Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Get insights from 2.6k questions on Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
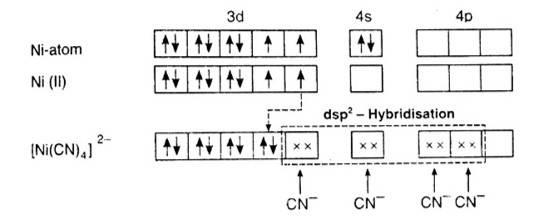
According to the valence band theory, the central metal atom or ion under the influence of ligands can use its (n-1)d, ns, np (inner orbital complex) or ns, np, and (outer orbital complex)orbitals for hybridisation to form equivalent set of orbitals of definite geometry.
In [Ni (CN)4]2-, oxidation state of Ni can be calculated as :
Using overall charge balance as the whole ion has overall -2 charge:
x + 4 (-1) = -2 (? CN- has -1 negative charge) x = + 2
Ni is in + 2 oxidation state.
Electronic configuration of Ni is: [Ar]3d84s2 Where, [Ar] = 1s22s22p63s23p6
Electronic configuration of Ni+2 = [Ar]3d8 Outer electronic configuration of Ni+2 = 3
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.27
Vitamins can be defined as the essential dietary factors required by an organism in minute quantities and whose absence causes specific deficiency Vitamins are broadly classified into two types:-
(i) Fat-soluble vitamins:
These are oily substances not readily soluble in water. These include vitamins A, D, E and K. Vitamin K is responsible for the coagulation of blood.
(ii) Water-soluble vitamins:-
Vitamins that are soluble in water belong to this group. For example :B group vitamins (B1, B2, B6, B12, etc.) and vitamin C.
Vitamin H (Biotin) as an exception, it is neither soluble in water nor in fat
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.26
During denaturation, 2-degree and 3-degree structures of proteins are destroyed but 1- degree structure remains intact. As a result of denaturation, The globular proteins (soluble in water) are converted into Fibrous proteins (insoluble in water) and their biological activity is lost. For example, boiled egg which contains coagulated proteins cannot be hatched to produce chickens.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
These compounds give different ions in aqueous solution. This can be tested by using AgNO3 solution and BaCl2
[Co (NH3)5Cl]SO4 (aq) + BaCl2 (aq) → BaSO4 (ppt)
[Co (NH3)5Cl]SO4 (aq) + AgNO3 (aq) → no reaction
[Co (NH3)5 (SO4)]Cl (aq) + BaCl2 (aq) → no reaction
[Co (NH3)5 (SO4)]Cl (aq) + AgNO3 (aq) → AgCl (ppt)
Hence, they give different precipitates with different solutions. Thus, they are ionisation isomers.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.25
Enzymes are naturally occurring simple conjugate proteins acting as specific catalysts in all processes. In contrast to ordinary chemical catalyst, it loses activity by pH or temperature change.
For example:- the enzyme used to catalyze the hydrolysis of maltose into glucose is named as maltase.

Enzymes are highly specific, i.e., a particular enzyme catalyses a specific reaction. For example, urase attacks on urea. This specific action is due to active sites present in the enzyme molecule (E) that fits into substrate (S) and forms E-S complex which changes into product P and E.
Enzymes increase the speed of reactions. They can cataly
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) K [Cr (H2O)2 (C2O4)2 exhibits geometrical isomerism (Cis and trans) and optical isomerism of cis and trans
(ii) Optical isomerism exhibiting mirror
(iii) Ionisation isomerism- [Co (NH3)5 (NO3)] (NO3) (NO2) and Linkage isomerism- [Co (NH3)5 (ONO)] (NO3)2
(iv) Geometrical isomers are seen in [Pt (NH3) (H2O)Cl2]
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) Hexaminecobalt (III)chloride
(ii) Pentaaminechloridecobalt (III)chloride
(iii) Potassium hexacyanoferrate (III)
(iv) Potassium trioxalatoferrate (III)
(v) Potassium tetrachloridopalladate (II)
(vi) Diaminechloride (methylamine)platinum (II)chloride
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.24
Amino acids contain an acidic (carboxyl group) and a basic (amino) group within the same molecule. In aqueous solution, they neutralize each other. The carboxyl group loses a proton while the amino group accepts it. S a result, a dipolar or zwitter-ion is formed.
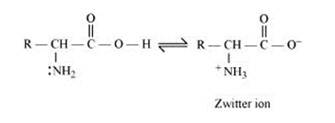
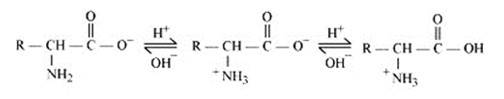
In zwitter ionic form, the amino acid show amphoteric behaviour as they react with both acids and bases. In the acidic medium, COO- ion of the zwitter-ion accepts a proton to form the cation first, while in the basic medium, +NH3 ion loses a proton to form the anion, as shown below:-
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) [Co (NH3)4 (H2O)2]Cl3
(ii) K2 [Ni (CN)4]
(iii) [Pt (en)3]NO3
(iv) [Pt (NH3)BrCl (NO2)]
(v) [Pt (Cl)2 (en)2] (NO3)2
(vi) Fe4 [Fe (CN)6]3
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.23
Globular proteins | Fibrous proteins |
It is usually soluble in water. | It is insoluble in water. |
All enzymes are globular protein. Some hormones such as insulin are also globular protein. | Fibrous proteins are usually used for structural purposes. For example, keratin is present in nails and hair; collagen in tendons; and myosin in muscles. |
The polypeptide chain in this protein is folded around itself, giving rise to spherical structure. | It is a fibre-like-structure formed by the polypeptide chain. These proteins are held together by strong and disulphide bonds. |
They are soluble in acids and bases. | They are insoluble in acids and bases. |
Examples:- egg albumin, casein of milk. | Examples :- Silk, Skin, Wool. |
They have weak intermolecular hydrogen bonding. | They have comparatively stronger intermolecular forces of attraction. |
They have folded, ball like structure. | They have thread like structure. |
Globular proteins are also called as spheroproteins owing to their shape. | Fibrous proteins are also called as scleroproteins. |
More sensitive to the changes in pH, temperature etc. | Less sensitive to the changes in pH, temperature etc. |
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 679k Reviews
- 1800k Answers