Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Get insights from 279 questions on Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
This addition reaction is carried out in accordance with Markovnikoff's rule, which states that in a double bond, the hydrogen from the hydrogen halide is added to the carbon atom with the most hydrogen atoms attached to it, while the halogen atom is attached to the carbon atom with the fewest hydrogens attached to it. The main product in the combination will be the molecule that follows this guideline. As a result, the molecule (B) will be the reaction's main product.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) Br2 gas is produced when NaBr and H2SO4 are combined. Because of the stable molecule created as a result of resonance stabilisation, molecule
(b) Will not react with Br2 gas.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
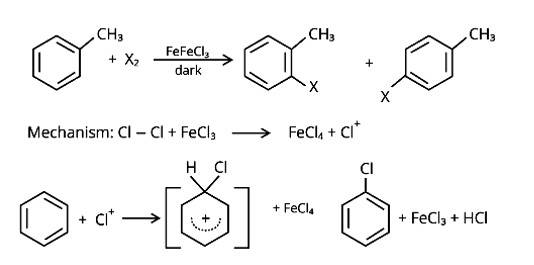
In the presence of Lewis acid catalysts (iron or iron chloride), aryl bromides and chlorides can be made by electrophilic replacement of arenas with bromine and chlorine, respectively.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
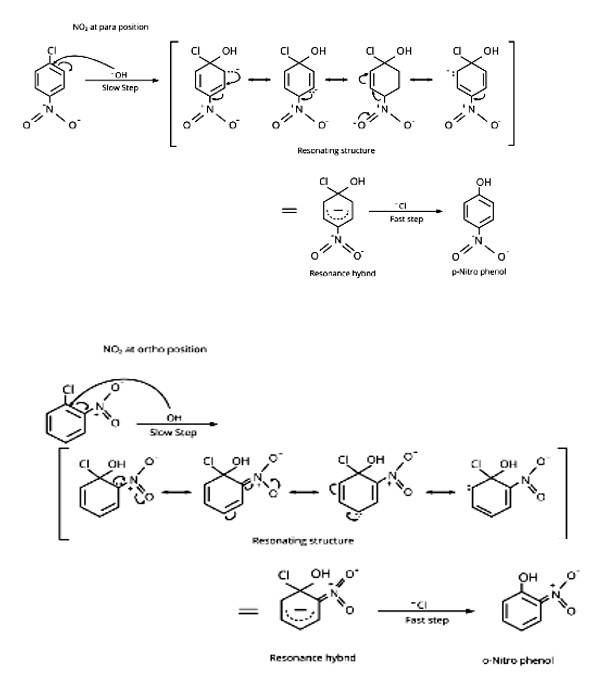
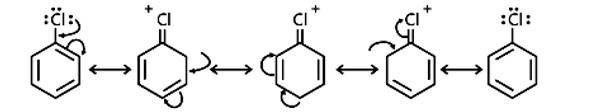
The resonance stabilisation of the aryl ring is the main reason haloarenes are less reactive than haloalkanes and haloalkenes. The electron pairs on the halogen atom, for example, are conjugated with the ring's -electrons in C6H5 - Cl. The C-Cl link takes on a partial double bond character as a result of resonance, making it less reactive to nucleophilic substitution than haloalkanes and haloalkanes.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Triiodomethane is the chemical name for iodoform. Because of its ability to liberate free iodine, it has antibacterial properties.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In an SN1 reaction with the OH ion, C6H5−CH2−Cl will react quicker. This is owing to the carbocation's stability in the compound. The C6H5 group is already stable owing to resonance, and the CH2 attached will receive that stability after the cleavage in the first stage of the SN1 reaction, resulting in a stable C6H5CH2+ carbocation. CH3-CH2-Cl does not have the same sort of carbocation.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The melting point of p-dibromobenzene is greater because p-symmetry of bromobenzene allows it to fit better in a crystal lattice. As a result, breaking the bonds between the molecules requires a greater temperature, resulting in a higher melting point.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Because HI is produced throughout the process, iodination reactions are reversible in nature. To keep the reaction moving ahead, we must remove the HI by an oxidation process using oxidising agents such as HIO4.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Because of the following reasons, aryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution processes than alkyl halides:
(i) The halogen atom's electrons are conjugated to the aryl ring's -electrons, giving the C-X bond a partial double bond character. The whole molecule is then resonance stabilised, allowing for the formation of the following configurations. C-X bond cleavage in haloarenes is more difficult than in haloalkanes due to this bond creation.
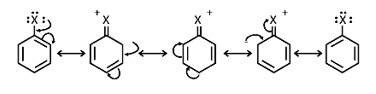
ii) The carbon linked to the halogen in haloalkanes is sp3 hybridised, whereas the carbon coupled to the halog
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Multiple halogen groups are present in these carbon compounds, which have a wide range of applications in industry. Polyhalogen compounds are what they're called. The following are the different chemicals and their impact on life:
1. Dichloromethane, commonly known as methylene chloride, is a solvent that is used as a paint remover, an aerosol propellant, a process solvent in drug manufacturing, and a metal cleaning and finishing solvent. The central nervous system has been documented to be harmed by dichloromethane. Low amounts of this chemical might cause mild hearing
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers