Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Get insights from 2.6k questions on Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Given -
Molarity, C = 0.00241 M
Conductivity, κ = 7.896 * 10–5 S cm–1
Molar conductivity? m =?
? 0m for acetic acid = 390.5 S cm2mol–1
Molar conductivity? m = k/c X 1000 S cm2 mol-1
= 7.896 X 10–5 S cm–1X 1000 cm3 L-1 / 0.00241 mol L-1
∴? m = 32.76 S cm2 mol-1
To calculate the dissociation constant, Ka, we use
Ka = → Equation 1
Here, we need to find the value of α (degree of dissociation), by the formula,

The molar conductivity? m is 32.76 S cm2 mol-1 and the dissociation constant, Ka is 1.86*10-5
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.10
All those carbohydrates which reduce Fehling's solution to red precipitate of Cu2O or Tollen's reagent to metallic Ag is called reducing sugars. All monosaccharides (both aldoses and ketoses) and disaccharides except Sucrose are reducing sugars.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
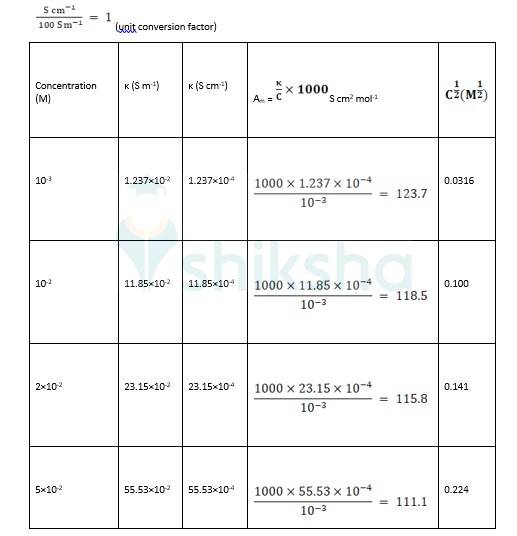
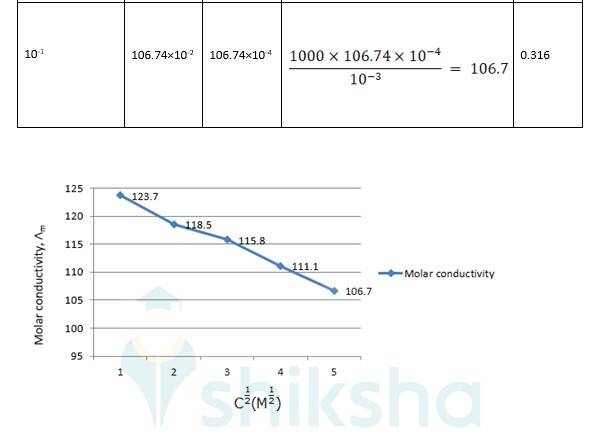
? 0 R = Intercept on the? axis = 124.0 S cm2 mol-1, which is obtained by extrapolation to zero concentration.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.9
Monosaccharides are the only the simplest units of carbohydrates and they are the simplest form of sugar. In other words, It is the most basic form of carbohydrates. They are made up of hydrogen, carbon and oxygen atoms. They are the building blocks of more complex carbohydrates i.e., they can join together and form complex carbohydrates.
For example:
i. Monosaccharides form
ii. 3-10 of them form
iii. 11 or more of them form
Monosaccharides are used to produce and store energy. Most organisms create energy by breaking down the monosaccharide glucose and harvesting the energy released from the bonds. Other Monosaccharides are
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Given -
Resistance of a conductivity cell, R = 1500 Ω
Electrolytic conductivity of a solution, κ = 0.146 * 10-3 S cm-1
Cell constant =?
Conductivity, κ = cell constant/resistance
Cell constant = κ * R
= 0.146 * 10-3 S cm-1*1500 Ω
Cell constant = 0.219 cm-1
The cell constant of the cell containing 0.001M KCl solution at 298 K is 0.219 cm-1
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Given -
Molarity, C = 0.20 M
Electrolytic conductivity of a solution, κ = 0.0248 S cm-1
Molar conductivity =?
Molar conductivity, ∧m = K/C X 1000 S cm2 mol-1
=0.0248S cm-1 X 1000 Cm3L-1 / 0.20 mol L-1
∴ ∧m = 124 S cm2 mol-1
Molar conductivity (∧m) of 0.20 M solution of KCl at 298 K is 124 S cm2 mol-1
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.8
A DNA is a double-stranded molecule (two polynucleotide chains whose nitrogenous bases are connected by hydrogen bonds).
In this molecule pairing or connection of bases occurs. Adenine always pairs with thymine, while cytosine always pairs with guanine.
So when DNA is hydrolyzed the amount of adenine produced is exactly equal to the amount of thymine produced, similarly, the amount of cytosine produced is equal to that of guanine.
But as given when RNA is hydrolyzed, there is no relationship between the quantities of different bases obtained. This suggests that RNA is a single-stranded molecule.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
The conductivity of a solution is defined as the conductance of one unit volume of solution kept between two platinum electrodes with a unit area of cross-section and at a distance of unit length.The molar conductivity of the solution is defined as the conducting power of all the ions produced by
one gram mole of an electrolyte in a solution. It is denoted by ∧m.
The conductivity of a solution (both for strong and weak electrolytes) always decreases with the decrease in concentration of the electrolyte i.e., on dilution. This pattern is seen because the number of ions per unit volume that carry the current in the solution d
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.7
When a nucleotide from DNA containing thymine is hydrolyzed β-D-2 deoxyribose and phosphoric acid are obtained.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Given - Zn → Zn2+ + 2e -, E0 = 0.76V (anode)
Ag2O + H2O + 2e - →2Ag + 2OH -, E0 = 0.344V (cathode), n = 2
ΔrG0 =?
Ecell0=?
Zn is oxidized and Ag2O is reduced.
Hence, the standard cell potential, Ecell0 is given as,
Ecell0 = ER0 - EL0
E0 cell = 0.344 + 0.76
∴ E0cell = 1.104 V
To calculate the standard Gibb's free energy? rG0, we use,
? rG0 = - nE0F → Equation 1
= - 2*96487*1.104 J
= - 213043.296 J
∴? rG0 = - 2.13*105 J
The standard cell potential, E0cell is 1.104 V and the standard Gibb's free energy? rG0 is - 2.13*105 J
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 679k Reviews
- 1800k Answers

