylindrical region, r = 10 cm = 0.1 m
Current in the wire passing through the cylindrical region, I = 7 A
If the wire intersect the axis, then the length of the wire is the diameter of the cylindrical region, then l = 2r = 0.2 m
Angle between the magnetic field,
Magnetic force acting on the wire is given by the relation,
F = BIl = 1.5 = 2.1 N
Hence, a force of 2.1 N acts on the wire in a vertically downward direction.
If the wire is turned from N-S to NE-NW direction, new length of the wire can be given as
Angle between magnetic field and current = 45
Force on the wire,
F = BI =
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.22 Current in both the wires, I = 300 A
Distance between the wires, r = 1.5 cm = 0.015 m
Length of the two wires, l = 70 cm = 0.7 m
Now, force between the two wires is given by the relation:
F = , where = Permeability of free space = 4 T m
Hence F = N/m = 1.2 N/m
Since the direction of the current in the wires is opposite, a repulsive force exists between them.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.21 Length of the rod. l= 0.45 m
Mass suspended by the wire, m = 60 g = 60 kg
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/
Current, I = 5 A
To achieve zero tension, the magnetic field = weight of the wire
BIl = mg or
B = = = 0.26 T
The magnetic field should be set up such that it gives an upward magnetic force.
If the direction of current is reversed, then the magnetic force will act downwards and total tension in the wire will be
mg + BIl = 60 = 1.173 T
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.20 Magnetic field, B = 0.75 T
Accelerating voltage, V = 15 kV = 15 V
Electrostatic field, E = 9.0 V/m
Let the mass of electron = m, Charge of the electron = e, Velocity of the electron = v
Then kinetic energy of the electron = eV
m = eV or = ………….(1)
Since the particle remains un-deflected by electric and magnetic field, we can infer that the electric field is balancing the magnetic field.
Hence eE = evB or v = ………(2)
Combining equation (1) and (2), we get
= = = 48 C/kg
This value of specific charge e/m is equal to the value of deuteron or deuterium ions. This is not a unique answer. Other possible answers ar
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 687k Reviews
- 1800k Answers