Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Get insights from 2.6k questions on Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Given, PAo = 450 mm Hg
PBo = 700 mm Hg
ptotal = 600 mm of Hg
By using Rault's law,
ptotal = PA + PB
ptotal = PAoxA + PBoxB
ptotal = PAoxA + PBo ( 1 - xA )
ptotal = (PAo- PBo)xA + PBo
600 = (450 - 700) xA + 700
-100 = -250 xA
xA = 0.4
∴ xB = 1 - xA
xB = 1 – 0.4
xB = 0.6
Now,
PA = PAoxA
PA = 450 * 0.4
PA = 180 mm of Hg and
PB = PBox
PB = 700 * 0.6
PB = 420 mm of Hg
Composition in vapour phase is calculated by
Mole fraction of liquid,
A =PA / PA + PB
= 180/180+420
= 0.30
Mole fraction of liquid,
B =PB / PA + PB
= 420 / 180+420
= 0.70
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
16.31
If calcium salts are present in water, then it is recommended to use synthetic detergent because soap will precipitate to give white scums and it will not clean the clothes.
On the other hand, if we use synthetic detergents, it will be dissolved in hard water also and provide effective cleaning of dirty clothes.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
According to Henry's law, "At a constant temperature, the amount of a given gas that dissolves in a given type and volume of liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of that gas in equilibrium with that liquid."
Stated as,
p = KHx
Where,
P = partial pressure of the solute above the solution
KH = Henry's constant
x = concentration of the solute in the solution
Given,
KH = 1.67x108 Pa
PCO2 2.5 atm = 2.5 * 1.01325 * 105Pa
According to Henry's law,
p = KHx
x = P/KH
x = 2.5 X 1.01325 X 105 / 1.67 X 108
x = 0.00152
In 500 ml of soda water there is 500 ml of water (neglecting soda)
Mole of water = 500/18
=
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
16.30 Soap molecules form micelles around an oil droplet [dirt] in such way that the hydrophobic parts of the stearate ions attach themselves to the oil droplet and the hydrophilic parts projects outside the oil droplet. Due to the polar nature of the hydrophilic parts, the stearate ions [along with the dirt] are pulled into the water, thereby removing the dirt from the cloth.
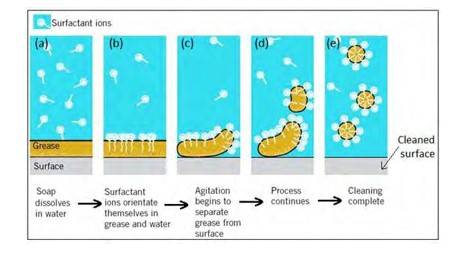
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
According to Henry's law,"At a constant temperature, the amount of a given gas that dissolves in a given type and volume of liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of that gas in equilibrium with that liquid."
Stated as,
p = KHx
Where, P = partial pressure of the solute above the solution
KH = Henry's constant
x = concentration of the solute in the solution
Given,
Solubility of H2S in water at STP is 0.195 m
We know,
At STP pressure p = 0.987 bar
0.195 mol of H2S is dissolved in 1000g of water
Moles of water = 1000/18
= 55.56 g/mol
∴ the mole fraction of H2S = Moles of H2S / Moles of H2S + Moles of water
&
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
16.29
Soaps can be very easily used for checking the hardness of water as soap lathers with soft water and with hard water, soap is precipitated.
On the other hand, synthetic detergents are soluble in hard water and soft water. Hence it cannot be used for checking the hardness of water.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) Molality, also called molal concentration, is a measure of the concentration of a solute in a solution in terms of amount of substance in a specified amount of mass of the solvent. Molar mass of KI = 39 + 127 = 166 g/mol.
20% aqueous solution of KI means 200 g of KI is present in 1000 g of solution. Therefore,
Molality = Moles of KI / Mass of Water in kg
= (200/166) / (0.8) = 1.506 m
(b) Molarity is the concentration of a solution expressed as the number of moles of
solute per litre of solution.
Given,
Density of the solution = 1.202 g/mL
Volume of 100 g solution = mass/ density
= 100/1.202
= 83.1
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
16.28
The commonly used soaps are the sodium and potassium salts of higher fatty acids. They are soluble in water and give good lather to it. On the other hand, calcium and magnesium salts of higher fatty acids (calcium and magnesium soaps) are insoluble in water and do not produce lather. Hard water contains Ca2+and Mg2+ ions. When a sodium or potassium soap is added to hard water, it gets converted into an insoluble calcium or magnesium soap as shown ahead.
Due to the conversion of sodium or potassium soaps into calcium or magnesium soaps in the presence of hard water, the common soaps are unable to emulsify the greasy dirt and c
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
2.5 kg of 0.25 molal aqueous solution.
Molar mass of urea (NH2CONH2) = (2 (1 * 14 + 2 * 1) + 1 * 12 + 1 * 16)
= 60 g/mol
1000 g of water contains 0.25 mol = (0.25 * 60) g of urea.
= 15 g of urea.
Means, 1015 g of solution contains 15 g of urea
Therefore,
2500 g of solution contains = 15 X 2500 / 1015
= 36.95 g
Hence, mass of urea required is 37 g (approx).
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
16.27
It has been found that the detergents having a great deal of branching in the hydrocarbon tail are not biodegradable and cause pollution in rivers and waterways. This is because the presence of side chains in the hydrocarbon tail stops bacteria from attacking and breaking the chains.
This results in slow degradation of detergent molecules leading to their accumulation in water ways. Alkylbenzene sulphonates having branched chain alkyl groups possess poor biodegradability and cause pollution in rivers and water Such detergents are termed as non-biodegradable or hard detergents.
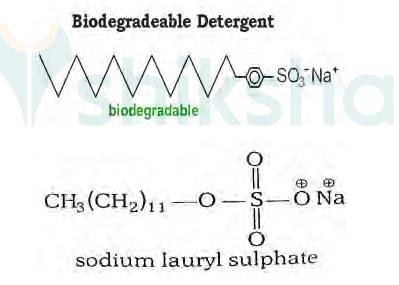
The alkyl sulphates do not possess branching and a
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 679k Reviews
- 1800k Answers

