Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Get insights from 2.6k questions on Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
16.4
Soaps are metallic salts of higher fatty acids such as palmitic acid, stearic acid, oleic acid etc. The process of saponification involves the hydrolysis of an oil or fat with an alkali (sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide). Oils and fats are glyceryl esters of fatty acids and may be regarded as mixed glycerides. Sodium soaps are prepared by heating the fats by sodium hydroxide.
(i) (C15H31COO)3C3H5 – Glyceryl palmitate
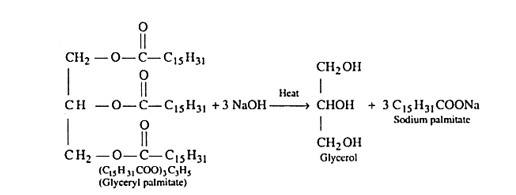
(ii) (C17H32COO)3C3H5 – Glyceryl oleate
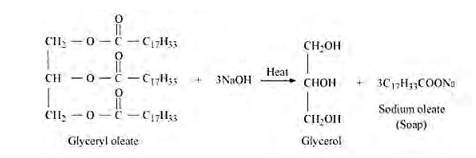
New question posted
6 months agoNew answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
16.3
Diabetes mellitus is the third leading cause of death in the world. It is a medical condition in which the glucose is not consumed in the body due to inefficiency in the secretion of insulin [hormone which converts glucose to glycogen and store in liver]. Diabetes is the precursor for many other diseases like obesity, heart attacks, stroke etc.
Therefore Diabetic people are advised to consume low-calorie diet [fewer carbohydrates & more proteinaceous and fiber rich]. The refined sugar like sucrose adds calorie to the diet but complex sugar and starches do not add to the calorie intake of a person and at the same time impart a
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Given:
Molar mass of non-volatile solute = 40g
Let no. of moles of solute be n.
Mass of octane = 114g
Molar mass of octane (C8H18) = 12 * 8 + 1 * 18 = 114g/mol
Moles of octane = given mass/molar mass
⇒ n = 114/114 moles
⇒ n = 1 mole
Molar fraction of solute,
x2 = moles of solute / moles of solute + moles of octane
⇒ x2 = n/n + 1
Let the vapour pressure of original solvent (without solute) be p1?
Accordingly after addition of solute vapour pressure of solution reduces to 80% i.e.
0.8 p1? = p1
Applying the formula:

⇒ n/n + 1 = 0.2
⇒ 0.2n + 0.2 = n
⇒ n = 0.25 moles
Hence, mass of solute is:
moles = given mass/molar mass
⇒ 0.25moles = ma
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Given: 1 molal solution means 1 mole of solute present in 1000g of water solvent)
Molecular weight of water = H2O = 1 * 2 + 16 = 18g/mol
No. of moles of water, n = given mass /molecular weight
⇒ n = 1000/18 = 55.56 gmol-1
Mole fraction of solute in solution, x2 = moles of solute/ (moles of solute + moles of water)
⇒ x2 = 1/ (1 + 55.56)
⇒ x2 = 0.0177
Given vapour pressure of pure water at 300k is 12.3 kpa
Apply the formula:
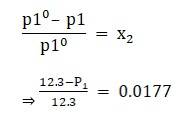
⇒ P1 = 12.0823kpa
which is the vapour pressure of the solution.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Given: Temperature = 373k
Vapour pressure of pure heptane (p10 ) = 105.2 kpa and that of octane (p20 ) = 46.8 kpa
Mass of heptane = 26 g
Mass of octane = 35 g
Molecular weight of heptane = C7H16 = 12 * 7 + 1 * 16 = 100 gmol-1
Molecular weight of octane = C8H18 = 114 gmol-1
Moles of heptane, n1 = given mass /molecular weight = 26/100
⇒ n1 = 0.26mol
Moles of octane, n2 = given mass /molecular weight = 35/114
⇒ n2 = 0.307mol
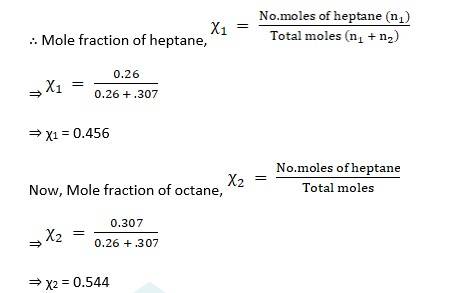
∴ Partial pressure of heptane, p1 = χ1 * p10
⇒ p1 = 0.456 * 105.2 = 47.97kpa
∴ Partial pressure of octane, p1 = χ2 * p20
⇒ p2 = 0.544 * 46.8 = 25.46 kpa
∴ Total pressure exerted by solution = p1 + p2
= 47.97 + 25.46
=
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
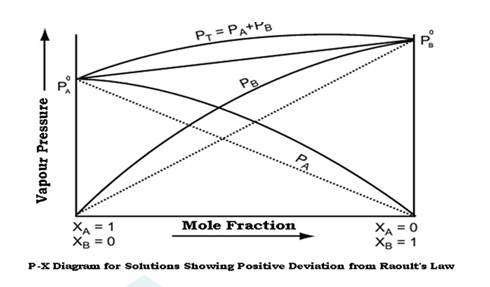
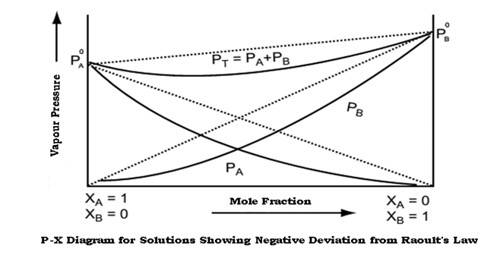
Raoult's law states that at a given temperature, the vapour pressure of a solution containing non volatile solute is directly proportional the mole fraction of the solvent.
Non ideal solutions show positive and negative deviations from ideal behaviour.
Non ideal solutions showing positive deviations from Raoult's law-
A solution is said to show positive deviation from Raoult's Law when at any composition, its vapour pressure is higher than that given by Raoult's Law.
The positive deviation is shown by those liquid pairs in which the A-B molecular interaction forces are weaker than the corresponding A-A or B-B molecular interaction forces.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Given:
Mass of ethane in solution A = 6.56 * 10–3 g
Partial pressure of solution A = 1 bar
Mass of ethane in solution B = 5.00 * 10–2 g
To find: Partial Pressure of gas
Formula:
By Henry's law:
Mass of dissolved gas M = k * P Where
k = proportionality constant
P = Partial Pressure
Solution:
⇒ M1 = k * P1. [1]
⇒ M2 = k * P2. [2]
Dividing the [2] by [1], we get
M2/M1 = P2/P1
P2 = M2 X P1 / M1
P2 = 5 X 10–2 X 1 / 6.56 X 10–3
P2 = 7.62 bar
Therefore the partial pressure of the gas is 7.62 bar.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
The solubility of a gas in water depends on following three parameters:
- Nature of gas
- Temperature
- Pressure
The solubility decreases with increase in temperature. Temperature and pressure follow inverse proportionality. So solubility increases with increase with pressure. A quantitative relation between pressure and solubility of a gas in a solvent was given by W. Henry [1803]. This relationship is known as Henry's law.
Statement:
Henry's law can be expressed as follows.
At constant temperature, the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas.
Mathematically,
Solubility? Pressure of the gas
Some of the imp
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 679k Reviews
- 1800k Answers