Physics
Get insights from 5.6k questions on Physics, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New question posted
4 months agoNew answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
For series combination: s = R? + R?
For parallel combination: p = (R? ) / (R? + R? )
Given the condition s = np:
R? + R? = n * (R? ) / (R? + R? )
(R? + R? )² = nR? R?
R? ² + 2R? R? + R? ² = nR? R?
R? ² - 2R? R? + R? ² + 4R? R? = nR? R?
(R? - R? )² = (n - 4)R?
(R? - R? )² / (R? ) = n - 4
n = 4 + (R? - R? )² / (R? )
Since (R? - R? )² is always non-negative, the minimum value of the term (R? - R? )² / (R? ) is 0. This occurs when R? = R?
Therefore, the minimum value of n is 4.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
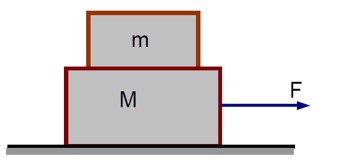
For the combined system of mass M and m, the acceleration under an applied force F is:
a = F / (M + m)
The static friction force (f_s) on the top block (m) provides its acceleration:
f_s = MA = m * [F / (M + m)] = mF / (M + m)
For the top block not to slip, the required static friction must be less than or equal to the maximum possible static friction (μmg):
f_s ≤ μmg
mF / (M + m) ≤ μmg
F ≤ μ (M + m)g
Using the values implied in the solution:
F ≤ 21 N
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
The force (F) exerted by radiation is the rate of change of momentum (p).
F = Δp/Δt
For photons, p = E/c. So, F = (1/c) * (ΔE/Δt).
Since Power (P) is ΔE/Δt, F = P/c.
Intensity (I) is Power per unit Area (P/A).
The formula provided in the document is F/A = (nE)/ (Δt c A) which leads to a final calculated value of 25 W/cm².
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
The formula for escape velocity (v_e) is v_e = √ (2GM/R).
According to the question, the new escape velocity (v_e') from a new radius R' is related to the original escape velocity by 10v_e' = v_e.
10 * √ (2GM/R') = √ (2GM/R)
Squaring both sides:
100 * (2GM/R') = (2GM/R)
100/R' = 1/R
R' = R/100
If R is the radius of Earth (6400 km), then:
R' = 6400 km / 100 = 64 km
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
The number of revolutions can be found using the rotational kinematic equation for angular displacement (θ):
θ = (ω_initial + ω_final)/2 * t
Number of revolutions = θ / 2π
Number of revolutions = [ (ω_final + ω_initial) * t] / (2 * 2π)
Based on the numerical values provided in the document, the calculation is:
Number of revolution = [ (2π * 3360/60 + 0) * t] / (2 * 2π) . with further calculation yielding the result:
Number of revolution = 728
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
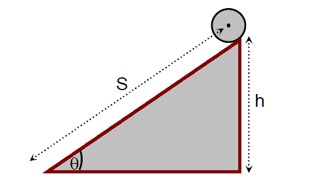
The equations for an object rolling down an inclined plane without slipping are:
· Force equation: mg sinθ - f_s = ma
· Torque equation: f_s R = Iα
Since a = αR, we can write f_s = Iα/R = Ia/R².
Substituting this into the force equation:
mg sinθ - Ia/R² = ma
mg sinθ = a (m + I/R²)
a = (mg sinθ) / (m + I/R²)
The time taken to travel a distance S is given by S = ½ at², which means t ∝ 1/√a. Therefore, the object with the largest acceleration (a) will arrive first.
The problem is analyzed for different bodies:
· Ring: I =
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
Initial charge Q = CV = 14 * 10? ¹² * 12 = 168 * 10? ¹² C
Initial energy U_in = ½ CV² = ½ (14 * 10? ¹²) * 12² = 1008 pJ
When the battery is disconnected and a dielectric (k=7) is inserted, the new capacitance is C' = kC.
The charge Q remains constant.
Final energy U_f = Q²/2C' = Q²/ (2kC) = (CV)²/ (2kC) = CV²/ (2k)
U_f = (14 * 10? ¹² * 12²) / (2 * 7) = 144 pJ
Mechanical energy available for oscillation
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers