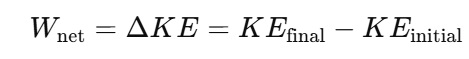Work, Energy and Power
Get insights from 177 questions on Work, Energy and Power, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Work, Energy and Power
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
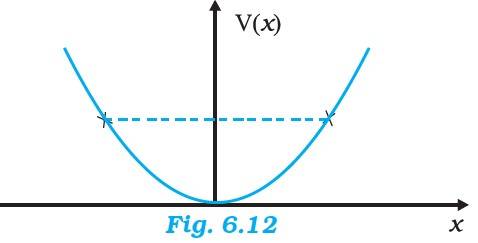
6.4 Given, particle energy, E = 1 J,
Force constant, k = 0.5 N/m
Kinetic energy, KE = mv2
From the equation, total energy, E = KE +PE, we get
1 = (1/2)mv2 + (1/2) kx2
when it turns back, v becomes 0
1 = (1/2) , x = ± 2
New question posted
8 months agoNew answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
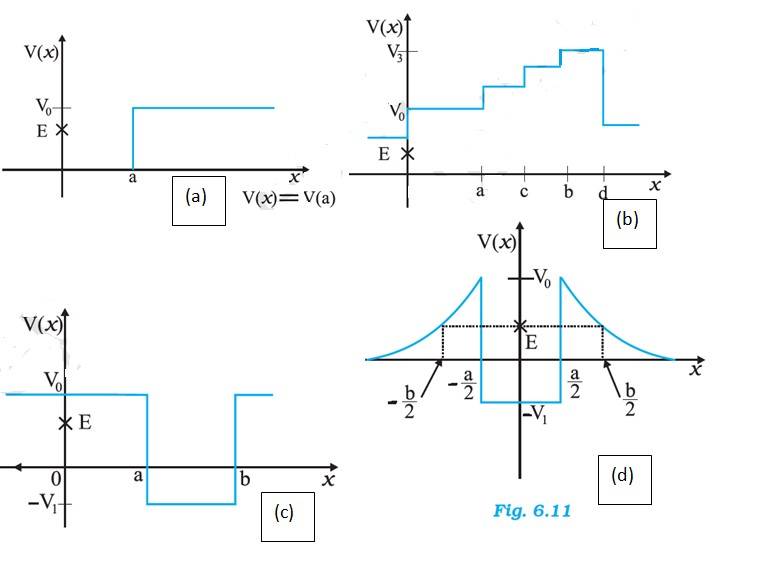
6.3 We know the total energy E is given by E = Kinetic energy (KE) + Potential energy (PE)
(a) In figure (a), we have at x=0, the potential energy is zero. So KE is positive. At x>a, the potential energy has a value greater than E, so the KE becomes 0. Thus the particle will not exist in the region x>a. Minimum total energy is zero.
(b) For the entire x-axis, PE >E, the KE of the object would be negative. Thus the particle will not exist in this region.
(c) In x=0 to x=a and x>b, PE is greater than E, so he KE has to be negative. The object cannot exist in this region.
(d) For x=-b/2 to x =-a/2 and x=a/2 to x=b/2, KE
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.2 Given, mass of the body, m = 2 kg
Horizontal force applied, F = 7 N
Coefficient of friction, = 0.1
Acceleration, a = F/m = 7/2 = 3.5 m/s2
Frictional force, f = 0.1 1.96 N
Retardation produced by the frictional force, = -f/m = -1.96 /2 = 0.98 m/s2
The net acceleration by which the body moves forward
= a - = 3.5 – 0.98 = 2.52 m/s2
Distance moved by the body in 10 s is given by
s = ut + (1/2) = 0 = 126 m
(a) Work done in 10 s is given by
W = Force
(b) Work done by friction in 10 s is given by
W = -f - 247J
(c) Work done by the net force
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.1 (a) While the person lifts a bucket out of a well by means of a rope tied to the bucket, the direction of both the force and the displacement are same, hence the work done is positive.
(b) While lifting the bucket, he works against gravity, but the work done by the gravitational force is downward, hence the work done is negative.
(c) The direction of motion of the object is in the opposite direction of the frictional force; hence the work done is negative.
(d) While a body moves on a rough horizontal plane, the frictional forces try to oppose the motion. But since the applied force maintains uniform velocity
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Conservative forces (like gravity or spring force) conserve mechanical energy and do not depend on the path taken. The work done by the conservative forces is recoverable.
Non-conservative forces (like friction or air resistance) dissipate energy as heat or sound. It depends on the path. When non-conservative forces act, mechanical energy is not conserved.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Energy is measured in joules (J). It is the capacity to do work while power is the rate of using energy or doing work. Power is measured in watts (W). One watt equals one joule per second. Power talks about how fast the work is done, and energy is about how much work is possible.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
The work-energy theorem in Physics Work, Energy and Power refers to that net work done on an object is equal to its change in kinetic energy. The following is the formula:
Work-energy theorem means that when work is done on an object, the object gains kinetic energy and when an object does the work, it loses kinetic energy. This theorem helps in solving problems related to motion and forces without directly using kinematic equations. It is especially useful in conservative and non-conservative forces cases and it helps in simplifying complex motion analysis.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
Energy in Physics means the ability to do work and it can exist in different forms:
- Kinetic Energy (? ) – It is the energy of a moving object. The formulae are KE=1/2mv2
- Potential Energy (PE) - It is stored energy due to position. Formulae are PE=mgh for gravitational potential energy.
- Mechanical Energy - Total of KE and PE.
- Thermal Energy - Energy generated due to heat.
- Chemical Energy - Energy stored in chemical bonds.
- Nuclear Energy - Related to atomic nuclei.
- Electrical Energy - Related to electric charges.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers