Chemistry
Get insights from 6.9k questions on Chemistry, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemistry
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
3 months agoContributor-Level 10
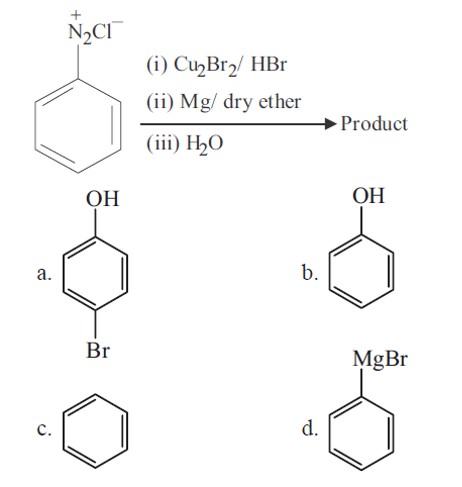
Bromobenzene is formed in first step (Sandmeyer reaction), which further gives phenyl magnesium bromide. Phenyl magnesium bromide further gives benzene with water.
+Mg (Br)OH
New answer posted
3 months agoContributor-Level 10
CH? CONH? - (i) LiAlH? , (ii) H? O? )-> CH? NH?
CH? CONH? - (Br? /KOH)-> CH? NH?
CH? CN - (i) LiAlH? , (ii) H? O? )-> CH? NH?
CH? NC - (i) LiAlH? , (ii) H? O)-> CH? NHCH?
Methyl isocyanide gives a secondary amine, CH? NHCH? upon reduction.
New question posted
3 months agoNew answer posted
3 months agoContributor-Level 10
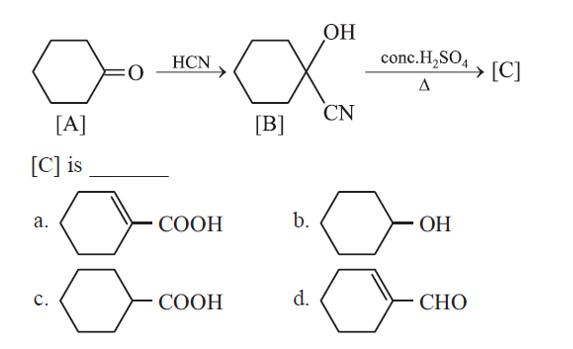
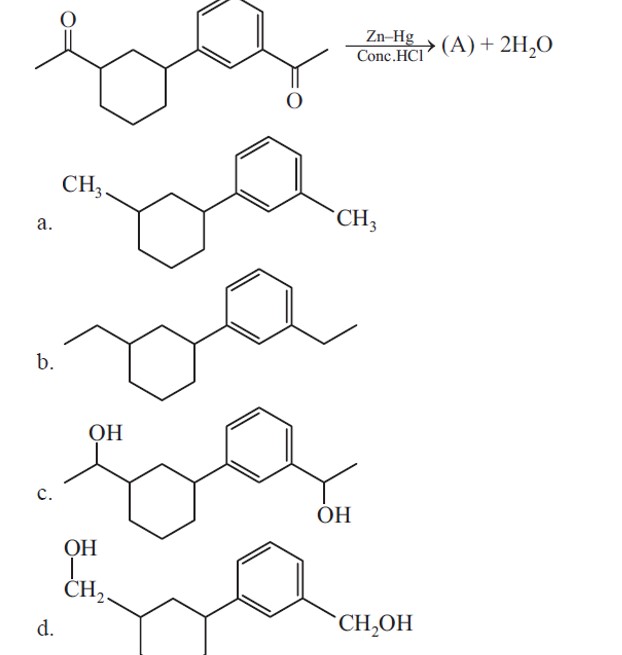
Ketones are reduced into hydrocarbons using Zn – Hg/HCl (Clemmenson reduction).
New answer posted
3 months agoContributor-Level 10
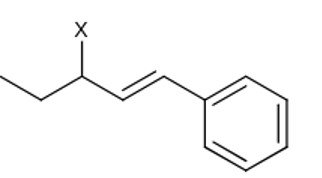
Allylic halide have halogen bonded to sp³ carbon which is adjacent to > C = C <
New answer posted
3 months agoContributor-Level 10
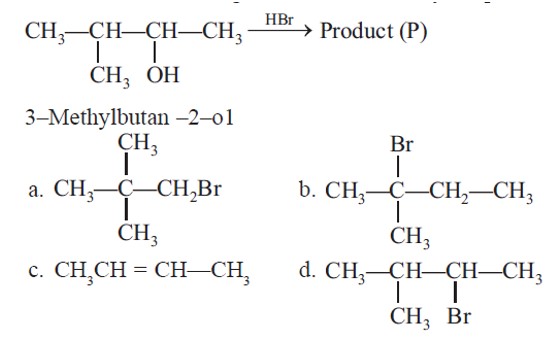
Initially, after protonation followed by loss of water, secondary carbocation is formed, further Hydride shift leads to 3° carbocation.
New answer posted
3 months agoContributor-Level 10
Homoleptic complexes have all ligands identical. Potassium trioxalatoaluminate (III) is K? [Al (C? O? )? ] which has only oxalate ion as ligand. All others have more than one type of ligands.
New answer posted
3 months agoContributor-Level 10
The greater stability of Cu²? (aq) rather than Cu? (aq) is due to the much more negative ΔhydH of Cu²? (aq) than Cu? , which more than compensates for the second ionisation enthalpy of Cu.
New answer posted
3 months agoContributor-Level 10
BF? behaves as Lewis acid due to incomplete octet in valence shell of Boron. Hence it can accept a lone pair of electrons.
New answer posted
3 months agoContributor-Level 10
When the reactants and the catalyst are in different phases, then the catalysis is known as heterogenous catalysis.
1. N? (g) + 3H? (g) - (Fe (s)-> 2NH? (g) (Heterogenous catalysis)
2. 2SO? (g) + O? (g) - (NO (g)-> 2SO? (g) (Homogenous catalysis)
3. C? H? O? (aq) + H? O (l) → C? H? O? (aq) + C? H? O? (aq) (Homogenous catalysis)
4. NO (g) + O? (g) → NO? (g) + O? (g)
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers