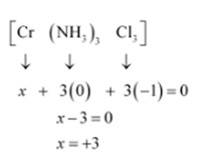Coordination Compounds
Get insights from 147 questions on Coordination Compounds, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Coordination Compounds
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Two types of ligand : chloride ion is unidentate ligand and -en (ethylenediamine) is bidentate ligand with two sites of attachment. The complexes in which two symmetrical bidentate chelating ligands AA and two monodentate ligands a, are coordinated to central metal atom M, exhibit the phenomenon of optical isomerism and can be resolved into their optical isomers.
An example of this type of complexes is given as shows both geometrical as well as optical isomerism. Its cis form is unsymmetrical, while the trans form is symmetrical because it contains a plane of symmetry. Hence, optical isomerism is shown by cis form.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Optical isomers are the one which rotate the plane polarized light by a certain angle when passed through them and are mirror images of each other, also called as stereoisomer.
(i) C2O4 2- is a bidentate ligand so it can attach to central atom at two sites, forming a chelate ring. In the complexes of this type, three symmetrical bidentate chelating ligands AA are coordinated to the central metal atom M. Such complexes do not possess any element of symmetry and are optically active. Moreover, these complexes can be resolved into optical
(ii) In this complex Cl is an unidentate ligand with one site of attachment whereas -en (ethyle
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) No geometrical isomer is possible for [Cr (C2O4)3]3– because the ligand C2O 2- is bidentate ligand (which have two sites of attachment to the central atom) and also in the coordination sphere it is the only ligand bond to it.
(ii) In the coordination sphere of [Co (NH3)3Cl3] there are two types of ligands present i.e NH3 and Cl- . Coordination number is There are 2 isomers possible for the complex:
Facial: In this isomer one type of ligand say NH3 forms the face of the square bipyramidal (triangular) structure.
Meridional: In this isomer one type of ligand are along the central axis of the pyramidal structure.
New answer posted
8 months ago9.18 List various types of isomerism possible for coordination compounds, giving an example of each.
Contributor-Level 10
Isomers are the compounds which have same chemical formula but different arrangement of atoms in space. There are principle two types of isomerism:
(i) Stereo isomerism
(ii) Geometrical isomerism
(iii) Optical isomerism
(iv) Structural isomerism
(v) Ionisation isomerism
(vi) Linkage isomerism
(vii) Coordination isomerism
(viii) Solvate isomerism
Geometrical isomerism comes into existence by the different spatial arrangement of groups around the central metal atom. Similar groups may either be arranged on the same side or on opposite sides of the central metal atom. This gives rise to two types of isomers called cis and trans isomers. Wh
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) Starting with cation, the complex ion contains six ammonia molecules with cobalt in + 3 oxidation The name of compound: [Co (NH3)6]Cl3 is hexaamminecobalt (III) chloride.
(ii) The complex ion is cation, so there are 2 ammonia molecules, one chloride ion and methyammine molecule qith platinum in + 2 state. Going in alphabetical order, the name of compound: [Pt (NH3)2Cl (NH2CH3)]Cl is diamminechloridomethylammineplatinum (II)
(iii) It is a complex cation with six water molecules and titanium atom in + 3 state. The name of the compound: [Ti (H2O)6]3+ is hexaaquatitanium (III) ion
(iv) The complex ion is cation with
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) Tetrahydroxidozincate (II) = [Zn (OH)4]-2
Tetrahydroxi means 4 hydroxide ions with zinc in + 2 oxidation state. Hydroxide ions have a negative charge of -1, so balancing the overall charge of the coordination compound to be zero we get the formula as : [Zn (OH)4]-2
(ii) Potassium tetrachloridopalladate (II) = K3 [PdCl4].
Tetrachlorido means 3 Chloride ions each having a negative charge. Platinum is in + 2 state. Balance overall charge as 0, no. Of potassium ions are 3. Formula: K3 [PdCl4].
(iii) Diamminedichloridoplatinum (II) = [Pt (NH3)Cl2]2+
Diammine means 2 ammonia molecules, dichlorido means 2 chloride ions, platinum
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) Let Oxidation of Co be x and charge on the complex is given as + 2
H2O has Oxidation Number: 0
CN has Oxidation Number: -1
en has Oxidation Number :0
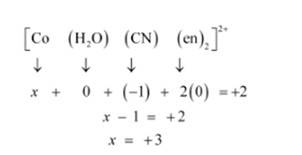
(ii) Let Oxidation number of Co be x and charge on the complex is given as + 1
Br has Oxidation number: 1
en has oxidation number : 0
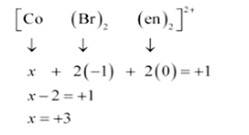
(iii) Let Oxidation number of Pt be x and charge on the complex is given as -2
Cl has oxidation number : -1
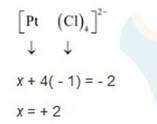
(iv) This complex can also be seen as [Fe (CN)6]3-
Let Oxidation number of Fe be x and charge given on the complex is given as -3
CN has oxidation number : -1
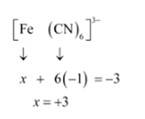
(v) Let Oxidation number of Cr be x and charge given on the complex is given
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Ligands are the neutral or negatively charged entities surrounding the central metal atom of the coordination complex which possesses at least one unshared pair of electrons.
Based on the number of donor sites of these ligands, Ligands are classified as:
Unidentate ligands: These Ligands which have only one donor site are called unidentate ligands.
Example: F-, Cl – etc.
Didentate ligands: These Ligands which have only two donor site are called didentate ligands.
Example: Ethane-1,2-diamine, Oxalate ion etc.
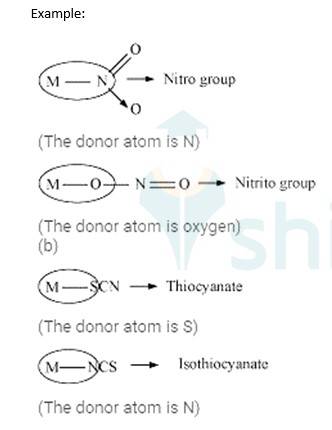
Ambidentate ligands: These ligands which can attach them with the central metal atom by two different atoms are called as ambidentate
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(1) Coordination Entity: Coordination entity is a charged entity having positive or negative charge in which the central atom is surrounded by molecules which may be neutral/negatively charged called Ligands
Examples:
i. Cationic Complexes: [Cu (H2O)6]2+, [Al (H2O)6]3+
ii. Anionic Complexes: [CuCl4]2-, [Al (H2O)2 (OH)4]-
iii. Neutral Complexes: [Co (NH3)4 Cl2], [Ni (CO)4]
(2) Ligands: Ligands are the neutral or negatively charged entities surrounding the central metal atom of the coordination complex which possesses at least one unshared pair of electrons
Example: F-, Cl-, Br-, I-, H20, and NH3
(3) Coordination Number: Coordina
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The reaction is given below:
FeSO4 + (NH4)2SO4 + 6H2O → FeSO4 (NH4)2SO4.6H2O (Mohr Salt)
FeSO4, when reacted with (NH4)SO4, does not form any complex whereas they form a double salt, FeSO4. (NH4)2SO4.6H2O - (Mohr salt) which dissociates into ions in the solution. So, it gives the test of Fe2+ ions.
CuSO4 + 4NH3 + 5H2O→ [Cu (NH3)4SO4].5H2O
CuSO4 solution when mixed with aqueous ammonia in 1: 4 molar ratio forms a complex with formula [Cu (NH3)]SO4 in which the complex ion, [Cu (NH3)4]2+ does not dissociate to give Cu2+ ions. Therefore, it does not give the tests of the Cu2+ ion.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers