Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Get insights from 2.6k questions on Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
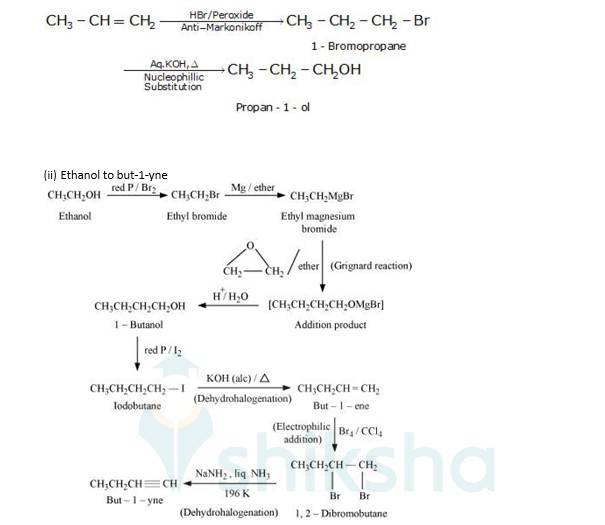
(i) Propene to propan-1-ol
It is an antimarkovnikoff reaction in which under the presence of a peroxide an alkene undergoes substitution, wherein the halo group is attached to that carbon which has least no. Of alkyl groups attached to it.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
7.37
Chemical reactivity of group 15 elements towards hydrogen, oxygen, halogens, and metals are discussed below.
Reactivity towards hydrogen: Group 15 elements react with H to form hydrides of type EH3 where E=N, P, As, Sb or On moving down from NH3 to BiH3, the stability of the hydrides decreases. For example, the P-H bond in PH3 is less stable than the N-H bond in NH3. The strength of the E-H bond gets weaker as the size of the central atom increases.
Stability order of E-H bond (where E is group 15 elements) can be represented as
N-H > P-H > As-H >Sb-H > Bi-H
Reactivity towards oxygen: Group 15 elements react with O to form oxides
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
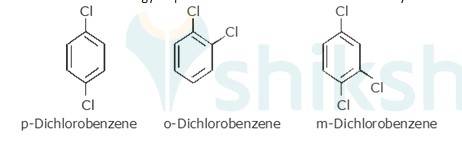
p-Dichlorobenzene is more symmetrical than o-and m-isomers. Because it fits more closely and easily in the crystal lattice than o-and m-isomers. Therefore, more energy is required to break the crystal lattice of p-dichlorobenzene. Therefore, p-dichlorobenzene is symmetrical and has a higher melting point and lower solubility than o-and m-isomers due to strong force of attraction in crystal.
Therefore more energy required to break lattice and will not easily be soluble.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
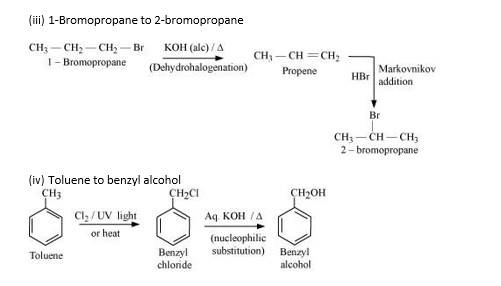
Hydrolysis by KOH results in the formation of the carbocation. Those compounds which leads to the formation of stable carbocation are easily hydrolysed.C6H5CH2Cl leads to formation of 1°- carbocation, while C6H5CHClC6H5 forms 2°-carbocation, which is more stable than 1°-carbocation. Hence C6H5CHClC6H5, is hydrolyzed more easily than C6H5CH2Cl by aqueous KOH.
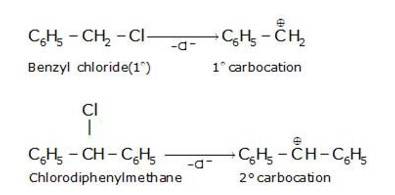
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
The reaction involves the approaching of the nucleophile to the carbon atom to which the leaving group is attached. When the nucleophile is sterically hindered (does not have any free space or very crowded), then the reactivity towards SN2 displacement decreases. Due to the presence of substituents, hindrance to the approaching nucleophile increases in the following order.
- Bromopentane < 2-bromopentane < 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane. The structures are shown below:
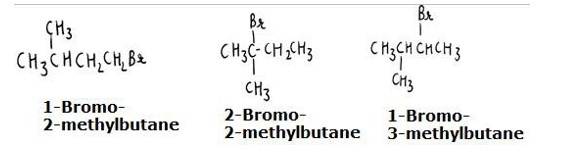
Hence, the increasing order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement is:
- Bromo-2-methylbutane < 2-Bromopentane < 1-Bromopentane
- The stearic hinderance in alkyl halides increases in the order of 1° < 2 < 3, the increasing order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement is given as-
3° < 2 < 1.
The structures are given below:

Hence, the given set of compounds can be arranged in the in
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
7.2
Nitrogen atom can bond with another nitrogen atom by strong p–p overlap resulting in NN. The triple bond in N2 has high bond strength resulting in high bond dissociation energy. Phosphorous do not show this property of p–p overlap. Hence, nitrogen is less reactive than phosphorous.

New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
The given reaction is a nucleophillic reaction:

The given reaction is an SN2 reaction. In this reaction, CN acts as the stronger nucleophile and attacks the carbon atom to which Br is attached in nBuBr.
And, CN- ion is an ambident nucleophile and can attack through both C and N. In this case, it attacks through the C-atom.
The mechanism is shown below:
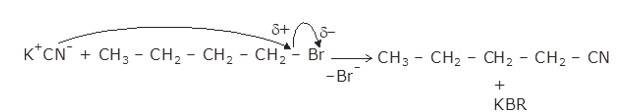
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
7.1
The general characteristics of Group 15 elements are:
Electronic configuration: All Group 15 elements have 5 electrons in their valence The general electronic configuration of these elements is ns2 np3
Oxidation state: Group 15 elements have 5 valence electrons and they require 3 more electrons to complete their However, the gaining of 3 electrons is difficult
Atomic size: Atomic size increases as we move down the group due to increase in the number of
Ionisation enthalpy: Ionisation enthalpy decreases as we move down the group because of increase in atomic
Electronegativity: Electronegativity decreases on moving down the group due to in
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
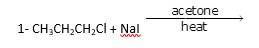
It is a simple substitution reaction with Cl being replaced by iodide ion.
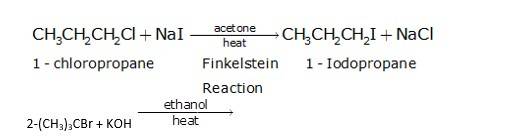
Since ethanol is a alcohol, so in presence of alcoholic KOH, alkyl chloride undergo elimination reaction, which results in the removal of proton and being substituted by a bromide ion.
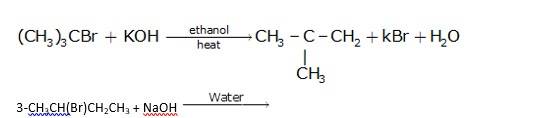
It is also a simple substitution reaction in which under the presence of aqueous NaOH, bromide ion is replaced by hydroxide ion as it is a better leaving group than hydroxide ion.
It is a simple substitution reaction in which a better leaving group leaves and is being substituted by an ion.
CH3CH2Br + KCN - CH3CH2CN + kBr
5-C6H5ONa + C2H5Cl
It is a simple substitution reaction in
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 679k Reviews
- 1800k Answers

