Physics
Get insights from 5.6k questions on Physics, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Consider the diagram

Θ= θ1+ θ2/2
Let temperature varies linearly in the rod from its one end to other end, let θ be the temperature of the midpoint of the rod. At steady state
Rate of flow of heat,
dQ/dt =
where k is the coefficient of thermal conductivity of the rod
so θ1- θ= θ- θ2
θ= θ1+ θ2/2
L=L0 (1+ )
L= Lo (1+ )
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
By applying Pythagoras theorem in given figure
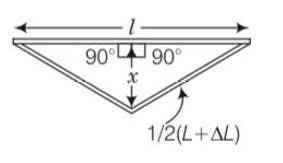
2
x=
=1/2
= ½
=1/2
As Increase in is very small so we neglect it
=1/2
By using this value in above in equation
x=1/2 = ½ L
=
= 5
= 5
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Decrease in temperature = 57-37= 200C
Coefficient of linear expansion = 1.7 oC
Bulk modulus for copper B = 140
Coefficient of cubical expansion = 3 = 5.1
Let initial volume of the cavity be V and its volume increases by due to increase in temperature.
Thermal stress produced = B
= B
= 140
= 1428 2
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As difference in volume is constant
By considering the diagram
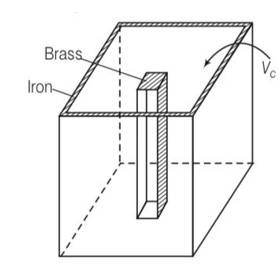
Let Vio , Vbo be the volume of iron and brass vessel at 00C
Vi,Vb be the volume of iron and brass vessel at 0C
be the coefficient of volume expansion of iron and brass.
Vio -Vbo= 100cc= Vi-Vb
Vi =Vio(1+ i )
Vb =Vbo(1+ b )
Vi-Vb = (Vio -Vbo)+
Since Vi-Vb= constant
Vio i= Vbo
Using above equations
Vbo = 144.9cc
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As liron-lbrass =10cm= constant at all temperature
Let lo be the length of temperature at 00C and l be the length after change in temperature
liron-lbrass =10cm
liron (1+ )-lbrass (1+ )=10cm
Iiron iron= Ibrass brass
=1.8/1.2=3/2
Lbrass=20cm and liron=30cm
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b), (c) Streamline flow is more likely for liquids having low density. We know that greater the coefficient of viscosity of a liquid more will be velocity gradient hence each line of flow can be easily differentiated. Also higher the coefficient of viscosity lower will be Reynolds number, hence flow more like to be streamline.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c), (d) For liquids coefficient of viscosity
i.e with increase in temperature decreases.
For gases coefficient of viscosity
i.e with increase in temperature decreases.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
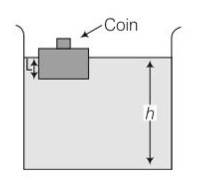
(a), (b) When the coin falls into the water, weight of the (block + coin) system decreases, which was balanced by the upthrust force earlier. As weight of the system decreases, hence upthrust force will also decrease which is only possible when l decreases.
As l decreases volume of water displaced by the block decreases, hence h decreases. As the coin falls into water, it displaces some volume of water which is very less. Hence, we neglect volume of the coin.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b), (c) Pressure is defined as the ratio of magnitude of component of the force normal to the area and the area under consideration.
As magnitude of component is considered, hence, it will not have any direction. So, Pressure is a scalar quantity.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
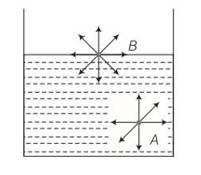
(b), (d) Consider the diagram where two molecules of a liquid are shown. One is well inside the liquid and other is on the surface. The molecule (A) which is well inside experiences equal forces from all directions, hence net force on it will be zero.
And molecules on the liquid surface have some extra energy as it surrounded by Only lower half side of liquid molecules.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 684k Reviews
- 1800k Answers