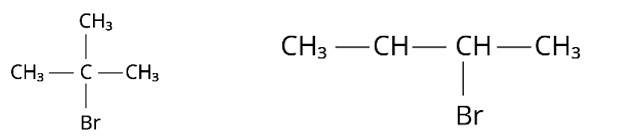Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Get insights from 279 questions on Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
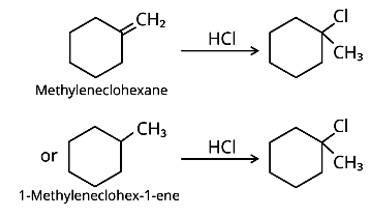
Methylenecyclohexane and 1-methylcyclohex-1-ene are two chemicals that can produce 1-chloro-1-methylcyclohexane.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The alkane C5H12 is a hydrocarbon with a molecular mass of 72gmol?1. On photo-chlorination, the tert-isomer of pentane yields a single monochloro derivative and two dichloro derivatives. The following is the structure of the alkane and its chloride derivatives.
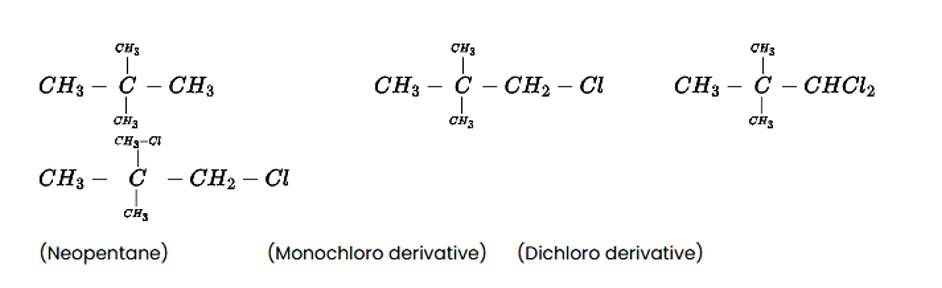
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The IUPAC name for this compound is 1-Bromo-2,2-dimethylpropane
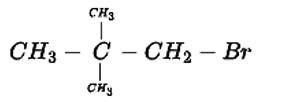
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
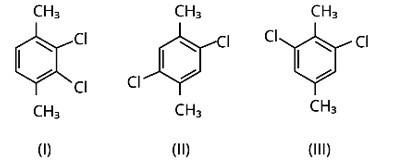
Because both methyl groups and chlorine atoms are symmetrically positioned at para-positions in compound (II), these molecules fit better in the crystal lattice than other isomers, and hence have the greatest melting point.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The addition reaction of the alkene produces two products, as indicated below.
CH3−CH2−CH=CH−CH3 + HCl→ A + B
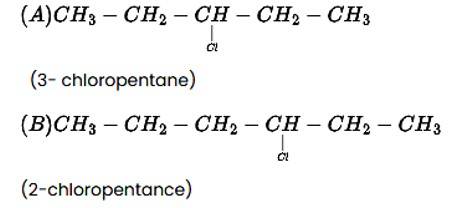
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
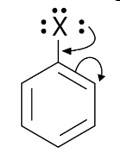
When an arene is treated with Cl2 in the presence of FeCl3, the electrophilic addition reaction chlorinates the arene to produce aryl chloride. As a result, the chemical provided is C6H5-CH3, often known as toluene. o-chlorotoluene and p-chlorotoluene are the results of electrophilic substitution chlorination.
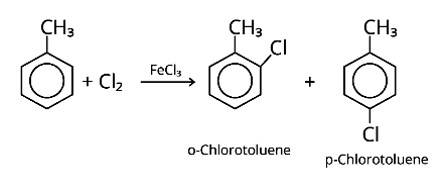
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) Because the rate of reaction of compound 'A' with aqueous KOH is solely dependent on the concentration of 'A, ' the reaction mechanism is SN1and 'A' is 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane (tertiary bromide).
'B', on the other hand, is an isomer of 'A' and is optically active. As a result, 'B' has to be 2-Bromobutane. Because the rate of reaction of 'B' with aqueous KOH is determined by its concentration, the reaction mechanism is SN2.
(ii) Compound 'B' will have an inverted conformation as a result of the SN2 reaction, resulting in an inverted product.
Structure 'A' i
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) 1-Bromobut-2-ene: It is a primary halide.
(ii) 4-Bromopent-2-ene: Here Bromine is attached to the secondary carbon. Hence, it is a secondary halide.
(iii) 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane: Here Bromine is attached to the tertiary carbon. Hence, it is a tertiary halide.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
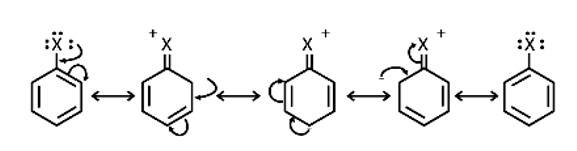
Because electron density is higher at ortho and para locations, the functional groups contained in these compounds are ortho-para directed.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Because energy is required to overcome the attractions between the haloalkane molecules as well as to break the hydrogen bonds between water molecules in order to dissolve a haloalkane in water, haloalkanes are only weakly soluble in water. New attractions between the haloalkane and the water molecules, on the other hand, release less energy since they are weaker than the water's initial hydrogen bonds.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers