Amines
Get insights from 162 questions on Amines, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Amines
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
1- When 3-methylaniline treated with NaNO2 + HCl it gets converted into chlorine complex.
When that complex reacted with HBF4 It gets converted into Barium Fluoride complex. This complex reacts with NaNO2 in presence of copper to give 3-Nitrotoluene.
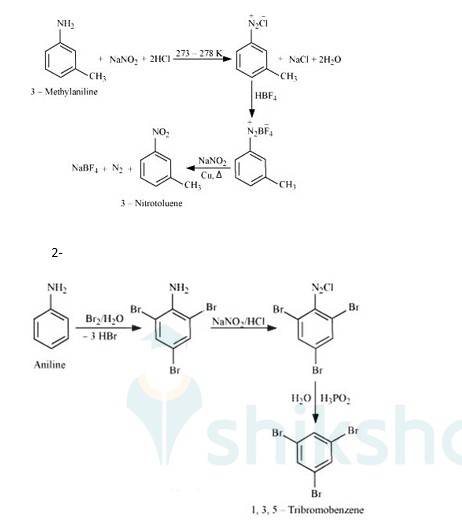
When aniline reacts with Br2 water it gets converted into 2,4,6 tribromobenzamine. When this further reacted with NaNO2/HCl it forms Chloride complex. This complex forms 1,3,5 tribromobenzene after treating with H3PO2 in presence of water.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
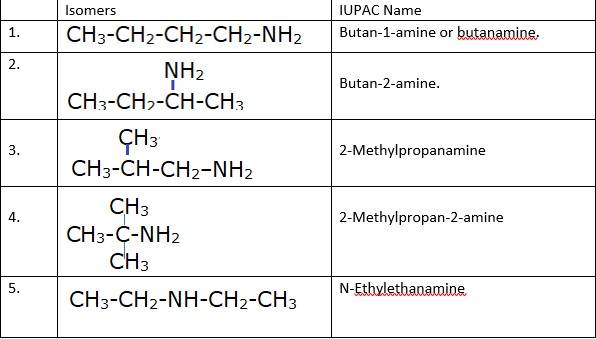
The different isomers of the molecular formula: C3H9N are given in the table. However only 1° amines will liberate nitrogen gas on the treatment with h=the nitrous acid are given as follows:
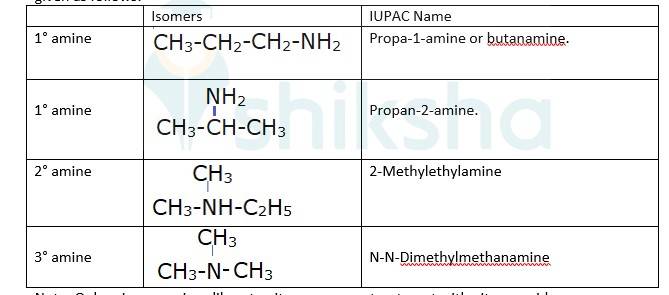
Note: Only primary amines liberate nitrogen gas on treatment with nitrous acid.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
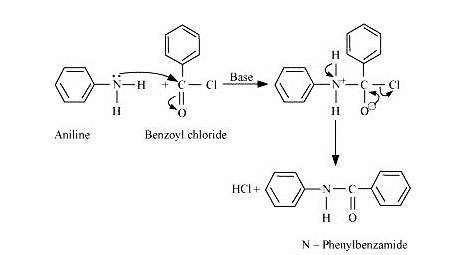
When aniline is treated with benzoyl chloride in the presence of base it gets converted into N-Phenylbenzamide.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
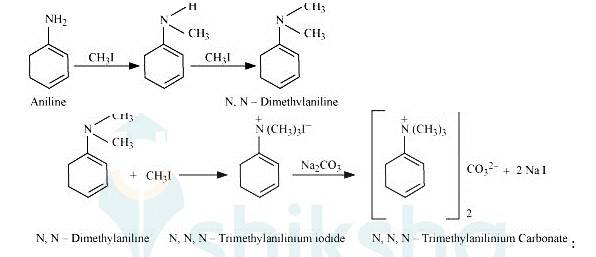
On excessive alkylation with methyl iodide aniline gets converted into N, N-Trimethylanilinium iodide. After reacting it with sodium carbonate it get converted into N, N-Trimethylanilinium carbonate.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) CH3CH2CH2NH2 + HCl → CH3CH2CH2N+H3Cl-
The final product is (N-propyl ammonium chloride.)
(ii) (C2H5)3N + HCl → (C2H5)3N+HCl-
The final product is (Tri ethyl ammonium chloride)
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
1- Alkyl group contribute inductive effect which increases the basic strength of
NH3
Then C6H5NH2 is having –I effect that reduces strength. And C6H5CH2NH2 increases the basic strength but not as much as C2H5 group.
Hence final order will be C6H5NH2<
2- By taking into consideration –R effect and steric hindrance of groups we can arrange them in the order
C6H5NH2< C2H5NH2< (C2H5)3N< (C2H5)2NH.
Because (C2H5)3N has a lot of steric hindrances that reduces the basic strength.
3- In C6H5NH2, N is directly attached to the ring that causes delocalization of electrons of the benzene ring. Whereas in case of C6H5CH2NH2 it is not directly connected to benze
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Benzene into aniline
When Benzene is treated with HNO3/H2SO4 it forms nitrobenzene. When Nitrobenzene reduced with Sn/HCL it forms Aniline because Sn/HCl is a reducing Mixture.
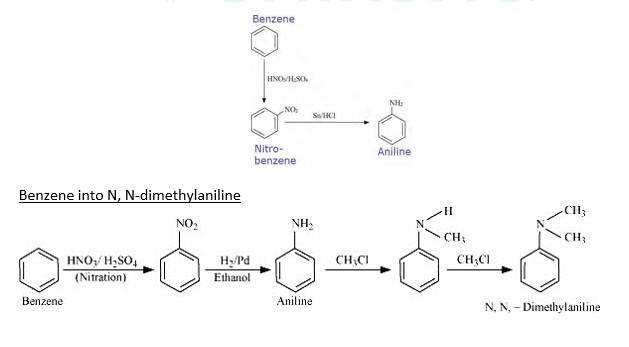
When Benzene is reacted with nitrating mixture it forms nitrobenzene. When it Reduced H2/Pd in ethanol or Sn/HCl, it forms Aniline. When Aniline reacts 2 times with CH3Cl It forms N, N- dimethylaniline.
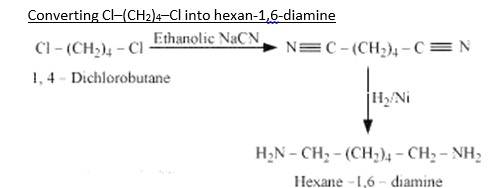
When 1,4-dichlorobutane reacts with NaCN it forms Di cyanide compound, After Hydrogenation it forms the Hexane 1,6-Diamine.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) & (ii) There are total 8 geometrical isomers of the given compound.
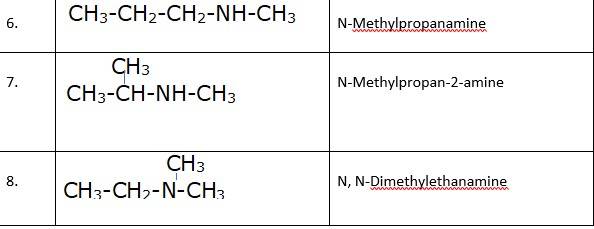
(iii) a) Pairs 1,2,6,7 Exhibit Position isomerism; means the change in position of the substituent.
b) Pairs 1,3 and 1,4 and 2,3 and 2,4 exhibit chain isomerism i.e. in this type of isomerism the different structures can be produced by changing the chain of the
c) Pairs 5,6 and 5,7 exhibit metamerism; e. different group on either side of the central atom.
d) All Primary amines exhibit functional isomers. All secondary amines share functional isomerism and same for The functional isomerism means same functional group.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
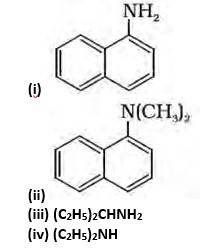
(ii) Tertiary, because the Nitrogen atom is attached to the 3 carbon atoms.
(iii) Primary, because the nitrogen atom is attached to the only 1 carbon atom.
(iv) Secondary, because the nitrogen atom is attached to the only 1 carbon.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 685k Reviews
- 1800k Answers