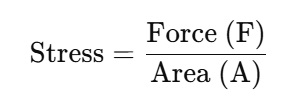NCERT
Get insights from 620 questions on NCERT, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about NCERT
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoBeginner-Level 5
Although NCERT is enough to prepare for CUET biology exam, according to the previous years' question papers, NTA may ask some questions that require analytical thinking skills. To be prepare for those questions, candidates can always take reference from books of other authors or publishers.
However, a candidate is advised to first cover the NCERT biology books, before studying from any other book.
New answer posted
8 months agoBeginner-Level 5
Students can check Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Amines NCERT Solutions, which can help you know name chemical reactions crucial for CBSE Board Exams and Competitive Exams like JEE and NEET:
Gabriel Phthalimide Synthesis – Used to prepare primary amines from phthalimide via hydrolysis.
Hoffmann Bromamide Degradation Reaction – Converts amides to primary amines with one less carbon atom using Br? and NaOH.
Carbylamine Reaction – A test for primary amines where they react with chloroform and KOH to form isocyanides (foul-smelling).
Acylation and Alkylation of Amines – Involves the reaction of amines with acid chlorides or alkyl h
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The chapter consists of fundamental topics that are important for board exams preparation as well as for competitive tests:
Composition and Size of the Nucleus: Understanding protons, neutrons, and nuclear density.
Nuclear Force: The forces that hold the nucleus together.
Mass-Energy Equivalence (E = mc²): Einstein's equation and its significance in nuclear reactions.
Nuclear Binding Energy: Understanding nuclear stability and energy release.
Radioactivity: Concepts of alpha, beta, and gamma decay.
Laws of Radioactive Decay: Half-life, mean life, and decay constant derivations.
Nuclear Fission and Fusion: Their
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Students can download the Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Nuclei NCERT Solutions PDF from various online platforms or they can visit the Shiksha homepage.
These PDFs are useful for students who want to study anywhere even if there is no internet access, which makes it easier to practice important numerical problems related to decay laws, nuclear binding energy, and nuclear reactions. To get access to NCERT Solutions PDF Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Nuclei students mucst click on the following link.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Nuclei is a detailed explanation of all the important concepts, solved numerical problems, and step-by-step derivations, that can be asked in competitve exams JEE, NEET, and other entrance exmas. There are various competitive exams that consists of questions on half-life, nuclear reactions, radioactive decay, and mass-energy equivalence, all of which are thoroughly included in NCERT solutions PDFs.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
While studying the mechanical properties of solids, stress and strain are fundamental concepts.
Stress: It refers to the condition when the external force is applied to a solid body and it experiences an internal restoring force per unit area. The resisting deformation due to the internal force is called stress. The formula is:
The SI unit of stress is N/m² (Pascal, Pa).
There are three types of stress -
- When the applied force increases the length of the body, it is called tensile stress.
- When the applied force decreases the length of the body, it is termed as the compressive stress.
- When the force is applied tangentially and creates defor
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
NCERT Class 12 Physics Ch 13 Nuclei is a important to lay the foundation for advanced topics in energy generation, nuclear physics, and medical applications. The Class 12 Physics chapter Nuclei includes important topics such as nuclear binding energy, radioactivity, mass-energy equivalence (E = mc²), and nuclear reactions, which are not only crucial for CBSE Board Exams but also asked in JEE, NEET, and other competitive exams. Understanding these important topics helps students build a solid conceptual understanding for higher studies in physics and engineering.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia (NH3 ) by replacing hydrogen atoms with alkyl or aryl groups. They are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary based on the number of hydrogen substitutions. Their nomenclature follows IUPAC rules, using the suffix “-amine.” There are several important topics discussed throghout the chapter 9 amines such as Preparation methods, physical properties, chemical properties and named reactions.
Amines are synthesized through methods like reduction of nitro compounds, ammonolysis, Gabriel phthalimide synthesis, and Hoffmann bromamide degradation. In terms of physical properties,
New answer posted
8 months agoBeginner-Level 5
Students can find the difference between aldehydes and ketones with the help of some chemical reactions. Aldehydes can be distinguished from ketones using tests like Tollens' test and Fehling's test. Aldehydes reduce Tollens' reagent to produce a silver mirror and Fehling's solution to yield a red precipitate, whereas ketones do not react in these tests.
New answer posted
8 months agoBeginner-Level 5
Name reactions are always feverouites of the examinaers. That's why Students are so eager to know and learn name chemical reactions of this chapter. Hers's few important reactions of this chapters below;
- Aldol Condensation: A reaction where two aldehyde or ketone molecules combine to form a? -hydroxy aldehyde or ketone.
Cannizzaro Reaction: A reaction where non-enolizable aldehydes undergo disproportionation in the presence of a strong base to yield a primary alcohol and a carboxylic acid.
Wolff-Kishner Reduction: A method to reduce carbonyl compounds to alkanes using hydrazine and a strong base.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 680k Reviews
- 1800k Answers