P Block Elements
Get insights from 254 questions on P Block Elements, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about P Block Elements
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
SO3 generates a dense fog of sulphuric acid that does not condense quickly, it is not absorbed directly in water to form H2SO4.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
A = NH4NO2
B = N2
C = NH3
D = HNO3
(i) NH4NO2→N2 + 2H2O
(ii) N2 + 3H2→2NH3
(iii) 4NH3 + 5O2→4NO + 6H2O
4NO + O2→4NO2
3NO2 + H2O→2HNO3 + NO
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Here, 'A' is NO2 (Nitrogen dioxide)
'B' is N2O4 (dinitrogen tetraoxide)
'C' is N2O3 (dinitrogen trioxide)
A brown gas is produced when lead nitrate (II) is heated
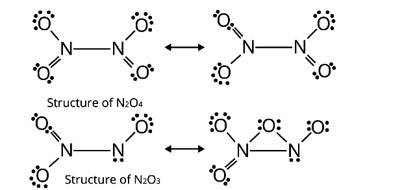
2Pb (NO3)2 ![]() 2PbO + 4NO2 + O2
2PbO + 4NO2 + O2
2NO2 ![]() N2O4
N2O4
2NO + N2O4  2N2O3
2N2O3
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
'A' is S8 'B' is SO2 gas
S8 + 8O2 ![]() 8SO2
8SO2
2MnO4 – + 5SO2 + 2H2O → 5 SO42– + 4H+ + 2Mn2+
(violet) (colourless)
2Fe3+ + SO2 + 2H2O → 2Fe2+ + SO42– + 4H+
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
7.70
As Bond dissociation energy generally decreases on moving down the group as the atomic size of the element increases. However, among halogens, the bond dissociation energy of F2 is lower than that of Cl2 and F2 due to the small atomic size of
Thus increasing order for bond dissociation energy among halogens is as follows:I22
As Bond dissociation energy of H-X molecules where X is the halogen decreases with increase in the atomic HI is the strongest acid as it loses H atom easily due to weak bonding between H and I.
So Increasing acid strength is as follows: HF
Basic strength decreases as we move from Nitrogen to Bismuth down the group
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
7.69
(i) XeO3 can be produced by hydrolysis of XeF4 and XeF6 under controlled pH of the medium in which reaction is taking place as shown below:
6XeF4 + 12H2O → 4Xe + 2XeO3 + 24HF + 3O2
XeF6 + 3H2O → XeO3 + 6HF
(ii) XeOF4 can be obtained on partial hydrolysis of XeF6 as shown below:
XeF6 + H2O → XeOF4 + 2HF
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
7.68
ClO- isisoelectronic to ClF as both the compounds contain 26 electrons in all. ClO- : 17+8+1 = 26
ClF : 17+9 = 26
Yes, ClF Molecule is a Lewis base as it accepts electrons from F to form ClF3.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
7.33
Xe and F2 combine under different conditions to produce XeF2, XeF4, XeF6 as follows:
Ratio | Temperature & Pressure Condition | Reaction |
Excess | at {673K,1bar} | Xe (g) + F2 (g) → XeF2 (s) |
1:5 ratio | at {873K,7bar} | Xe (g) + 2F2 (g) → XeF4 (s) |
1:20 ratio | at {573K,60-70bar} | Xe (g) + 3F2 (g) → XeF6 (s) |
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
7.66
4NaCl + MnO2 + 4H2SO4 MnCl2 + 4NaHSO4 + 2H2O + Cl2
Manganese (IV) oxide reacts with sodium chloride and sulfuric acid to produce manganese (II) chloride, chlorine, sodium bisulfate and water.
This reaction takes place at a temperature near 100°C.
Cl2 + NaI 2NaCl + I2
Chlorine reacts with sodium iodide to produce sodium chloride and iodine. Chlorine - diluted solution.
Sodium iodide - cold solution.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers

