Solid State
Get insights from 127 questions on Solid State, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Solid State
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoNew answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
17. Option (ii) Quartz glass (SiO2) is correct since quartz glass (SiO2)is amorphous in nature as there is no long range ordered arrangement of the constituent particles being present in it and hence it is an amorphous solid.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
Ferromagnetism: The substances that are strongly attracted by a magnetic field are called ferromagnetic substances can be permanently magnetised even in the absence of a magnetic field. Some examples of ferromagnetic substances are iron, cobalt, nickel, gadolinium, and CrO2. In solid state, the metal ions of ferromagnetic substances are grouped together into small regions called domains and each domain acts as a tiny magnet. In an un-magnetised piece of a ferromagnetic substance, the domains are randomly-oriented and so, their magnetic moments get cancelled. However, when the substance is placed in a magnetic field, all the domains get
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.49 NaCl is doped with 10−3 mol % of SrCl2
100 moles of NaCl are doped with 0.001 moles of SrCl2
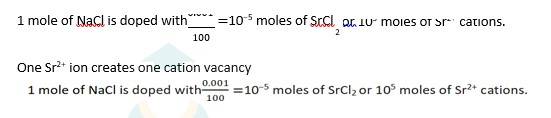
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.48 It is given that aluminum crystallises in a cubic closed packed structure.
Its metallic radius is 125 pm.
For cubic close-packed structure
a=2√2r=2√2*125=354 pm
Here, a is the edge length of the unit cell and r is the atomic radius.
(ii) Volume of one unit cell = a3 =(354 pm)3=4.4*10−23cm3(1 pm=10−10cm)
Number of unit cells in 1.00cm3= 1.00 cm3 / 4.4*10-23 cm3
= 2.27*1022
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
Schottky defect: Schottky defect is basically a vacancy defect shown by ionic solids. In this defect, an equal number of cations and anions are missing to maintain electrical neutrality. It decreases the density of a substance. Significant number of Schottky defects is present in ionic solids. For example, in NaCl, there are approximately 106 Schottky pairs per cm3 at room temperature. Ionic substances containing similar-sized cations and anions show this type of defect. For example: NaCl, KCl, CsCl, AgBr, etc.
Frenkel defect: Ionic solids containing large differences in the sizes of ions show this type of defect. When the smaller ion (
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
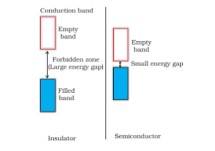
1.47 The energy gap between the valence band and conduction band in an insulator is very large while in a conductor, the energy gap is very small or there is overlapping between valence band and conduction band.
(ii) In a conductor, the valence band is practically filled or there is overlapping between valence band and conduction band while in semiconductor, there is always a small energy gap between them.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.45 For fcc unit cell, a=2√2?.
Here, a is the edge length and r is the atomic radius (0.144 nm).
a = 2√2 *0.144 = 0.407 nm
Hence, the length of a side of a cell is 0.407 nm.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.44 Ge is group 14 element and In is group 13 element. Hence an electron deficient hole is created and therefore, it is p–type.
2. B is group 13 elements and Si is group 14 elements, there will be a free electron. Hence, it is n-type
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers

