Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Get insights from 2.6k questions on Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Bonding in coordination compounds in terms of Werner's postulates is explained as:
(a) Metals can show two types of valencies which are Primary valency and Secondary
1. Primary Valency: Primary Valency shows Oxidation Primary valencies are ionizable.
2. Secondary Valency: Secondary Valency shows coordination These are non-ionizable.
(b) Both Primary and secondary valency of the metal are to be satisfied which is done by negative ions in case of primary valency and negative or neutral species in case of secondary
(c) Metals have a fixed number of secondary valencies/ Coordination number around the central atom, these secondary
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.31
In the helical structure of DNA, the two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between specific pairs of bases.
Cytosine from hydrogen bond with guanine, while adenine forms hydrogen bond with thymine. As a result, the two strands are complementary to each other.
DNA consists of two strands of nucleic acid chains coiled around each other in the form of a double helix. The base of one strand of DNA is paired with bases on other strand by means of hydrogen bonding.
This hydrogen bonding is very specific as the bases can only base pair in a complementary manner.
Adenine pairs with only thymine via 2 hydrogen bonds and guanine pairs
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
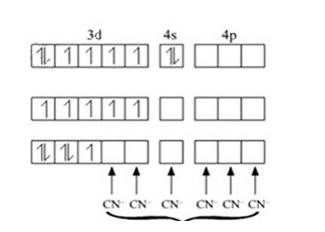
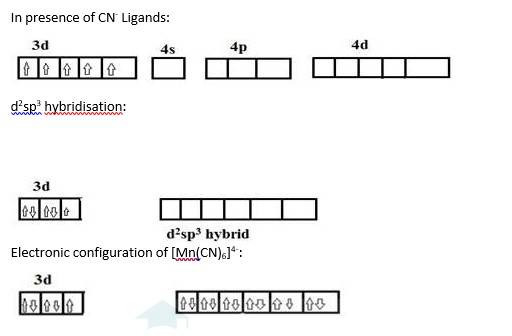
[Mn (H2O)6]+2 | [Mn (CN)6]4- |
Oxidation state of manganese: Overall charge balance: X + 6 (0) = 2 X = + 2 | Oxidation state of manganese: Overall charge balance: X + 6 (-1) = -4 X = + 2 |
Outer electronic configuration of Mn = d5 | Outer electronic configuration of Mn = d5 |
H2O is a weak field ligand so it does not cause pairing of the electron. Therefore Mn undergoes sp3d2 hybridization. Geometry is octahedral. Therefore the 5 unpaired electrons from the d orbital remain as it is. | CN is a strong field ligand so it causes pairing of the electron (5 electrons get paired to form 2 pairs and one unpaired electron). Therefore Mn undergoes d2sp3 hybridization. Geometry is octahedral. |
Mn in + 2 oxidation state:
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
In Pt [ (CN)4]2- ion:
Overall charge balance:
X + 4 (-1) = -2 X = + 2.
The oxidation state of Pt is + 2.
Since CN- is a strong field ligand, it causes pairing of the unpaired electrons.
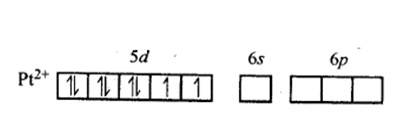
Therefore, now the 2 unpaired electrons from 5d orbital get paired and it undergoes dsp2 hybridisation. It forms square planar geometry. Since all the electrons are paired,
No. of unpaired electrons = 0.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.30
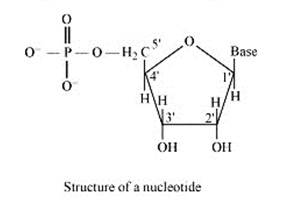
A nucleoside is formed when l-position of a pyrimidine (cytosine, thymine or uracil) or 9- position of a purine (guanine or adenine) base is attached to C-l of sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) by a linkage. Thus in general, nucleosides may be represented as: Sugar-Base.
Nucleoside = sugar + base
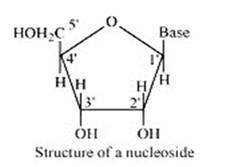
On the other hand, all the three basic components of nucleic acids (i.e., pentose sugar, phosphoric acid and base) are present in a nucleotide.These are obtained by esterification of C5' –OH group of the pentose sugar by phosphoric acid. Thus, in general, a nucleotide is represented as:-
Nucleotide= sugar + base + phosphoric acid
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
[Co (NH3)6]3+ | [Ni (NH3)6]2+ |
Oxidation state of cobalt: Overall charge balance: X + 6 (0) = 3 X = + 3 | Oxidation state of nickel: Overall charge balance: X + 6 (0) = 2 X = + 2 |
Outer electronic configuration of cobalt = d6 | Outer electronic configuration of nickel = d8 |
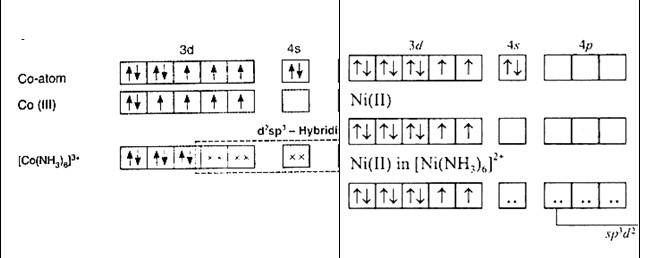
NH3 is a strong field ligand so it causes pairing of electron. Therefore cobalt undergoes d2sp3 hybridisation. As in the hybridisation d2 orbitals are used from the (n-1)d orbitals (inner orbitals as n = 4 being quantum number) . hence it is a inner orbital complex. | NH3 is a strong field ligand so it causes pairing of electron. Therefore, nickel undergoes sp3 d2 hybridisation. As in the hybridisation, d2 orbitals are used from the and orbitals (outer orbitals as n = 4 being quantum number). Hence, it is an outer orbital complex |
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.29
Nucleic acids are Biomolecules which are found in the nuclei of all living cells, inform of nucleoproteins or chromosomes (proteins containing nucleic acids as the prosthetic group). Nucleic acids are of two types: – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Nucleic acids are also known as Polynucleotide as they are long- chain polymers of nucleotides.
The two important functions of nucleic acids are listed below:-
(i) DNA which is responsible for the transference of hereditary effects from one generation to another, which is due to their property of replication during cell division as a result of which two identica
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
In [Fe (H2O)6]3+
Electronic configuration of Fe is: [Ar]3d64s2
[Ar] = 1s22s22p63s23p6
Electronic configuration of Fe+3 = [Ar]3d5
Outer electronic configuration of Fe+3 = 3d5
Overall charge balance:
X + 6 (0) = 3
X = + 3
In [Fe (CN)6]3-
Overall charge balance:
X + 6 (-1) = -3
X = + 3
In both the compounds Fe is in + 3 oxidation state.
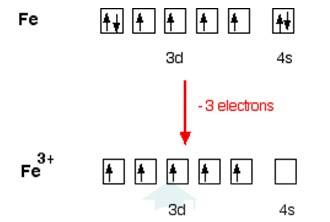
In case of [Fe (H2O)6]3+
H2O is weak field ligand so it does not pair the unpaired electron. Total no. of the unpaired electron, n =5, Spin only magnetic moment is given by:
μ = [n (n + 2)]1/2
μ = [5*7]1/2
μ = 5.916BM
In case of [Fe (CN)6]3-
CN- is a strong field ligand so it pairs up the electron.
Total no. of unpaired e
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.28
The deficiency of Vitamin A leads to Xerophthalmia which is hardening of the cornea of the eye and night blindness as well. Vitamin-C is essential to us because its deficiency causes scurvy which is a phenomenon of bleeding gums; and pyorrhoea which is phenomenon of loosening-bleeding of teeth.
The sources of vitamin A are fish, cod liver oil, carrots, butter and milk.
The sources of vitamin C are citrus fruits, lemon, amla and green leafy vegetables.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
In [Ni (Cl)4]2- ion, Cl- is a weak field ligand so it will not pair the unpaired electrons of Ni+2 ion. Electronic configuration of Ni is: [Ar]3d84s2 where [Ar] = 1s22s22p63s23p6
Electronic configuration of Ni+2 = [Ar]3d8 Outer electronic configuration of Ni+2 = 3d8 Overall charge balance:
X + 4 (-1) = -2 X = + 2.
Therefore it undergoes sp3 hybridization. So it will have tetrahedral geometry.

Since there are 2 unpaired electrons in the d orbital so it is a paramagnetic compound. In [Ni (Co)4]:
Overall charge is neutral and oxidation state of Ni can be calculated as:
X + 4 (0) = 0
x = 0
Ni is in zero oxidation state.
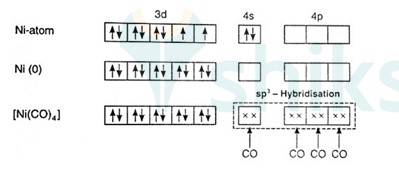
Co is a strong field ligand
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 679k Reviews
- 1800k Answers