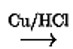Amines
Get insights from 162 questions on Amines, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Amines
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (A)
The basic strength of an atom is determined by its electron-donating capacity; in this case, the amide is the most basic due to the presence of a negative charge and two lone pairs of electrons on the nitrogen atom.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (D)
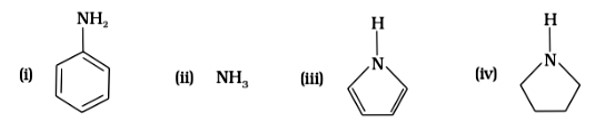
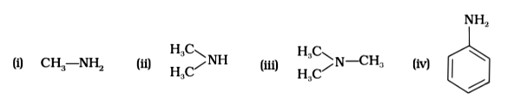
Pyrrolidine is the strongest of two bases because the lone pair of nitrogen does not involve sin resonance, and the presence of two alkyl basic compounds increases the basic strength among the given four compounds.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (D)
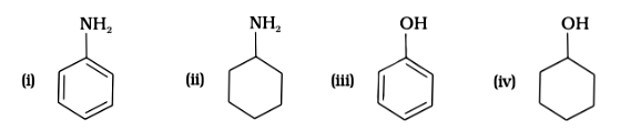
Since phenol is the strongest acid among the four options listed above, it is the weakest Brönsted base. The stronger the acid, the weaker the conjugate base.
Amines have a strong tendency to accept electrons thus they are a strong bronsted base while phenol is the strongest acid among all, therefore as per the relation of conjugative strong acids and weak bases, phenol is the weakest base.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (D)
Weak electrophile such as Diazonium cation readily reacts with electron-rich compounds which are having electron-rich compounds such as hydroxyl group, amino group. They don't react with electron-withdrawing groups like nitro groups. Therefore, nitrobenzene will not undergo an azo coupling reaction with benzene diazonium chloride.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (B)
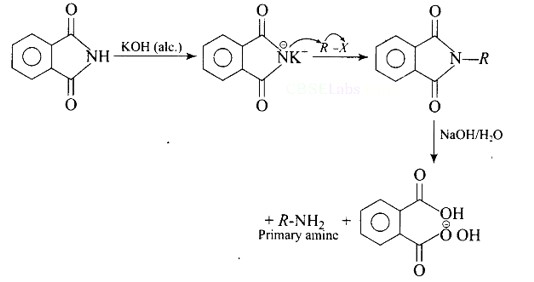
The reaction of transformation of primary alkyl halides to primary amines using potassium phthalimide is the Gabriel phthalimide reaction.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (B)
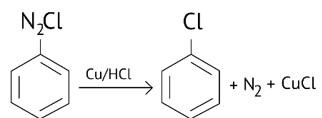
Diazonium salts react with copper powder and halogen acid to form aryl halide.
Gattermann reaction is a Sandmeyer reaction variant in which Cu powder replaces CuCl.
This substitution produces aryl halide more easily and under milder conditions than the Sandmeyer reaction.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (A)
On Reaction of acid anhydrides with primary amines, amides are formed as the primary product along with carboxylic acid.
(RCO)2O + RNH2? RCONH2 + RCOOH
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (B)
Greater will be the basic character, greater will be its reactivity towards dilute hydrochloric acid. As, (B), secondary amine, it will be the most basic among all and hence the most reactive amine towards acid.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (C)
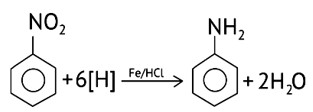
Using active metals like iron in acidic conditions can be efficiently used for the reduction of nitro compounds.
Under the acidic conditions, the intermediate compounds that may form are readily reduced to primary amine and pure product of primary amine is obtained.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (C)
In the process of nitration of benzene, firstly H2SO4 dissociates into H+ and HSO4−. The proton produced further reacts with HNO3 to give a positively charged complex that is unstable and dissociates into nitronium ions and water as products. The nitronium ion is an electron-deficient species i.e. electrophile that attacks the electron cloud of the benzene ring.
H2SO4 (conc.) ? H++HSO4−
H++HNO3? H2NO3+
H2NO3+? NO2+ + H2O
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 685k Reviews
- 1800k Answers