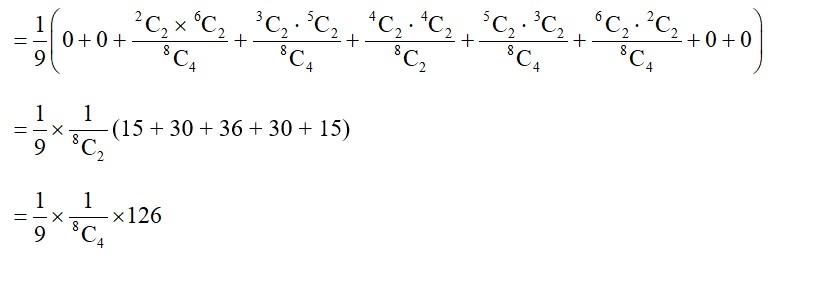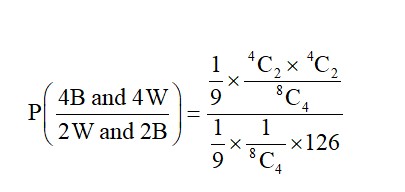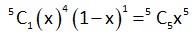Probability
Get insights from 206 questions on Probability, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Probability
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
4 months agoNew answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
If x = 0, y = 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
If x = 1, y = 7, 8, 9, 10
If x = 2, y = 8, 9, 10
If x = 3, y = 9, 10
If x = 4, y = 10
If x = 5, y = no possible value
Total possible ways = (5 + 4 + 3 + 2 + 1) * 2
= 30
Required probability
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
P (2W and 2B) = P (2B, 6W) * P (2W and 2B)
+ P (3B, 5W) * P (2W and 2B)
+ P (4B, 4W) * P (2W and 2B)
+ P (5B, 3W) * P (2W and 2B)
+ P (6B, 2W) * P (2W and 2B)
(15 + 30 + 36 + 30 + 15)
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
Let probability of tail is
⇒ Probability of getting head =
∴ Probability of getting 2 heads and 1 tail
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
ax2 + bx + c = 0
D = b2 – 4ac
D = 0
b2 – 4ac = 0
b2 = 4ac
(i) AC = 1, b = 2 (1, 2, 1) is one way
(ii) AC = 4, b = 4
(iii) AC = 9, b = 6, a = 3, c = 3 is one way
1 + 3 + 1 = 5 way
Required probability =
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
Let
A : Missile hit the target
B : Missile intercepted
P (B) =
Required Probability =
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 9
Each element of ordered pair (i, j) is either present in A or in B.
So, A + B = Sum of all elements of all ordered pairs {i, j} for and
= 20 (1 + 2 + 3 + … + 10) = 1100
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 9
P (H) = x . P (T) = 1 – x
P (4H. 1T) = P (5H)
6x = 5 = 0
P (atmost 2H)
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 9
so vectors
are coplanar, hence their Scalar triple product will be zero.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
Fix the unit place, find the chances for the first three digits
unit digit as 1, total ways = 9.102
unit digit as 2, total ways = 4.52
unit digit as 3 total ways = 3.42
unit digit as 4 total ways = 2.32
unit digit as 5 total ways = 1.22
unit digit as 6 total ways = 1.22
unit digit as 7 total ways = 1.22
unit digit as 8 total ways = 1.22
unit digit as 9 total ways = 1.22
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers