Work, Energy and Power
Get insights from 177 questions on Work, Energy and Power, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Work, Energy and Power
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.24 Mass of the bullet, = 0.012 kg
Initial speed of the bullet, u = 70 m/s
Mass of the wooden block , = 0.4 kg
Initial speed of the wooden block = 0
Let's assume, final speed of the bullet = v
Applying the law of conservation of momentum
Hence v = ( = 2.04 m/s
Let h be the height by which the block rise. Applying law of conservation of energy
Potential energy of the combined bullet + block = Kinetic energy of the combination
(1/2)
h = /2g = 0.212 m
The heat produced = Initial kinetic energy of the bullet – final kinetic energy of the combination
= (1/2) - (1/2)
= (1/2
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.23 Power used by the family = 8 kW = 8000 W
(a) Solar energy received = 200 W/
Percentage conversion of Solar energy to Electrical energy = 20%
If the area required is A then 0.2
A = 200 . The comparable roof size is 14.14 X 14.14 m
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.22 Mass lifted, m = 10 kg
Height to which the mass lifted, h = 0.5 m
No of repetitions, n = 1000
(a) Work done against gravitational force,
W = nmgh = 1000 49050 J
(b) Mechanical energy supplied by 1 kg fat, with 20% efficiency rate = 0.2 3.8 = 0.76 J/kg
Fat used by dieter = 49050 / (0.76 kg = kg
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.21 Given, the area of the windmill sweep = A, Wind velocity = v
The volume of air passing through the blade = Av
Let the density of air be , the mass of air passing through the blade =
(a) The mass of air passing through the blade in time t =
(b) The kinetic energy of air = = = /2 …. (1)
(c) Area, A = 30 , v = 36 km/h = 10 m/s, density of air be = 1.2 kg/
Total wind energy, from eqn. (1) = 18 kW
Electrical energy = 25 % of wind energy = 0.25
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.20 Mass of the body = 0.5 kg
Velocity, v = a x 3/2
a = 5 m–1/2 s–1
At x =0, the initial velocity, u = 0
At x = 2, the final velocity, v = 5 = 14.142 m/s
Work done by the system = increase in K.E. of the body = (1/2)m ( - )
= (1/2) 14.142 = 50 J
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.19 Given, the mass of the trolley, = 300 kg, mass of the sand bag, = 25 kg, uniform velocity of the trolley, v = 27 kmph = 0.75 m/s
Since there is no external force acting on the system, the speed of the trolley will remain unchanged even after entire sand is empty. 27 kmph is the answer.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.18 The length of the pendulum, l = 1.5 m
The potential energy of the bob at horizontal position = mgl
Since it dissipates 5% of its kinetic energy to come to the horizontal position, from the law of conservation of energy we get,
= (0.95)
= 2
v = 5.287 m/s
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
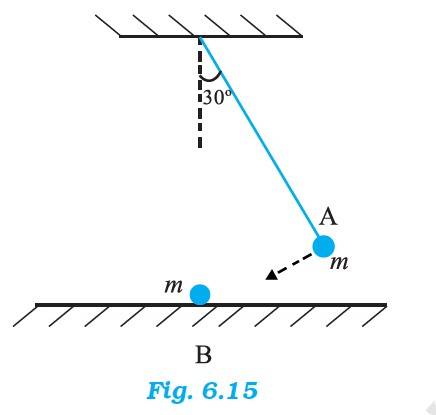
6.17 In an elastic collision, when the ball A will hit the ball B, A comes to rest immediately and the ball B acquires the velocity of ball A. The momentum thus gets transferred from a moving body to a stationary body.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
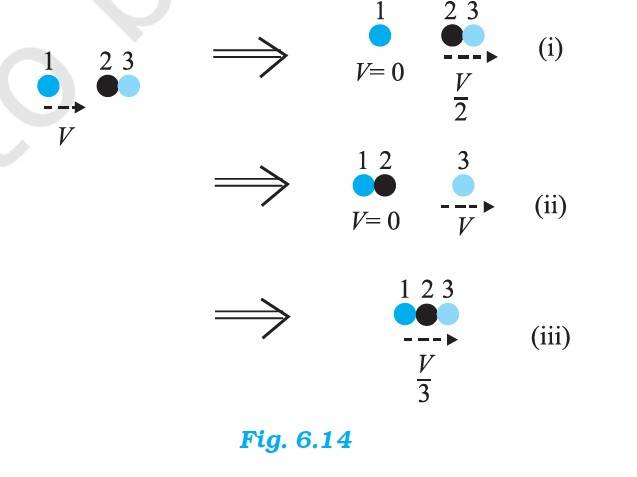
6.16 The mass of the ball bearing = m
Before the collision, the total K.E. of the system = K.E. of the stationary ball bearing + K.E. of the striking ball bearing = 0 +
After the collision, the K.E. of the total system is
(a) Case (i) = 0 + =
(b) Case (ii) = 0 +
(c) Case (iii) = =
Case (ii) is possible since K.E. is conserved in this case.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.15 Given, the volume of the tank, V = 30
Time required to fill the tank, t = 15 min = 900 s
Height of the tank above the ground, h = 40 m
The efficiency of the pump? = 30%
The density of water, = kg/
Now, the mass of the water pumped, m = = 30 kg = 3 kg
Power consumed = W/t = mgh/t = 3 40 / 900 = 13066 W
P input = Power consumed /? = 43.6 kW
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers