Amines
Get insights from 162 questions on Amines, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Amines
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (C)
SN1 reaction: A nucleophilic reaction that occurs in two steps, first is the bond-breaking step and the second is the production of the carbocation. The stability of carbocation formed in the second step determines the rate of reactivity of reactant toward SN1 reaction. Here, C6H5CH2Br,
In the process of ionization, removal of bromine, a stable Benzyl carbocation is produced. Therefore, it is best suited for reaction through the SN1 mechanism.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (A)
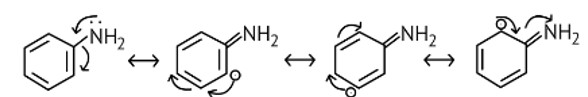
The NH2 group is directly attached to the benzene ring in aniline and other aryl amines. As a result, the unshared electron pair on the nitrogen atom is conjugated with the benzene ring, making it less available for protonation.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (C)
Because of the electron-releasing nature of the alkyl group, it (R) pushes electrons towards nitrogen, making the unshared electron pair more available for sharing with the acid's proton. Furthermore, the +I effect of the alkyl group stabilizes the substituted ammonium ion formed from the amine by dispersing the positive charge.
As a result, alkylamines are more powerful bases than ammonia.
As a result, the basic nature of aliphatic amines should increase as the number of alkyl groups increases.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct answer: (D)
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
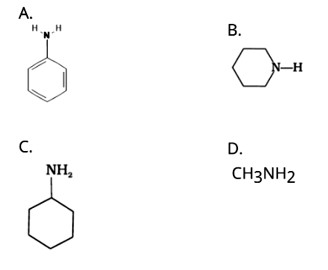
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (B) Triethylamine
The structure of the given amines are shown below.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) Aromatic amines react with nitrous acid (prepared in situ from NaNO2and a mineral acid such as HCl) at 273 - 278 K to form stable aromatic diazonium salts e., NaCl and water.
(ii) Aliphatic primary amines react with nitrous acid (prepared in situ from NaNO2and a mineral acid such as HCl) to form unstable aliphatic diazonium salts, which further producealcohola and acid called as hydrochloric acid and evolution of nitrogen
(iii) Aliphatic amines are stronger bases than aromatic amines due to following reasons:
(a) The lone pair of electrons of the nitrogen atom of aromatic amines is involved in
conjugation with the π−
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) Aromatic amines react with nitrous acid (prepared in situ fromNaNO2 and a mineral acid such as HCl) at 273 - 278 K to form stable aromatic diazonium salts i.e., NaCl and water. This reaction is widely used for preparation of variety of compounds.
(ii) Aliphatic primary amines react with nitrous acid (prepared in situ from NaNO2 and a mineral acid such as HCl) to form unstable aliphatic diazonium salts, which is very reactive, which further produce alcohol and HCl with the evolution of nitrogen gas.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is used for the preparation of aliphatic primary amines. It involves nucleophilic substitution (SN2) of alkyl halides by the anion formed by the phthalimide.But aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with the anion formed by the phthalimide.
Therefore aromatic primary amines cannot be formed by gabriel phthalimide process.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
1- C6H5NH2 + CHCl3 + KOH
It is a carbylamine reaction in which a isocyanide compound is formed along with side products of potassium chloride.Basically the name of reaction is given is due to formation of a foul smelling compound called as isocyanide.
2- C6H5N2Cl + H3PO2 + H2O
Benzenediazonium chloride is a very reactive compound which oxidises hypophosphorous acid to hypophosphoric acid and the reactant is reduced to benzene.
3- C6H5NH2 + H2SO4 (conc.)
Aniline undergoes sulphonation to anillium hydrogensulphate.
4- C6H5N2Cl + C2H5OH
Aniline is very activating group which undergoes reaction to give ortho and para product. But in acidic medium
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
It is given that compound 'C' having the molecular formula, C6H7N is formed by heating compound 'B' with Br2and KOH. This is a Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction (in which isocyanide compound is formed). Therefore, compound 'B' is an amide and compound 'C' is an amine. The only amine having the molecular formula, C6H7N is aniline. Therefore, compound 'B' (from which 'C' is formed) must be benzamide.
Further, benzamide is formed by heating compound 'A' with aqueous ammonia. Therefore, compound 'A' must be benzoic acid. The given reactions can be explained with the help of the following equations:
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 685k Reviews
- 1800k Answers