Kinetic Theory
Get insights from 102 questions on Kinetic Theory, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Kinetic Theory
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.9 Temperature of the helium atom, = – 20 °C = 253 K and temperature of argon atom be =
Atomic mass of helium, = 4.0 u
Atomic mass of Argon, = 39.9 u
Let be the rms speed of Argon and be the rms speed of Helium
From the relation of we get
rms speed of Argon,
rms speed of Helium,
Since both the speeds are equal, we get
= or = or = = = 2523.675 K = 2.523 K
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.8 (a) According to Avogadro's law, the three vessels will contain an equal number of the respective molecules. This number is equal to Avogadro's number, N = 6.023
(b) The root mean square speed ( of a gas of mass m and temperature T is given by the relation . Where k is Boltzmann constant. For the given gases, k and T are constants. Hence depends only on the mass of the atoms ![]()
Therefore, the root mean square speed of the molecules in the three cases is not the same. Among Neon, Chlorine and Uranium hexafluoride, the mass of the neon is the smallest, so Neon will have the highest root mean square sp
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.7 (i) At room temperature, T = 27 = 300 K
is Boltzmann constant = 1.38
Average thermal energy = = = 6.21 J
Hence, the average thermal energy of a helium atom at room temperature is 6.21 J
(ii) On the surface of the Sun, T = 6000 K
Hence average thermal energy = = = 1.242 J
Hence, the average thermal energy of a helium atom on the surface of the Sun is 1.242 J
(iii) Inside the core of a star, T = K
Hence average thermal energy = = = 2.07 J
Hence, the average thermal energy of a helium atom
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.6 Volume of the room, V = 25.0
Temperature of the room, T = 27 = 300 K
Pressure of the room, P = 1 atm = 1 1.013 Pa
The ideal gas equation relating to pressure (P), volume (V) and absolute temperature (T) can be written as
PV = NT, where is Boltzmann constant = 1.38
N is the number of air molecules in the room.
N = = = 6.117
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.5 Volume of the air bubble = 1.0 = 1
Height achieved by bubble, d = 40 m
Temperature at a depth of 40 m, = 12 = 285 K
Temperature at the surface of the lake, = 35 = 308 K
The pressure at the surface of the lake, = 1 atm = 1.013 Pa
The pressure at 40m depth: = 1 atm + d
Where is the density of water = kg/
G = acceleration due to gravity = 9.8 m/
Hence = 1.013 = 493300 Pa
From the relation = , where is the volume of bubble when it
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.4 Volume of oxygen, = 30 litres = 30
Gauge pressure, = 15 atm = 15 Pa
Temperature, = 27 = 300 K
Universal gas constant, R = 8.314 J/mole/K
Let the initial number of moles of oxygen gas cylinder be
From the gas equation, we get
= = 18.276
But = , where = initial mass of oxygen
M = Molecular mass of oxygen = 32 g
= M = 18.276 g
After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, the pressure and temperature reduces, but volume remained unchanged.
Hence, Volume, = 30 litres = 30
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
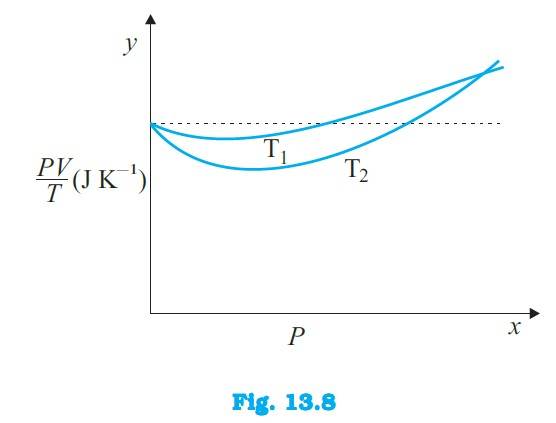
13.3 (a) The dotted plot in the graph signifies the ideal behaviour of the gas, i.e. = R, (where is the number of moles and R is the universal gas constant) is a constant quantity. It is not dependent on the pressure of the gas. The curve of the gas at temperature is closer to the dotted plot than the curve of the gas at temperature
(b) A real gas approaches the behaviour of an ideal gas when its temperature increases. Therefore > is true for the given plot.
(c) The value of the ratio , where the two curves meet, is R. This is because the ideal gas e
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.2 The ideal gas equation relating to pressure (P), volume (V) and absolute temperature (T) is given by the relation
PV = nRT, where
R is the universal gas constant = 8.314 J /mol/K
N = number of moles = 1 (given)
T = standard temperature = 273 K
P = standard pressure = 1 atm = 1.013 N/
Therefore V = = = 0.02240 = 22.4 litres
Hence the molar volume of a gas at STP is 22.4 litres.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.1 Diameter of the oxygen molecule, d = 3Å
Radius, r = = 1.5 Å = 1.5 cm
Actual volume occupied by 1 mole of oxygen gas at STP = 22.4 lit = 22400
Molecular volume of oxygen gas, V = N,
where N = Avogadro's number = 6.023 molecules/mole
Therefore, V = 6.023 = 8.51
Ratio of the molecular volume to the actual volume of oxygen = = 3.8
New question posted
9 months agoTaking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 687k Reviews
- 1800k Answers