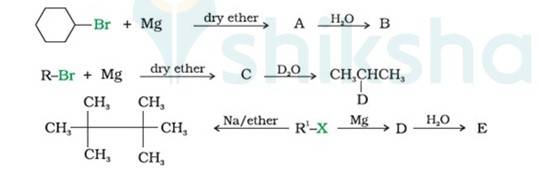Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Get insights from 2.6k questions on Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Double bond equivalent is used to find the level of unsaturations present in an organic molecule.
DBE = C +1-H/2+X/2-N/2
Where C= number of carbon atoms present H=number of hydrogen atoms present N=number of nitrogen atoms present X=number of halogen atoms present Double bond equivalent (DBE) for C4H9Br
= 4+1-9/2+1/2
=0
So none of the isomers has a ring or unsaturation, so the isomers are positions or chain isomers as shown below in the table:

New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
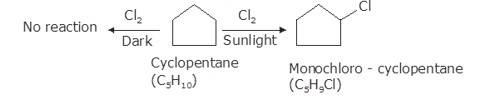
As per the molecular formula , one thing can be confirmed; the hydrogen is either cycloalkane or it is an alkene. However, alkenes readily react with chlorine in even dark because of the double bond. Therefore, it is possible that the hydrocarbon is cycloalkane.
Now, let us consider the reactivity. Cycloalkanes are the saturated hydrocarbons with no double bonds. These do not react with Chlore in dark because such a reaction needs UV light for initiating the process of free radical substitution. Haloalkane and Haloarenes NCERT solutions cover this as well as other questions in further detail.
In bright sunlight, the UV light star
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Dipole moment of a molecule depends on the electronegativity difference between atoms bonded covalently and geometry of the molecule (how far the atoms are from each other). Dipole moment is important to understand the polarity of a molecule.
The three dimensional structures of the three compounds along with the direction of dipole moment in each of their bonds are given below:-
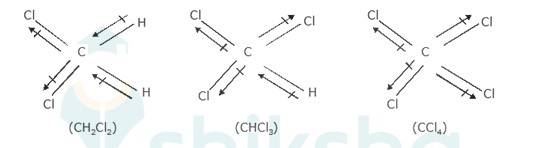
CCl4 being symmetrical has zero dipole moment. In CHCl3, the resultant of the two C-Cl dipole moments is opposed by the resultant of C-H and C-Cl bonds. Since the dipole Moment of latter resultant is expected to be smaller than the former, CHCl3 has a finite dipo
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
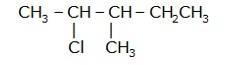
- Write the longest chain first e. in this case it is 'pentane' consisting of 5 carbons.
- Now, place the substituents at their respective place. For eg. Chlorine(Cl) at second carbon and methyl(CH3) at third carbon.
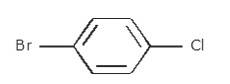
- Write the longest chain first i.e. in this case it is 'benzene' a cyclic structure consisting of 6 carbons
with 3 double bonds.
Now, place the substituent Bromine(Br) at the para position i.e. at the fourth carbon.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
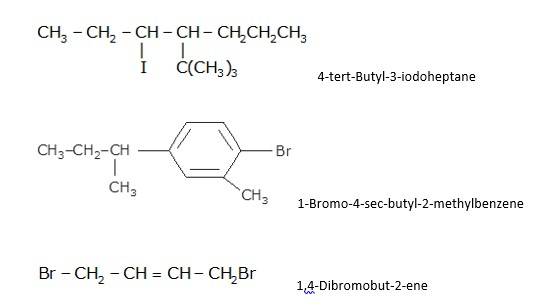
CH3CH (Cl)CH (Br)CH3: 2-Bromo-3-chlorobutane
- Write the name of side substituent according to the alphabetical order. Example: bromo is written before chloro as B comes before
- Always use a hyphen {-} between a number and a Since Br is attached to 2 position and Cl is attached to third position i.e. it is written as 2-Bromo and 3-chloro.
- Lastly, write the name of the longest hydrocarbon chain e. butane of 4 carbons.
CHF2CBrClF :1-bromo-1-chloro-1,2,2-trifluoroethane
- While writing the IUPAC name, write the name of side substituent according to the alphabetical Eg: bromo is written before chloro and fluoro as B comes before C and F.
- Always use a
New question posted
6 months agoNew answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
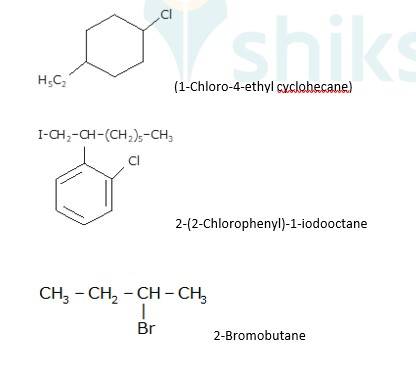
(i) 2-chloro-3-methylbutane, (2? alkyl halide)
Explanation: The Cl atom is attached with two alkyl groups therefore 2? alkyl halide.
(ii) 3-chloro-4-methylhexane (2? alkyl halide)
Explanation: The Cl atom is attached with two alkyl groups therefore 2? alkyl halide.
(iii) 1-iodo-2,2-dimethylbutane (1? alkyl halide)
Explanation: The atom I is attached with one alkyl group therefore 1? alkyl halide.
(iv) 1-bromo-3,3-dimethyl-1-phenylbutane (2? benzylic halide)
Explanation: The atom Br is attached with two alkyl groups with the benzene group therefore 2? benzylic halide.
(v) 2-bromo-3-me
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) Bromocyclohexane is reacting with the metal Mg to give organo-metallic compound/Grignard reagent
i.e. Cyclohexyl Magnesium Bromide (A).
Grignard reagents are highly reactive with hydrocarbons to give alkanes. Cyclohexyl Magnesium Bromide reacts with water to cyclohexane (B) and Mg (OH)Br.
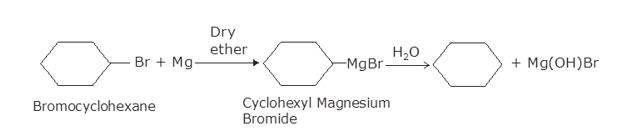
(ii) As the above reaction, haloalkane with metal Mg react to form the Grignard reagent, alkyl magnesium halide, RMgX, and further with hydrocarbon gives alkane.
∴ C is CH3CH (MgBr)CH3, a Grignard Reagent, R is CH3CH (Br)CH3 and D ≅ H
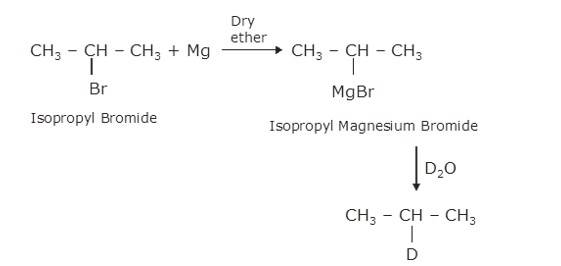
(iii) In the Wurtz Reaction, alkyl halide in the presence of sodium in dry ether gives the double number of
Now,
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
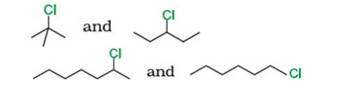

Reason: SN1 occurs in two steps. In the first step, carbocation forms. The rate of reaction in SN1 depends upon the stability of the carbocation, greater the stability faster the reaction. Tertiary (3°) carbocation is more stable than secondary (2°), which is further stable than primary (1°)
By using this
- Tert-Butyl Chloride (3°) reacts faster than 3-Chloropentane (2°)
- 2-Chloro heptane (2°) is more reactive than 1-Chloro hexane (1°)
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
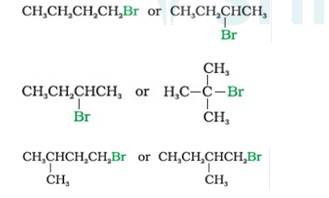
In SN2 Reaction, the product will be formed in a single step with no intermediates. Nucleophile attack will be easier for simple halides than hindered haloalkanes. Therefore,

- Bromobutane (1°)reacts faster than 2-Bromobutane (2°)
- 2-Bromobutane (2°) reacts faster than 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane or tert-Butyl bromide (3°) 1-Bromo-3-methyl butane reacts faster than the 1-Bromo-2-methyl bu
- tane as the former is less hindered with respect to leaving halide than the later which is more hindered comparatively
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 679k Reviews
- 1800k Answers