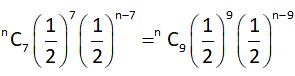Probability
Get insights from 206 questions on Probability, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Probability
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
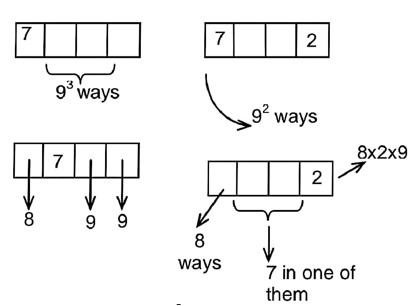
3, 4, 5, 5
In remaining six places you have to arrange
3, 4, 5,5
So no. of ways
Total no. of seven digits nos. =
Hence Req. prob.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
Let total number of throws = n
Probability of getting 2 times = Probability of getting an even number 3 times.
[as probability of getting odd number = probability of getting even number = ]
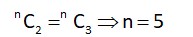
Probability of getting an odd number for odd number of times =
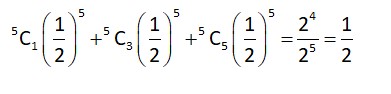
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
Let P (B1) = a P (B2) = b P (B3) = c
Given a (1 – b) (1 – c) = a . (i)
b (1 – a) (1 – c) = b . (ii)
c (1 – b) (1 – a) =
(1 – a) (1 – b) (1 – c) = p . (iv)
->a – ab – 2b + 2ab = ab Þ a = 2b . (v)
Again
->b – bc – 3c + 3bc = 2bc Þ b = 3c . (vi)
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
Total possibilities = 25 * 25
Farounable case = 5C2 * 33 = 10 * 33
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers