Class 12th
Get insights from 12k questions on Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
Let x be the radius of the sphere ad x be radius of the right circular cone.
Let height of cone = y
Then, in ΔOBA,
(y-r)2 + x2 = r2
y2 + r2- 2ry + x2 = r2
x2=2ry - y2
So, the volume V of the cone is
So,
And
At
4x -y- 3y2 = 0
asy> 0.
At y = =
Ø V is maximum when y =
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
We have,
f (x) = cos2x + sin x, x∈ [0, π ].
So, f (x) = 2 cos x ( -sin x) + cos x = cos x (1 - 2 sin x).
At f (x) = 0
cosx (1 - 2 sin x) = 0
cosx = 0 or 1 - 2 sin x = 0
cosx = cos or sin x = = sin = sin
x= , x = and x = [0, π ].
So, f = cos2 + sin = 1.
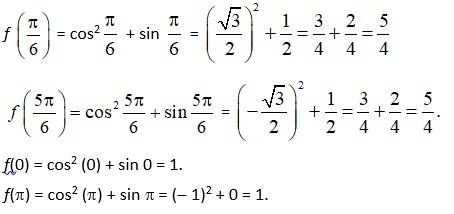
Absolute minimum of f (x) = and absolute minimum of f (x) = 1.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Semi permeable membranes are continuous sheets or films (natural or synthetic) that have a network of submicroscopic holes or pores through which small solvent molecules like water may pass but larger molecules of solute cannot. Osmosis is the process of diffusion via this membrane.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
We have,
f (x) = (x- 2)4 (x + 1)3.
So, f (x) = (x- 2)4. 3 (x + 1)2 + (x + 1)3. 4 (x- 2)3.
= (x- 2)3 [x + 1)2 [3 (x- 2) + 4 (x + 1)]
= (x- 2)3 (x + 1)2 (3x- 6 + 4x + 4)
= (x- 2)3 (x + 1)2 (7x- 2).
At f (x) = 0.
(x- 2)3 (x + 1)2. (7x- 2) = 0.
x = 2, x = -1 or x =
As (x + 1)2> 0, we shave evaluate for the remaining factor.
At x = 2,
When x< 2, f (x) = ( -ve) (+ ve) (+ ve) = ( -ve) < 0.
When x> 2, f (x) = (+ ve) (+ ve) (+ ve) = (+ ve) > 0.
Øf (x) change from ( -ve) to (+ ve) as x increases
So, x = 2 is a point of local minima
At x = -1.
When x< -1, f (x) = ( -ve) (+ ve) ( -ve) =, ve > 0.
When x> -1, f (x) = ( -ve) (+ ve) (+ ve) =∉, ve > 0.
So, f (x) does not change through x -1.
Hence, x = -1 is a point of infixion
At x =
When x< f (x)
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
'Depression in the freezing point of water when a nonvolatile solute is dissolved in it' is the phenomenon involved in removing snow-covered roads in hilly places. As a result, when salt is spread over snow-covered roads, snow melts from the surface due to a drop in the freezing point of water, which aids in road cleaning.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
Let P be the point on hypotenuse of a triangle. ABC, t angle at B.
Which is at distance a& b from the sides of the triangle.
Let < BAC = < MPC = .
Then, in… ΔANP,

At tan Ø =
{ Øall trigonometric fxn are + ve in Ist quadrant}.
So, z is least for tanØ =
As, Sec2Ø = 1 + tan2Ø = 1 + =
secØ = =
And tan2Ø =
cot2Ø =
And cosec2Ø = 1 + cot2Ø = 1 + =
cosecØ =
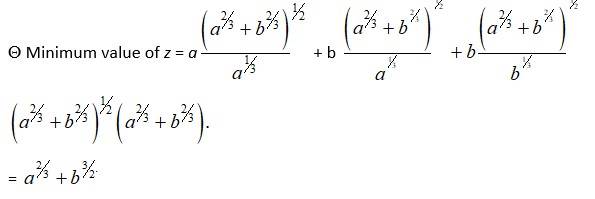
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The fleeing tendencies of water molecules from the liquid level/surface create vapour pressure in any solvent or water. Only water molecules are present at the surface of pure water, but when a nonvolatile solute such as glucose is dissolved in it, a certain number of nonvolatile glucose molecules with no escape tendency are also present at the aqueous solution's surface.
As a result, the quantity of water molecules near the surface decreases, resulting in a lower number of water molecules being able to escape as vapours. When compared to pure water/solvent, this lowers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
Let 'x' metre be the radius of the semi-circular opening mounded on the length '2x' side of rectangle. Then, let 'y' be the breadth of the rectangle.
Then, perimeter of the window = 10m
x + 2x + 2y + = 10.
Let the area of the window be A.
Then, A =
= [-πx2- 4x2 + 20x].
So, [ -2πx - 8x + 20]
And [ -2π - 8] = -π -4 = -( π+ 4)
At
[ -2πx - 8x + 20] = 0
2x + 8x = 20
x = =
At x = = -( π+ 4) < 0
Øx = is a point of minima.
And y =
Ø Dimensions of the window are
length = 2x =
breadth = y
radius = y =
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) (i) According to Henry's law, a gas's pressure is proportional to its solubility. The air pressure gradually falls as scuba divers approach the surface. This lower pressure causes the dissolved gases in the blood to be released, resulting in the development of nitrogen bubbles in the blood. This causes capillaries to constrict, resulting in bends, a painful and life-threatening medical condition.
(ii) The partial pressure of oxygen at high altitude is lower than at ground level. People living at high altitudes have reduced oxygen concentrations in their
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
Let r and s be the radius of the circle and length of side of square.
Then, sum of perimeter of circle and square = k
2πr +4s = k
s =
The area A be the total areas of the circle and square.
Then, A = πr2 + s2
So,
And
At
At
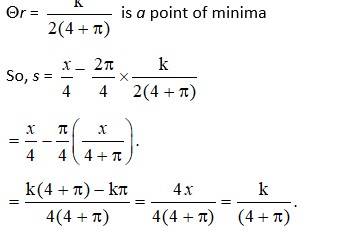
s =
s = 2r.
Hence, proved.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 684k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
