Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Get insights from 2.6k questions on Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
16.14
Antibiotics that are effective against a wide range of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria are known as broad spectrum antibiotics. Chloramphenicol is an example of a broad spectrum antibiotic. It has the following structure: -
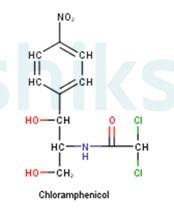
It can be used for the treatment of typhoid, dysentery, acute fever, pneumonia, meningitis, and certain forms of urinary infections. Two other examples of broad spectrum antibiotics are vancomycin and ofloxacin. Ampicillin and amoxicillin? synthetically modified from penicillin are also broad spectrum antibiotics.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Mass of ions = 92g
Molar mass of ions = Na+ = 23g (neglect the mass lost due to absence of a electron)
Moles of ions = mass of ions/molar mass
⇒ n = 92/23 moles
⇒ n = 4moles
Molality of solution = moles of solute/mass of solvent (in kg) Molality = 4/1 = 4M
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
16.13
Anti-depressant drugs are needed to counteract the effect of depression. These drugs function by inhibiting the enzymes catalysing the degradation of the neurotransmitter, noradrenaline. As a result, the important neurotransmitter is slowly metabolised and then it can activate its receptor for longer periods of time.
Two anti-depressant drugs are:
(i) Iproniazid
(ii) Phenelzine
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
- Water is a polar compound (due to electronegativity difference between O and H) . We know that “like dissolves like”. So, a non-polar compound will be more soluble in non-polar solvent as compared to polar compound.
- Phenol has the polar group -OH and non-polar group –C6H5 and it can not form H bonding with water (presence of bulky non-polar group) . Thus, phenol is partially soluble in water
- Toluene has no polar Thus, toluene is insoluble in water.
- Formic acid (HCOOH) has the polar group -OH and can form H-bond with water. Thus, formic acid is highly soluble in water
- Ethylene glycol (OH-CH2-CH2-OH) has polar -OH group and can form H-
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
16.12
Specific drugs affect only some specific or particular receptors. Antacids and anti-allergic drugs work on different receptors. This is the reason why antacids and anti-allergic drugs do not interfere with each other's functions, but interfere with the functions of histamines.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Now n-octane is non-polar solvent due to long chain saturated structure. We know that “like dissolves like” so a non-polar compound will be more soluble in non-polar solvent as compared to polar compound.
So cyclohexane is non-polar due to symmetric structure. KCl is ionic in nature as it will dissociate into K + and Cl- ions. CH3CN is polar as mentioned above and CH3OH is also polar in nature.
The order of increasing polarity is:
Cyclohexane < CH3CN < CH3OH < KCl (O is more electronegative than N)
Therefore, the order of increasing solubility is:
KCl < CH3OH < CH3CN < Cyclohexane
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) Both the compounds are non-polar and they do not attract each other because they do not form any polar ions. Vanderwaals forces of attraction will be dominant in between them as vanderwaals forces of attraction are not a result of any chemical or electronic bond.
(ii) now here both the compounds are non-polar because in I2 both the atoms are same so they have same electronegativity and hence there will be no displacement of electron cloud, it will be in the centre. In case of CCl4 molecule, it has tetrahedral shape so two Cl atoms will cancel the attraction effect from two opposite Cl atoms, hence molecule as a whole is non polar.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Here,
T = 300 K
π = 1.52 bar
R = 0.083 bar L
Applying the relation, π = CRT
where
π = osmotic pressure of solution
C = concentration of solution
R = universal gas constant
T = temperature
⇒C = π / RT = 1.52 / 0.083 X 300
⇒ C = 0.061mol/L
Concentration of the solution is 0.061mol/L
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
16.11
Either of the following forces can be involved in holding the drugs to the active sites of enzymes: -
(i) Ionic bonding
(ii) Hydrogen bonding
(iii) Dipole? dipole interaction
(iv) Van there Waals force
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
let the molar masses of AB2 and AB4 be x and y respectively.
Molar mass of benzene (C6H6) = 12 * 6 + 1 * 6 = 78 g/mol
Moles of benzene = mass/molar mass = 20/78
n = 0.256mol
⇒ ΔTf = 2.3 K
Kf = 5.1K kg mol-1
For AB2
Applying the formula: ΔTf = Kf * M
Where
ΔTf = depression in freezing point
Kf = molal depression constant
M = molality of solution
⇒ 2.3 = 5.1 * M1
⇒ M1 = 0.451mol/kg
For AB4
Applying the formula: ΔTf = Kf * M
ΔTf = depression in freezing point
Kf = molal depression constant
M = molality of solution
⇒ 1.3 = 5.1 * M2
⇒ M2 = 0.255mol/kg
M1 = moles of solute/mass of solvent (in kg)
M1 = 1/x / 0.02 = 1 / 0.02x = 0.451
⇒ X = 110.86g
M2
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 679k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
