Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Get insights from 2.6k questions on Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
7.34
It is difficult to study the chemistry of radon because it is a radioactive substance having a half-life (the time period to decompose the substance half to its initial concentration) of only 3.82 days.
Radon belongs to the 18 group elements with chemical formula as Rn. In general, the elements at the bottom o periodic table are radioactive, they are very dangerous to study as they emit harmful radiations.
Also, compounds of radon such as RnF2 have not been isolated, they are still in the phase of discovery. They have only been identified by radiotracer technique and no any further properties have been determined.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) Freon 12:- the chlorofluorocarbon compounds of methane and ethane are collectively known as freons. They are extremely stable, unreactive, non-toxic and non-corrosive. Example of Freon 12 is CCl2F2. It is mainly used in refrigeration and eventually makes its way into the atmosphere where it diffuses unchanged into the stratosphere. In stratosphere, Freon is able to initiate the radical chain reactions that can upset the natural ozone balance.
- DDT: - it stands for p, p'-Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT). It is mainly used as an
- Iodoform: - it was earlier used as an antiseptic but the antiseptic properties are due the liberation o
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Let us explain each question from Haloalkane and Haloarenes chapter one by one. Students who are currently in school and plan to take the CBSE board exam for class 12th soon, need to prepare all these questions. Let us get started.
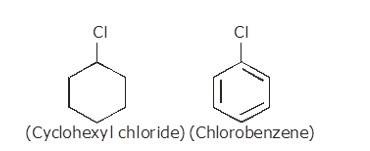
(i) The dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride.
Sp2 hybrid carbon (s-character=33.33%) in chlorobenzene is more electronegative than a sp3-hybrid carbon (s-character=25%) in cyclohexylchloride, due to greater s-character. Thus, Carbon atom of chlorobenzene has less tendency to release electrons to Cl than carbon atom of cyclohexylchloride.
Chlorine atom in chlorobenzene is atta
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
7.33
XeF6 + H2O XeO2F2 + HF
Balanced equation: XeF6 + 2H2O XeO2F2 +4HF. The steps for balancing the reaction are as follows:
1. The main element is First, check if the atoms of Xe on both sides are balanced. YES, they are.
2. Then take another element i.e. F. It is not balanced on the right side, there are 3 atoms of F missing. So, to balance it multiply HF by 4.
3. Now check the other secondary atoms which are oxygen and hydrogen. Oxygen is not balanced on the left side as there are 2 O atoms so multiply H2O by
4. Now check for the hydrogen They are balanced on both sides.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
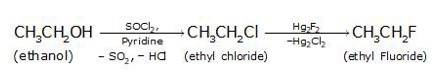
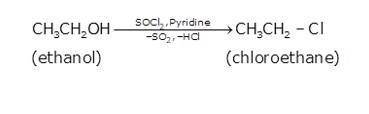
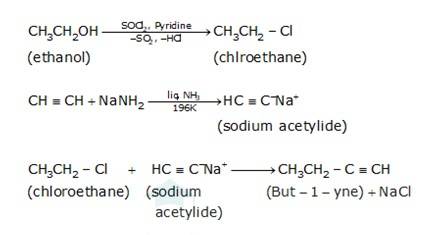
(i) Since the conversion of ethanol to but-1-yne involves the addition the two extra carbons that is why the conversion is carried out in 3 steps.
- In the first step ethanol is treated with thionyl chloride (SOCl2) in the presence of pyridine to give chloroethane
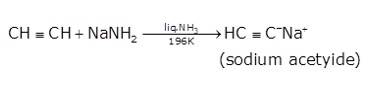
- In the second step the acetylene is treated with sodamide(NaNH2) in the presence of liquid ammonia to give sodium acetylide
- The last step involves the reaction between chloroethane and sodium acetylide to give the final product as the But-1-yne and NaCl as the by-product.
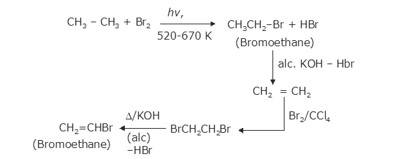
- The bromination of ethane (Br2 in the presence of light at 520-670K) gives bromoethane which on further treatme
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Carbon due to its chemical property of catenation, tetravalency and the ability to form stable covalent bonds form hydrocarbon and halo-alkanes easily.
The process of removal of hydrogen and halogen from adjacent carbon atoms of haloalkens is called dehydrohalogenation. NaOEt ( Sodium ethoxide) used in Dehydrohalogenation. It is a strong base and helps remove a β-hydrogen from the haloalkane.
The chemical reaction for
Reaction:
R–CH2 –CHX–R′+NaOEt ethanol > R–CH=CHR'+NaX+EtOH
(i) 1-Bromo-1-methylcyclohexane:
Br
|
CH3–C1–cyclohexane&
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
7.32
Helium mixed with oxygen under pressure is given to sea divers for respiration because pure oxygen can be toxic at a great concentration at the depth. Therefore oxygen can be mixed with helium to reduce oxygen concentration while eliminating nitrogen.
The main reason for adding helium to the breathing mix is to reduce the proportion of nitrogen and oxygen below those of air, to allow the gas mix to be breathed safely on deep dives.
A low proportion of nitrogen is required to reduce nitrogen narcosis and other physiological effects of gas at depth.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) Since I- ion is a better leaving group than Br- ion, therefore, CH3I reacts faster CH3Br in SN2 reaction with OH- ion.
Better the leaving group, faster is the SN2 reaction.
(ii) On steric grounds, 1? alkyl halides are more reactive than tert-alkyl halides in SN2 reactions. Therefore, CH3Cl will react at a faster rate than (CH3)3CCl in a SN2 reaction with OH- ion. (Bulkier the group, slower is the SN2 )
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Ambident Nucleophiles are those nucleophilies which can attack through different sites. For example:-cyanide ions are a resonance hybrid of the following two structures:

It can attack through carbon to form cyanide and through N to form is O cyanide. Example: NO2, NO3 - etc.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
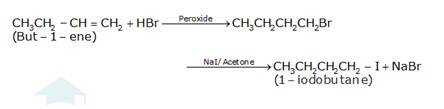
(a) 1-butanol is treated with KI in the presence of H3PO4 where the OH is being replaced by the iodine and gives H2O and KH2PO4 as the by-product with 1-iodobutane as the final
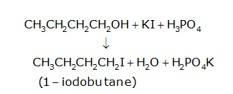
(b) The conversion of 1-chlorobutane to 1-iodobutane simply takes place by treating the reactant with KI in the presence of acetone. The iodine from KI normally replaces the chlorine from the reactant and gives 1-iodobutane as the final product with KCl as the by product.
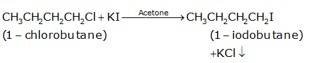
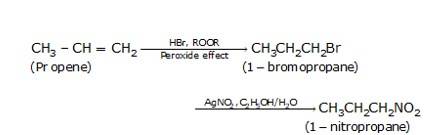
(c) The conversion of but-1-ene to 1-iodobutane takes place according to anti-markovnikoff (positive charged ion H+ goes to the carbon which has less number of hydrogens and negative part Br-
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 679k Reviews
- 1800k Answers