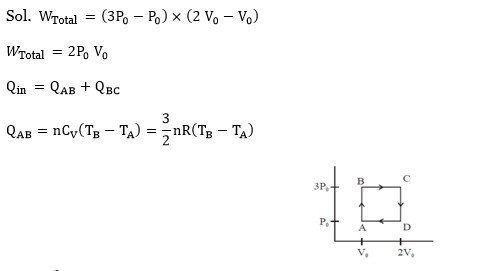Physics Thermodynamics
Get insights from 156 questions on Physics Thermodynamics, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics Thermodynamics
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
1/4 m (210)² = m (0.03) x (4.2) x 1000 x ΔT ; Q = mSΔt
ΔT = (210) (210)/ (4) (4.2) (0.03) (1000) = 87.5°C
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
T = constant
P = constant
PV = nRT
PdV = nRdT
PdV + VdP = 0
ΔV = nRΔT/P
dV = (-)VdP/P
|ΔV| = V (ΔP/P)
V/P ΔP = nRΔT/P
ΔT = V/nR ΔP
C = V/nR T/P = 300/2 = 150
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
ΔQ = heat supplied
ΔW = work done
ΔU = change in internal energy
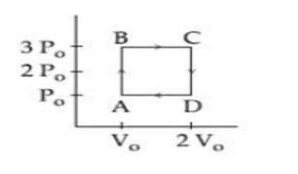
(i) adiabatic (B) Δθ = 0
(ii) isothermal (D) ΔU = 0
(iii) isochoric (A) ΔW = 0
(iv) isobaric (C) ΔU ≠ 0, ΔW ≠ 0, ΔQ ≠ 0
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
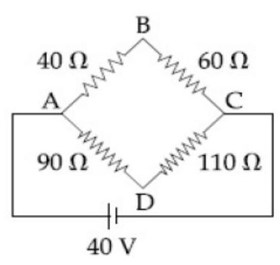
n? T? + n? T? = nT
⇒ (0.1) (200) + (0.05) (400) = (0.15)T
⇒ T = 266.67
New answer posted
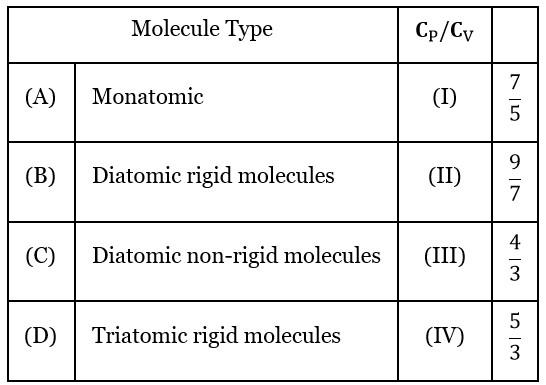
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
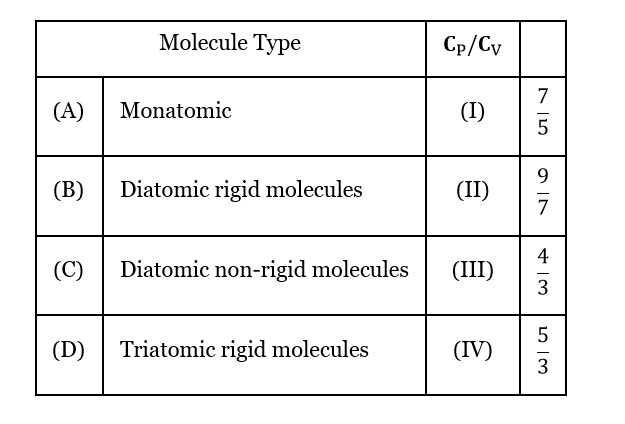
Mono atomic → Cv = 3R/2, Cp = 5R/2
Di-atomic → Cv = 5R/2, Cp = 7R/2
(Rigid)
Di-atomic → Cv = 7R/2, Cp = 9R/2
(Non-Rigid)
Tri-atomic → Cv = 3R, Cp = 4R
(Rigid)
New answer posted
6 months agoTaking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 687k Reviews
- 1800k Answers