Moving Charges and Magnetism
Get insights from 125 questions on Moving Charges and Magnetism, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Moving Charges and Magnetism
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer – (a)
Explanation- in biot savarts law magnetic field is perpendicular to v
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Answer – (d)
Explanation- it is determined by its pitch
Pitch = = constant
So charge by mass ratio is also constant
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
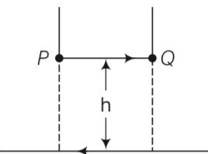
Explanation- magnetic field produced by a long straight current carrying wire is
B= = , for h height distance
Magnetic force on small conductor is F= ilBsin = ilB
Also force, F =mg = l
h= = 51 10-4cm
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
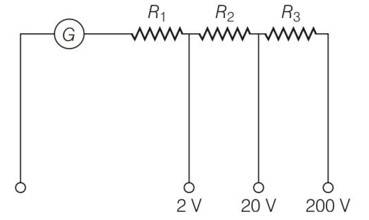
Explanation- applying expression in different situation
For iG (G+R1) = 2 , for 2V range
iG (G+R1+R2) = 20 , for 20V range
iG (G+R1+R2+R3) = 2 , for 200V range
on solving we get R1= 1990ohm, R2= 18kohm, R3= 180k ohm
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- In Biot-Savart's law, magnetic field B is parallel (II) to id * r and idl have its direction along the direction of flow of current.
Here, for the direction of magnetic field, At dl2, located at (0, R,0) due to wire d1 is given by B I | dl * r or I *j (because point (0, R,0)lies on y-axis), but I * j= k
So, the direction of magnetic field at d2 is along z-direction.
The direction of magnetic force exerted at d2 because of the first wire along the x-axis
F =i (l B) i.e., F| (i ) or along− j direction.
Therefore, force due to dl1 on
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- considering magnetic field along B=Bk and electron enters with a velocity v=vi into a cubical region
The force on electron using Lorentz force = -e (vi Bk)= evBi
So the force F= -eE0 k accelerates along z axis which in turn increases the radius of circular path and hence particle transversed on spiral path.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- for a charge particle to move in circular path
Mv2/r = qvB
v/r=w= bq/m
w= v/r = = T-1
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- general formula for magnetic field at center is
B=
B1= k for xy plane
B2= i for zy plane
B3= j for xz plane
After joining together B= (i+j+k)
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
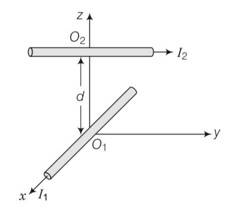
Explanation – in biot savart law, magnetic field B is parallel to idlr and idl have its direction along the direction of flow of current.
Here, for the direction of magnetic field at O2, due to wire carrying I1 current is B| parallel idl r or I k, but it is -j
So the direction at O2 is along y-direction.
The direction of magnetic force exerted at O2 because of the wire along x-axis
F= ilB=j (-j)=0
So the force is zero.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation – here, the condition of magnetic resonance is violated.
When the frequency of radio frequency field were doubled, the time period of the radio frequency field were halved. Therefore, the duration in which particle completes half revolution inside the dees, radio frequency completes the cycle.
Hence, particle will accelerate and decelerate alternatively. So the radius of path in the dees will remain same.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 687k Reviews
- 1800k Answers