Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Get insights from 279 questions on Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Nucleophilic substitution and elimination (β-elimination) reactions are both possible with alkyl halides.
Although, with the appropriate reaction conditions and reagent selection, a specific product can be produced. In most cases, the elimination reaction is best suited to strong and bigger bases, as well as high temperatures. The substitution reaction, on the other hand, is best for weaker and smaller bases at lower temperatures.
CH3CH2Br+alc.KOH![]() KCH2=CH2 + HBr
KCH2=CH2 + HBr
CH3CH2Br + aqKOH→CH3CH2OH + KBr
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The IUPAC names for DDT and benzene hexachloride are 2, 2-bis (4-chlorophenyl)-1, 1-trichloroethane and 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6-hexachlorocyclohexane, respectively.
They are poisonous and non-bio digestible at the same time. They are fat soluble, and their concentration in the food chain continues to rise. As a result, they are prohibited in India and other nations.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Diphenyls, such as p, p-dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT), which have been employed as organic pesticides, are a possible hazard to the environment since it was shown to have significant toxicity towards fish during its early years of widespread use, and many insects acquired resistance to it. The issue was exacerbated by DDT's chemical persistence and fat solubility. In terms of chemistry, DDT is not metabolised or solubilized well by mammals. The fatty tissues are where it is deposited and kept. DDT builds up within the animal over time if it is consumed at a con
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
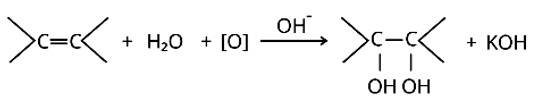
The bromine water test and Bayer's test are two methods for detecting the presence of an unsaturated double bond in an organic molecule.
Bromine is added to the carbon atoms across the double bond in the bromine water test when the molecule is introduced to bromine water. Bromine water changes colour from orange to brown to colourless at the end of the process.
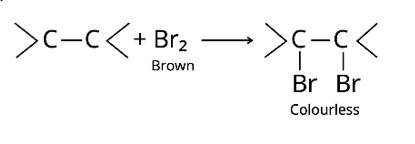
The alkaline KMnO4 is employed in Bayer's test to detect unsaturated carbon with a double bond. The chemical produces [O], which hydrolyzes the carbons across the double bond, resulting in a purple-to-colorless s
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The SN1 mechanism advances through the production of carbocation. The breakage of the C-halogen bond occurs during this phase. The solution of the halide ions is done with the protons of the protic solvent as a result. In this approach, polar solvents aid in the ionisation process by solvating the ions and stabilising them.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
RMgX+H2O→RH+Mg (OH)X
Because the Grignard reagents are very reactive in nature, even residues of moisture must be avoided. Even minute amounts of water can cause these reagents to generate hydrocarbons.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In nature, allyl chloride becomes very reactive due to the production of carbocation, which is extremely stable due to resonance. Due to carbocation, there will be no such stability in the case of n-propyl chloride.
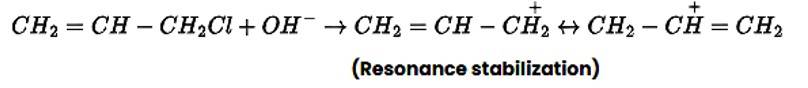
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
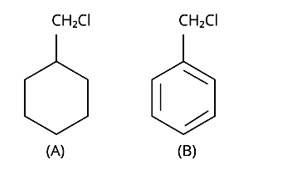
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
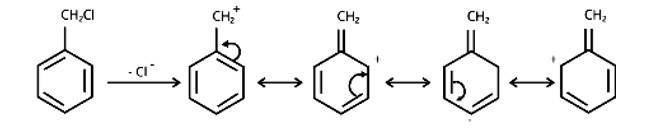
Due to the resonance stabilisation of the benzyl ring, compound (B) would conduct the SN1 reaction faster than compound (A). The carbocation C6H5CH2Cl+ is very stable when the -Cl from the ring is cleaved, and it is driven to carry out the SN1 reaction.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Phenol will not react with HCl in the presence of ZnCl2. This is owing to the presence of partial double bond properties between the benzene ring and O, which will result in resonance between the benzene ring and the OH - group. As a result, no aryl halide will be made.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
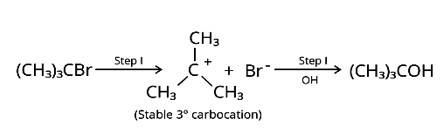
Nucleophilic substitutions occur when haloalkanes react with aqueous KOH. The tertiary halide 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane will react with aq. KOH the easiest of the compounds because the initial step involves cleavage of the alkyl and halide groups, resulting in the production of the extremely stable carbocation.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers